Discount window lending provides financial institutions with short-term liquidity to manage unexpected cash flow shortages or stabilize reserves. This facility allows banks to borrow directly from the central bank, often at a penalty rate, ensuring confidence in the banking system during periods of stress. Learn more about how discount window lending works and its impact on your financial stability in the full article.
Table of Comparison
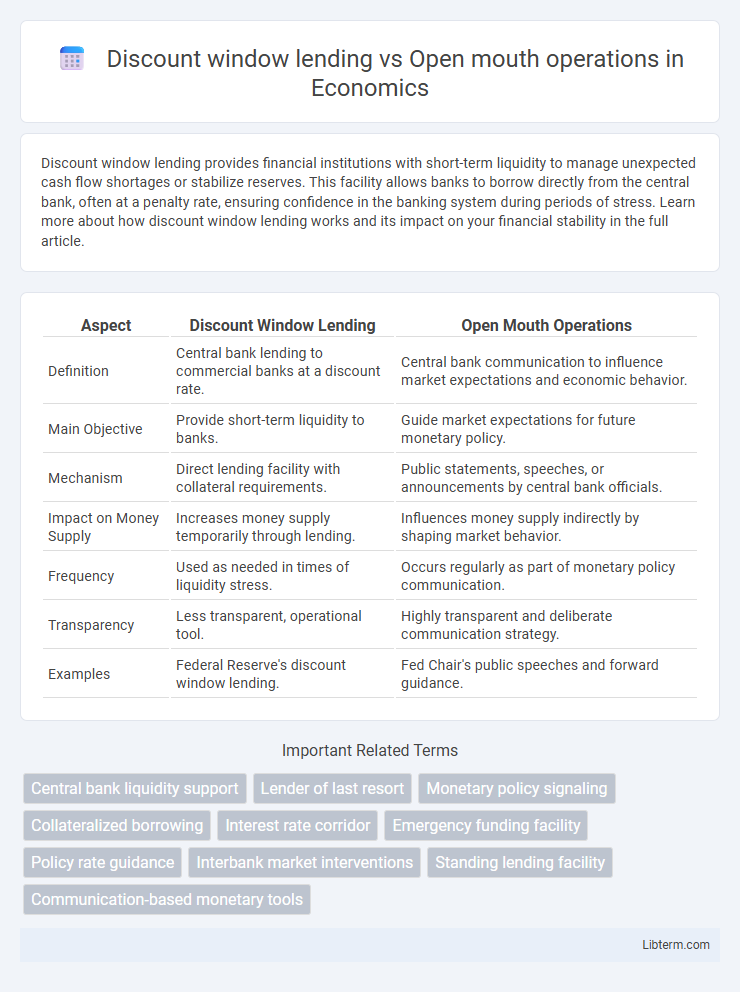
| Aspect | Discount Window Lending | Open Mouth Operations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Central bank lending to commercial banks at a discount rate. | Central bank communication to influence market expectations and economic behavior. |
| Main Objective | Provide short-term liquidity to banks. | Guide market expectations for future monetary policy. |
| Mechanism | Direct lending facility with collateral requirements. | Public statements, speeches, or announcements by central bank officials. |
| Impact on Money Supply | Increases money supply temporarily through lending. | Influences money supply indirectly by shaping market behavior. |
| Frequency | Used as needed in times of liquidity stress. | Occurs regularly as part of monetary policy communication. |
| Transparency | Less transparent, operational tool. | Highly transparent and deliberate communication strategy. |
| Examples | Federal Reserve's discount window lending. | Fed Chair's public speeches and forward guidance. |
Introduction to Central Bank Liquidity Tools
Discount window lending provides banks with short-term liquidity by allowing them to borrow funds directly from the central bank, typically at a penal interest rate to discourage frequent use. Open market operations involve the central bank buying or selling government securities in the open market to manage the money supply and influence interest rates, thereby indirectly affecting liquidity. Both tools are essential liquidity management mechanisms, with discount window lending serving as a safety valve for financial institutions and open market operations enabling broader monetary policy adjustments.
