The Engel curve illustrates the relationship between a consumer's income and their expenditure on a particular good, revealing how spending patterns change as income varies. Understanding this curve helps businesses and policymakers predict demand shifts and allocate resources efficiently. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your spending behavior fits into these economic insights.
Table of Comparison
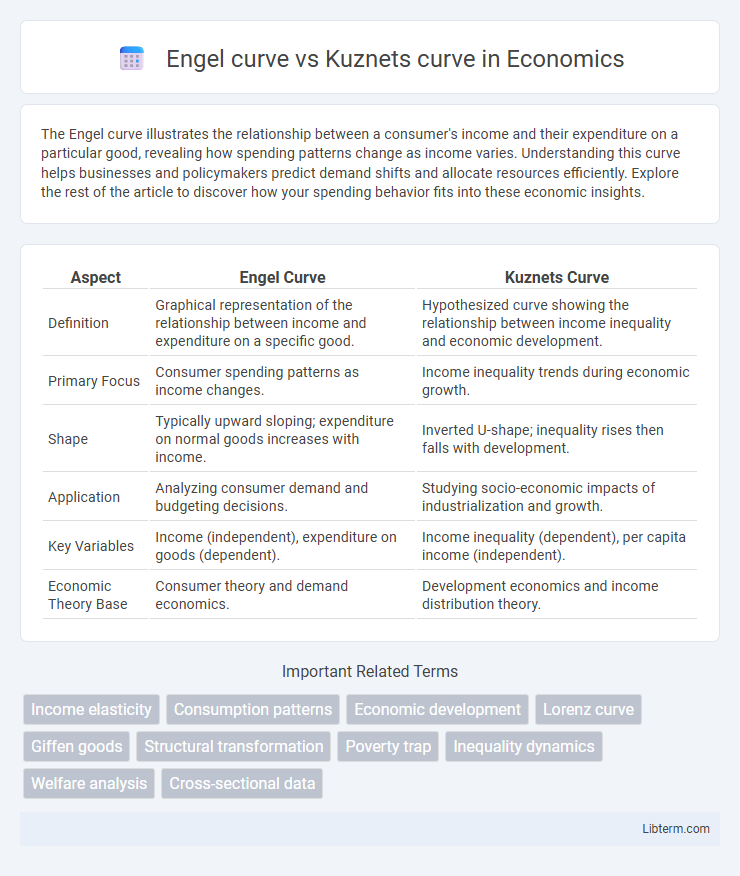
| Aspect | Engel Curve | Kuznets Curve |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Graphical representation of the relationship between income and expenditure on a specific good. | Hypothesized curve showing the relationship between income inequality and economic development. |
| Primary Focus | Consumer spending patterns as income changes. | Income inequality trends during economic growth. |
| Shape | Typically upward sloping; expenditure on normal goods increases with income. | Inverted U-shape; inequality rises then falls with development. |
| Application | Analyzing consumer demand and budgeting decisions. | Studying socio-economic impacts of industrialization and growth. |
| Key Variables | Income (independent), expenditure on goods (dependent). | Income inequality (dependent), per capita income (independent). |
| Economic Theory Base | Consumer theory and demand economics. | Development economics and income distribution theory. |
Introduction to Engel Curve and Kuznets Curve
The Engel Curve illustrates the relationship between household income and expenditure on a particular good, highlighting how consumption patterns change as income rises. The Kuznets Curve depicts the hypothesized relationship between economic development and income inequality, suggesting that inequality increases during early growth stages and decreases after reaching a certain income level. Both curves provide essential insights for analyzing economic behavior, consumer demand, and social inequality trends across different income groups.
Defining the Engel Curve
The Engel Curve illustrates the relationship between household income and expenditure on a particular good, demonstrating how consumer spending patterns change as income varies. It is a fundamental concept in demand theory, showing that as income rises, the proportion of income spent on necessities typically decreases while spending on luxury goods increases. In contrast, the Kuznets Curve represents the relationship between economic development and income inequality, often depicted as an inverted U-shape.
Defining the Kuznets Curve
The Kuznets Curve illustrates the relationship between economic inequality and economic development, typically showing that inequality rises in early development stages and falls after reaching a certain income level. It contrasts with the Engel Curve, which depicts the relationship between income and expenditure on a particular good, typically showing how spending patterns change as income increases. Understanding the Kuznets Curve is crucial for analyzing income distribution dynamics during economic growth and shaping policies aimed at reducing inequality.
Theoretical Foundations of Both Curves
The Engel curve illustrates the relationship between household income and expenditure on a particular good, emphasizing income elasticity and consumption patterns derived from utility maximization theory. The Kuznets curve hypothesizes an inverted U-shaped relationship between economic development and income inequality, grounded in structural transformation and capital accumulation models. Both curves serve as empirical tools rooted in economic behavior, with the Engel curve focusing on microeconomic consumer theory and the Kuznets curve emphasizing macroeconomic growth and distribution dynamics.
Key Differences Between Engel and Kuznets Curves
The Engel curve illustrates the relationship between household income and expenditure on a specific good, showing how consumption patterns change with income levels. The Kuznets curve depicts the relationship between economic development and income inequality, typically showing an inverted U-shape where inequality initially rises and then falls as income increases. Key differences include the Engel curve's focus on consumer behavior and spending patterns, while the Kuznets curve emphasizes macroeconomic trends in income distribution and inequality over time.
Economic Applications of the Engel Curve
The Engel curve is crucial in welfare economics, illustrating how household expenditure on a particular good varies with income, enabling policymakers to identify and target poverty by analyzing spending patterns on necessities. It aids in designing social welfare programs by estimating income elasticity of demand, facilitating optimized resource allocation for basic goods among low-income populations. Unlike the Kuznets curve, which explores income inequality over time relative to economic development, the Engel curve directly informs consumer behavior and poverty measurement for economic planning.
Socioeconomic Implications of the Kuznets Curve
The Kuznets Curve illustrates the relationship between economic development and income inequality, suggesting that inequality initially rises and then falls as a country industrializes. This pattern implies that early stages of economic growth may exacerbate social disparities, affecting poverty levels and social cohesion, before wealth distribution improves in later stages. Policymakers must consider this dynamic when designing interventions to balance growth with equitable social outcomes.
Criticisms and Limitations of Each Curve
The Engel curve faces criticism for oversimplifying consumer behavior by assuming stable income elasticity of demand, which can vary across different income groups and cultural contexts. The Kuznets curve is often challenged for its assumptions linking income inequality and economic growth, as empirical evidence shows inconsistent patterns across countries and time periods. Both curves struggle with limitations related to data quality, measurement errors, and the impact of external factors such as globalization and technological change.
Comparative Analysis: Engel Curve vs Kuznets Curve
The Engel curve illustrates the relationship between household income and expenditure on a particular good, showing how consumption patterns change as income varies. In contrast, the Kuznets curve depicts the relationship between economic development and income inequality, often hypothesizing an inverted U-shape where inequality rises then falls with growth. Comparative analysis highlights that while the Engel curve centers on microeconomic consumer behavior and demand elasticity, the Kuznets curve addresses macroeconomic structural shifts and social inequality dynamics during economic transformation.
Conclusion: Insights and Future Research Directions
Engel curve analysis reveals consumer behavior shifts across income levels, emphasizing changing expenditure patterns on necessities versus luxuries. Kuznets curve illustrates the inverted U-shaped relationship between economic development and income inequality, highlighting phases of rising and falling disparity. Future research should integrate micro-level consumption data with macroeconomic inequality measures to better understand socio-economic dynamics and inform targeted policy interventions.
Engel curve Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com