Fiscal policy involves government decisions on taxation and public spending to influence the economy, aiming to manage inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. Effective fiscal policies can stabilize the business cycle by adjusting budget deficits or surpluses to either stimulate or cool down the economy. Explore the rest of the article to understand how fiscal policy impacts your financial future and economic wellbeing.
Table of Comparison
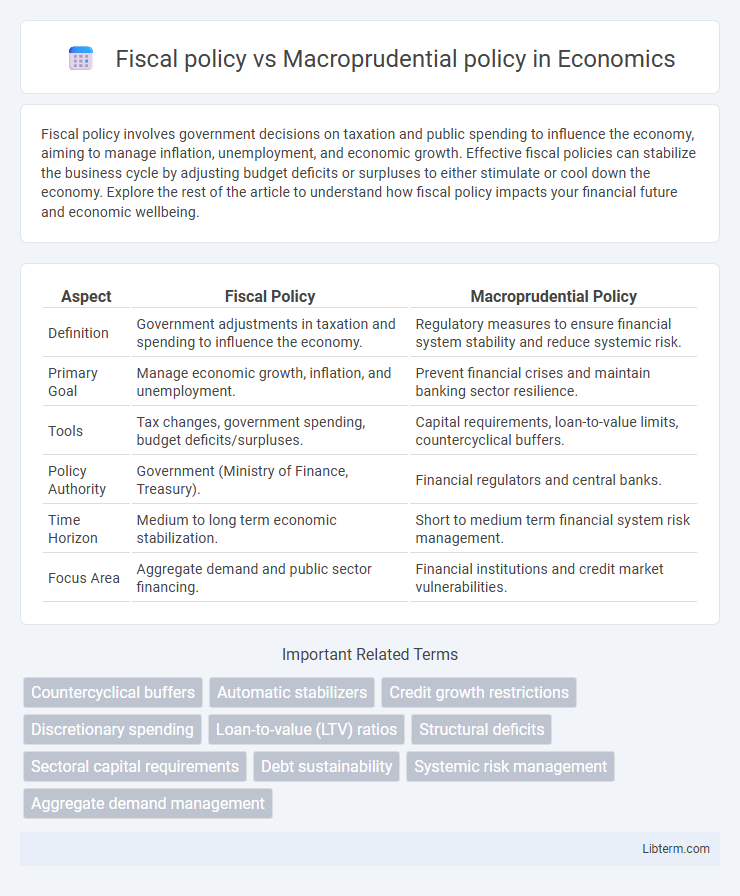
| Aspect | Fiscal Policy | Macroprudential Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government adjustments in taxation and spending to influence the economy. | Regulatory measures to ensure financial system stability and reduce systemic risk. |
| Primary Goal | Manage economic growth, inflation, and unemployment. | Prevent financial crises and maintain banking sector resilience. |
| Tools | Tax changes, government spending, budget deficits/surpluses. | Capital requirements, loan-to-value limits, countercyclical buffers. |
| Policy Authority | Government (Ministry of Finance, Treasury). | Financial regulators and central banks. |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long term economic stabilization. | Short to medium term financial system risk management. |
| Focus Area | Aggregate demand and public sector financing. | Financial institutions and credit market vulnerabilities. |
Introduction to Fiscal and Macroprudential Policies
Fiscal policy involves government decisions on taxation and public spending aimed at influencing economic activity and stabilizing growth. Macroprudential policy targets the financial system's stability by regulating and monitoring systemic risks to prevent crises. Both policies play crucial roles in managing economic and financial stability, with fiscal policy focusing on demand-side factors and macroprudential policy emphasizing financial institution resilience.
Defining Fiscal Policy: Tools and Objectives
Fiscal policy involves government decisions on taxation and public spending aimed at influencing economic activity, managing inflation, and promoting employment. Key tools include adjusting tax rates, modifying government expenditures, and implementing public investment projects to stabilize economic growth. The primary objectives target controlling budget deficits, stimulating demand during recessions, and ensuring sustainable fiscal health to support overall macroeconomic stability.