Overview of Discount Window Lending
Discount window lending serves as a critical liquidity provision mechanism through which central banks offer short-term loans to financial institutions facing temporary cash flow shortages. It functions as a safety valve, ensuring stability in the interbank lending market and preventing systemic crises by enabling banks to meet reserve requirements. This facility typically involves collateralized borrowing at an interest rate above the market level to discourage overreliance and maintain monetary policy effectiveness.
Understanding Open Mouth Operations
Open Mouth Operations refer to central banks' strategic use of public communication to influence market expectations and guide financial conditions without direct intervention. This approach contrasts with Discount Window Lending, where central banks provide liquidity through direct loans to financial institutions. Open Mouth Operations rely heavily on signaling and transparency to manage economic stability and market confidence effectively.
Key Differences between Discount Window Lending and Open Mouth Operations
Discount window lending involves the Federal Reserve providing short-term loans to commercial banks to address liquidity shortages, using collateral and charging an interest rate known as the discount rate. Open market operations consist of the Fed buying and selling government securities to regulate the money supply and influence short-term interest rates in the broader economy. The key difference lies in discount window lending being a lender-of-last-resort facility for individual banks, while open market operations systematically manage overall liquidity and monetary policy implementation.
Mechanisms of Discount Window Lending
Discount window lending involves central banks providing short-term loans to commercial banks facing liquidity shortages, using collateralized borrowing to stabilize the banking system. The mechanism includes setting an interest rate known as the discount rate, which influences borrowing costs and signals monetary policy stance. Unlike open market operations that manage liquidity by buying or selling government securities, discount window loans serve as a lender of last resort during financial stress.
Communication Strategies in Open Mouth Operations
Open mouth operations leverage central bank communication as a strategic tool to influence market expectations and interest rates without direct intervention. This approach relies on clear, credible messaging to signal future policy intentions, thereby enhancing transparency and reducing market uncertainty. Effective communication strategies include timely announcements and forward guidance, which help shape economic behavior and stabilize financial markets.
Effects on Financial Markets
Discount window lending provides short-term liquidity to financial institutions, stabilizing money markets by preventing sudden cash shortages and reducing panic during stress periods. Open market operations influence broader financial conditions by buying or selling government securities to adjust reserve levels, thereby controlling interest rates and overall monetary supply. Both tools impact market confidence and liquidity but differ in scope: discount window lending targets immediate institutional solvency, while open market operations drive systemic monetary policy adjustments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Approach
Discount window lending provides immediate liquidity to banks facing short-term funding shortages, enhancing financial stability but may carry stigma risks that discourage borrowing. Open market operations, involving the buying and selling of government securities, offer precise control over money supply and interest rates but can be slower to impact liquidity and less targeted to individual institutions. Both tools play crucial roles in monetary policy, with discount window lending suited for emergency support and open market operations for broader economic adjustments.
Historical Examples and Case Studies
Discount window lending, exemplified by the Federal Reserve's response during the 2008 financial crisis, allowed banks to access short-term liquidity directly to stabilize the banking sector. Open market operations, historically deployed by the Federal Reserve since the 1930s, involved buying and selling government securities to influence money supply and interest rates, as seen during the Great Depression and post-World War II economic adjustments. Case studies reveal that discount window lending serves as a lender of last resort during crises, whereas open market operations function as routine monetary policy tools for macroeconomic management.
Choosing the Right Tool: Policy Implications
Discount window lending provides short-term liquidity support directly to banks facing temporary funding shortages, making it a precise tool for stabilizing individual institutions without broad market interventions. Open market operations involve central banks buying or selling government securities to influence overall liquidity and interest rates, affecting the entire financial system with immediate policy impacts. Choosing between these tools depends on the central bank's goals: targeted assistance favors discount window lending, while systemic control of monetary conditions prompts open market operations.
Discount window lending Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com