Wharfage is a fee charged by ports for the use of their wharf facilities during cargo handling and storage. It covers the cost of loading, unloading, and storage services at the dock, directly impacting shipping expenses and logistics planning. Discover how understanding wharfage fees can help optimize your shipping costs by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
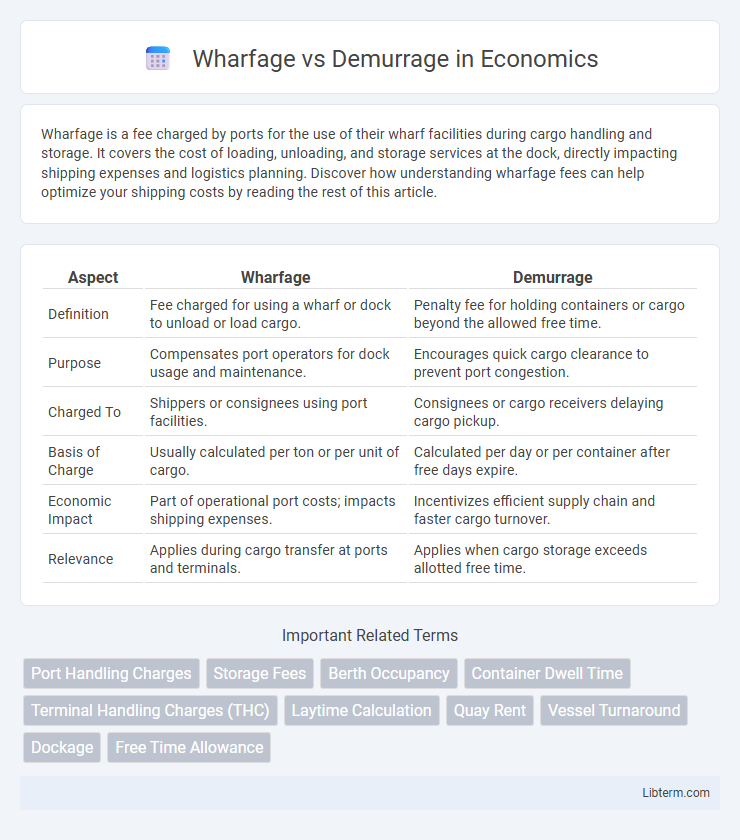
| Aspect | Wharfage | Demurrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fee charged for using a wharf or dock to unload or load cargo. | Penalty fee for holding containers or cargo beyond the allowed free time. |
| Purpose | Compensates port operators for dock usage and maintenance. | Encourages quick cargo clearance to prevent port congestion. |
| Charged To | Shippers or consignees using port facilities. | Consignees or cargo receivers delaying cargo pickup. |
| Basis of Charge | Usually calculated per ton or per unit of cargo. | Calculated per day or per container after free days expire. |
| Economic Impact | Part of operational port costs; impacts shipping expenses. | Incentivizes efficient supply chain and faster cargo turnover. |
| Relevance | Applies during cargo transfer at ports and terminals. | Applies when cargo storage exceeds allotted free time. |
Introduction to Wharfage and Demurrage
Wharfage is a port charge assessed for the use of a dock or wharf when goods are loaded or unloaded from a vessel, reflecting the cost of handling cargo at the port. Demurrage refers to the fee imposed on cargo or containers that remain at a terminal beyond the allotted free time, incentivizing swift unloading and clearance. Both charges are critical in maritime logistics, impacting the overall cost and efficiency of cargo handling operations.
Defining Wharfage
Wharfage is a fee charged by a port for the use of its wharves or docks when cargo is loaded or unloaded from a vessel, reflecting the handling or storage of goods at the port facility. It differs from demurrage, which applies to charges incurred when cargo or containers exceed the allocated free time for storage or use of equipment beyond the agreed period. Understanding wharfage fees is essential for maritime operators and shippers to manage port costs effectively during cargo transfer.
Understanding Demurrage
Demurrage refers to the charges applied when cargo or containers remain at a port or shipping terminal beyond the agreed free time, incurring storage fees due to delayed pickup or unloading. It is essential to understand that demurrage penalties incentivize timely clearance of goods to avoid congestion and extra costs for importers and exporters. Unlike wharfage, which is a fixed fee for using port facilities, demurrage fees increase with the duration of the delay.
Key Differences Between Wharfage and Demurrage
Wharfage is a fee charged for the use of a wharf or dock to load or unload cargo, calculated based on the quantity or weight of goods handled, while demurrage is a penalty fee imposed for exceeding the free time allowed for container or cargo storage at a port or terminal. Wharfage covers the infrastructure and operational costs related directly to handling cargo, whereas demurrage compensates for delays that disrupt the efficient use of port facilities. The key difference lies in wharfage being a service charge linked to cargo movement, whereas demurrage is a time-based charge triggered by extended storage or detention beyond agreed periods.
Cost Implications: Wharfage vs Demurrage
Wharfage is a one-time fee charged for using port facilities to load or unload cargo, typically calculated based on the weight or volume of the goods. Demurrage incurs when cargo remains at the port beyond the free time allowed, leading to daily charges that can escalate costs significantly. Understanding the distinction between these fees helps businesses optimize logistics expenses and avoid unexpected surcharges.
When Is Wharfage Charged?
Wharfage is charged when cargo is loaded onto or unloaded from a ship at the port's wharf, typically calculated based on the weight or volume of the goods. This fee covers the use of the dock facilities and port infrastructure during the transfer process. Unlike demurrage, which applies when cargo overstays the allotted free time in the storage area, wharfage is incurred immediately as part of the port handling services.
When Does Demurrage Apply?
Demurrage applies when cargo remains at the port or terminal beyond the allowed free time, causing delays in loading or unloading operations. It is typically imposed after the agreed laytime expires, resulting in additional charges for the consignee or shipper. Wharfage, on the other hand, refers to the fee for using the wharf facilities, charged regardless of cargo detention time.
Impact on Shipping Operations
Wharfage fees are charged for the use of port facilities during loading and unloading, directly affecting operational costs and port scheduling efficiency. Demurrage charges apply when cargo exceeds the free storage period at the terminal, leading to increased expenses and potential delays in vessel turnaround times. Both fees incentivize faster cargo movement, impacting overall shipping logistics and supply chain management.
Reducing Wharfage and Demurrage Charges
Reducing wharfage charges involves efficient cargo handling and minimizing the time goods spend on the dock to avoid storage fees imposed by ports. Demurrage charges can be lowered by ensuring timely pickup and delivery of containers, streamlining customs clearance, and enhancing coordination between shipping lines and consignees. Implementing advanced tracking systems and real-time communication helps reduce delays, ultimately controlling excessive wharfage and demurrage costs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Strategy
Selecting the appropriate strategy between wharfage and demurrage depends on the operational priorities and cost implications of port usage and cargo storage duration. Wharfage fees primarily cover the use of port facilities for cargo handling, while demurrage charges arise from delays in container pickup beyond free time limits. Optimizing logistics involves minimizing demurrage by improving cargo release efficiency and negotiating wharfage rates to reduce overall port handling expenses.
Wharfage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com