Understanding Macroprudential Policy: Scope and Mechanisms
Macroprudential policy targets the stability of the entire financial system by addressing systemic risks such as excessive credit growth, asset bubbles, and interconnected financial institutions. Unlike fiscal policy, which involves government spending and taxation to influence economic activity, macroprudential tools include countercyclical capital buffers, loan-to-value ratio limits, and stress testing to mitigate financial vulnerabilities. These mechanisms help prevent financial crises by enhancing resilience and reducing the likelihood of widespread banking sector failures.
Key Differences Between Fiscal and Macroprudential Policies
Fiscal policy involves government decisions on taxation and public spending to influence economic growth and stabilize demand, while macroprudential policy targets the stability of the financial system by managing systemic risks and preventing financial crises. Fiscal policy directly affects aggregate demand and employment, whereas macroprudential policy regulates financial institutions, credit growth, and asset bubbles to safeguard financial stability. The key difference lies in fiscal policy's focus on overall economic activity versus macroprudential policy's emphasis on mitigating risks within the financial sector.
Roles in Economic Stability: Fiscal vs Macroprudential Policy
Fiscal policy stabilizes the economy by adjusting government spending and taxation to influence aggregate demand, targeting growth and employment levels. Macroprudential policy aims to safeguard financial system stability by managing systemic risks through regulatory measures such as capital requirements and loan-to-value ratios. Together, these policies complement each other by addressing both aggregate economic fluctuations and financial market vulnerabilities to ensure overall economic stability.
Policy Transmission Channels: Fiscal and Macroprudential Perspectives
Fiscal policy transmission channels primarily operate through government spending and taxation adjustments that influence aggregate demand, consumption, and investment patterns. Macroprudential policy transmission channels work by altering financial institutions' risk-taking behavior, credit availability, and systemic stability to mitigate financial vulnerabilities. These distinct mechanisms highlight how fiscal tools impact the broader economy via demand-side factors, whereas macroprudential measures target financial sector resilience and credit conditions.
Coordination and Interaction in Modern Economies
Fiscal policy and macroprudential policy interact closely in modern economies to ensure financial stability and sustainable economic growth. Coordinated efforts between government spending, taxation measures, and regulatory tools like capital requirements and loan-to-value ratios enhance the effectiveness of both policies in mitigating systemic risks. Effective integration prevents conflicting outcomes, such as excessive credit growth or fiscal deficits, thereby fostering resilient economic environments.
Real-World Case Studies: Policy Effectiveness
Fiscal policy in real-world case studies, such as the 2009 U.S. stimulus package, effectively boosted aggregate demand and mitigated recession impacts through government spending and tax cuts. Macroprudential policy, exemplified by South Korea's counter-cyclical capital buffer and loan-to-value ratio limits, successfully curbed housing market overheating and reduced systemic financial risks. Comparative analyses highlight that fiscal policy directly stimulates economic growth, while macroprudential measures enhance financial stability, suggesting a complementary approach for robust economic management.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Policy Approach
Fiscal policy faces challenges such as time lags in implementation, political constraints, and difficulties in accurately timing and targeting stimulus or austerity measures to stabilize the economy. Macroprudential policy is limited by imperfect data, difficulties in identifying systemic risks early, and potential regulatory arbitrage where financial institutions evade controls. Both policies struggle with coordination complexities and balancing short-term economic growth with long-term financial stability.
Future Trends in Fiscal and Macroprudential Policy
Future trends in fiscal policy emphasize increased automation and data analytics to optimize tax collection and public spending, aiming for more responsive and adaptive budget management. Macroprudential policy is expected to integrate advanced financial technology and real-time monitoring systems to better detect systemic risks and enhance financial stability. Both policies are moving towards greater coordination, utilizing AI-driven models to anticipate economic shocks and implement preemptive interventions.
Fiscal policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com