Microprudential policy focuses on the stability and soundness of individual financial institutions by enforcing regulations that limit risks such as capital inadequacy and insolvency. Effective microprudential supervision helps prevent systemic crises by ensuring that banks and other entities maintain adequate buffers against financial shocks. Explore the rest of the article to understand how microprudential policy shapes financial regulation and protects your investments.
Table of Comparison
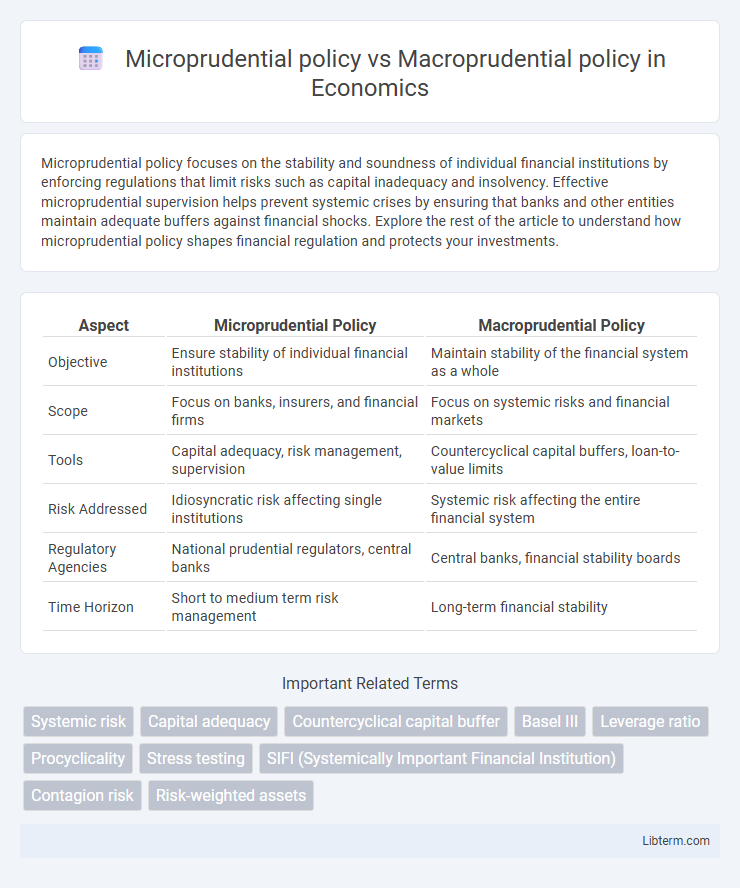
| Aspect | Microprudential Policy | Macroprudential Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Ensure stability of individual financial institutions | Maintain stability of the financial system as a whole |
| Scope | Focus on banks, insurers, and financial firms | Focus on systemic risks and financial markets |
| Tools | Capital adequacy, risk management, supervision | Countercyclical capital buffers, loan-to-value limits |
| Risk Addressed | Idiosyncratic risk affecting single institutions | Systemic risk affecting the entire financial system |
| Regulatory Agencies | National prudential regulators, central banks | Central banks, financial stability boards |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term risk management | Long-term financial stability |
Introduction to Prudential Policies
Microprudential policy targets the stability and soundness of individual financial institutions by enforcing regulatory standards such as capital adequacy, liquidity requirements, and risk management practices. Macroprudential policy, in contrast, aims to safeguard the entire financial system by addressing systemic risks, interconnectedness, and market-wide vulnerabilities that could lead to widespread instability. Both policies are essential components of prudential regulation, working together to promote financial resilience and prevent crises at both the institution and system-wide levels.
Defining Microprudential Policy
Microprudential policy targets the stability of individual financial institutions, aiming to prevent failures that could disrupt the financial system. It involves regulatory measures such as capital requirements, risk management standards, and supervisory oversight to ensure banks and other financial entities operate safely and soundly. These policies focus on minimizing institution-specific risks to protect depositors and maintain confidence in the financial system.
Understanding Macroprudential Policy
Macroprudential policy focuses on safeguarding the entire financial system by mitigating systemic risks, such as credit bubbles and interconnected bank failures, that can lead to widespread economic instability. Unlike microprudential policy, which targets the soundness of individual financial institutions, macroprudential regulation implements tools like countercyclical capital buffers and stress testing to prevent collective vulnerabilities. Central banks and regulatory bodies use macroprudential policies to enhance financial resilience and promote sustainable economic growth by addressing risks that emerge across the networked financial sector.
Key Objectives: Microprudential vs Macroprudential Approaches
Microprudential policy primarily aims to ensure the stability and soundness of individual financial institutions by focusing on risk management, capital adequacy, and solvency requirements. Macroprudential policy targets the resilience of the entire financial system, addressing systemic risks such as interconnectedness, market liquidity, and procyclicality to prevent widespread financial crises. While microprudential approaches concentrate on controlling risks at the firm level, macroprudential measures emphasize mitigating systemic vulnerabilities that can threaten economic stability.
Regulatory Tools and Instruments
Microprudential policy employs regulatory tools such as capital adequacy requirements, stress testing, and supervisory review processes to ensure the safety and soundness of individual financial institutions. Macroprudential policy utilizes instruments like countercyclical capital buffers, systemic risk surcharges, and macro-stress tests to mitigate risks that threaten the stability of the entire financial system. Both sets of regulatory tools aim to maintain financial stability, but microprudential focuses on individual firms while macroprudential addresses systemic vulnerabilities.
Differences in Scope and Focus
Microprudential policy targets individual financial institutions to ensure their safety and soundness, minimizing risks such as insolvency or liquidity shortfalls. Macroprudential policy addresses systemic risk within the entire financial system, aiming to prevent widespread instability and interconnected failures during economic downturns. The scope of microprudential policy is institution-specific, while macroprudential policy focuses on aggregate financial market conditions and systemic resilience.
Risk Management Strategies
Microprudential policy targets the stability of individual financial institutions by enforcing capital requirements, stress testing, and risk controls to prevent insolvency. Macroprudential policy oversees systemic risk across the financial system, employing tools like countercyclical capital buffers and leverage ratios to mitigate interconnected vulnerabilities and procyclicality. Effective risk management strategies integrate both approaches to enhance resilience against institution-specific failures and broader financial crises.
Impact on Financial Stability
Microprudential policy targets the soundness of individual financial institutions by enforcing capital requirements, risk management, and regulatory oversight to prevent insolvencies. Macroprudential policy focuses on the stability of the entire financial system by addressing systemic risks, such as interconnectedness and procyclicality, through tools like countercyclical capital buffers and stress testing. The coordinated implementation of both policies mitigates financial crises by enhancing resilience at both micro and macro levels, reducing systemic vulnerabilities and promoting sustainable economic growth.
Challenges and Limitations
Microprudential policy faces challenges in addressing systemic risk due to its focus on individual institutions, which may overlook interconnections and contagion effects within the financial system. Macroprudential policy struggles with data limitations, calibration of regulatory tools, and balancing financial stability objectives without stifling economic growth. Both policies encounter limitations in forecasting crises and adapting to rapidly evolving financial markets and innovations.
Future Trends in Prudential Regulation
Future trends in prudential regulation emphasize the integration of microprudential and macroprudential policies to enhance financial system stability. Advances in data analytics and machine learning enable more precise identification of systemic risks and institution-specific vulnerabilities, allowing regulators to implement dynamic, forward-looking capital requirements. Regulatory frameworks are increasingly focusing on climate-related financial risks, cyber threats, and cross-border spillovers, promoting resilience through stress testing and coordinated international supervision.
Microprudential policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com