The registered sector plays a crucial role in providing regulated financial services, ensuring transparency and consumer protection through strict compliance with legal standards. It encompasses institutions that are officially authorized to offer investment products and advisory services, safeguarding your interests in the financial market. Explore the rest of this article to understand how the registered sector can impact your financial decisions.
Table of Comparison
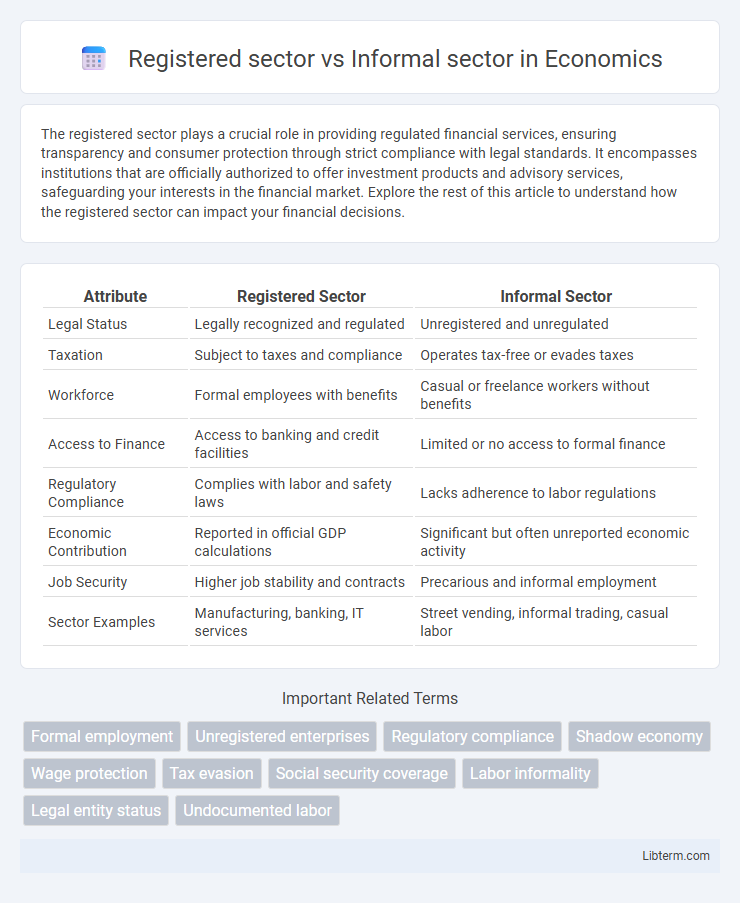
| Attribute | Registered Sector | Informal Sector |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Status | Legally recognized and regulated | Unregistered and unregulated |
| Taxation | Subject to taxes and compliance | Operates tax-free or evades taxes |
| Workforce | Formal employees with benefits | Casual or freelance workers without benefits |
| Access to Finance | Access to banking and credit facilities | Limited or no access to formal finance |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complies with labor and safety laws | Lacks adherence to labor regulations |
| Economic Contribution | Reported in official GDP calculations | Significant but often unreported economic activity |
| Job Security | Higher job stability and contracts | Precarious and informal employment |
| Sector Examples | Manufacturing, banking, IT services | Street vending, informal trading, casual labor |
Introduction to Registered and Informal Sectors
The registered sector comprises licensed businesses that comply with government regulations, maintain formal accounts, and pay taxes, contributing significantly to a country's GDP. In contrast, the informal sector includes unregistered, small-scale enterprises or self-employed individuals operating without formal recognition or regulatory oversight, often lacking social security benefits. Understanding the distinctions between these sectors is crucial for assessing economic policies, labor market dynamics, and development strategies.
Definition and Key Characteristics
The registered sector consists of formally recognized businesses and enterprises that comply with government regulations, pay taxes, and maintain official accounts, while the informal sector includes unregistered, small-scale activities lacking official oversight. Key characteristics of the registered sector include legal documentation, access to social security benefits, and adherence to labor laws, whereas the informal sector is marked by ease of entry, labor-intensive operations, and absence of social protection. The registered sector contributes significantly to GDP and government revenue, contrasting with the informal sector's vulnerability to economic fluctuations and limited access to credit.
Legal Framework and Compliance
The registered sector operates under a formal legal framework that mandates strict compliance with labor laws, taxation, and business regulations, ensuring transparency and accountability. In contrast, the informal sector lacks formal registration, resulting in minimal regulatory oversight, limited access to legal protections, and widespread non-compliance with statutory obligations. This disparity affects workers' rights, tax revenues, and the overall economic stability of a country.
Employment Structures and Labor Rights
The registered sector offers formal employment structures characterized by written contracts, social security benefits, and adherence to labor laws, ensuring workers receive protections such as minimum wage, working hours regulation, and access to dispute resolution mechanisms. In contrast, the informal sector largely operates outside legal frameworks, with workers often engaged in casual or temporary employment lacking formal contracts, social benefits, and legal labor rights, resulting in job insecurity and vulnerability to exploitation. This disparity significantly affects labor market stability, income security, and the enforcement of occupational health and safety standards.
Economic Contributions and GDP Impact
The registered sector significantly contributes to GDP through formal tax payments, regulated employment, and structured production processes, ensuring reliable economic data and sustainable growth. In contrast, the informal sector, while large in many developing economies, contributes substantially to employment and consumption but remains underrepresented in official GDP calculations due to unregulated activities and tax evasion. Bridging the gap between these sectors by formalizing informal businesses can enhance economic inclusivity, increase tax revenues, and provide accurate insights into overall economic performance.
Wage Patterns and Worker Security
In the registered sector, wage patterns are typically regulated with formal contracts, ensuring consistent salary payments, minimum wage compliance, and statutory benefits like social security and pensions, which enhance worker security. In contrast, the informal sector often features irregular wages, lack of formal agreements, and absence of social protections, exposing workers to higher economic vulnerability and job insecurity. This disparity significantly impacts income stability and the ability to access social safety nets for informal sector workers.
Access to Social Benefits and Protection
The registered sector offers formal workers access to social benefits such as health insurance, pensions, and unemployment protections, secured through legal employment contracts and regulatory oversight. In contrast, the informal sector lacks institutional recognition, leaving workers without guaranteed access to social security schemes, workplace safety standards, or labor rights enforcement. This disparity contributes to increased vulnerability among informal sector workers due to the absence of social protection mechanisms and limited legal recourse.
Taxation and Revenue Generation
The registered sector contributes significantly to tax revenue through formal mechanisms such as income tax, corporate tax, and value-added tax (VAT), facilitating better government resource allocation. In contrast, the informal sector often operates outside tax regulations, resulting in limited direct tax contributions and consequently lower revenue generation for public services. Governments face challenges in taxing the informal sector, which affects overall fiscal capacity and economic formalization efforts.
Challenges and Constraints in Both Sectors
The registered sector faces challenges such as high regulatory compliance costs, complex tax obligations, and limited access to credit, which can hinder business growth and innovation. The informal sector struggles with lack of legal recognition, unstable income, and exclusion from social protection programs, making it vulnerable to exploitation and financial insecurity. Both sectors encounter constraints related to market access and limited access to technology, impeding overall economic development and productivity.
Policy Recommendations and Future Outlook
Policies should prioritize formalizing informal sector activities through simplified registration processes, access to credit, and social protection schemes to increase economic inclusion and tax revenues. Future outlooks indicate that leveraging technology for digital identification and e-governance can significantly enhance sector registration and compliance rates. Strengthening labor rights and improving data collection within the informal sector will support evidence-based policymaking and sustainable economic growth.
Registered sector Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com