Minimum variance hedge minimizes the risk of price fluctuations by selecting a hedging position that reduces the variance of the portfolio's returns. This strategy aims to balance exposure between the spot and futures markets to achieve the least possible risk. Explore the rest of the article to understand how you can implement a minimum variance hedge effectively in your risk management approach.
Table of Comparison
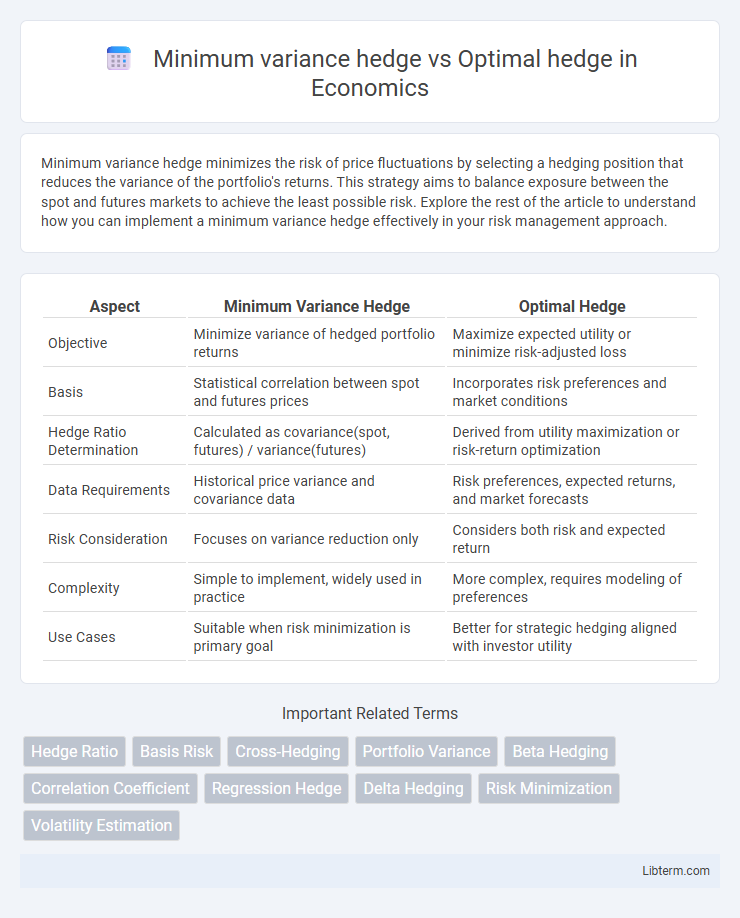
| Aspect | Minimum Variance Hedge | Optimal Hedge |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Minimize variance of hedged portfolio returns | Maximize expected utility or minimize risk-adjusted loss |
| Basis | Statistical correlation between spot and futures prices | Incorporates risk preferences and market conditions |
| Hedge Ratio Determination | Calculated as covariance(spot, futures) / variance(futures) | Derived from utility maximization or risk-return optimization |
| Data Requirements | Historical price variance and covariance data | Risk preferences, expected returns, and market forecasts |
| Risk Consideration | Focuses on variance reduction only | Considers both risk and expected return |
| Complexity | Simple to implement, widely used in practice | More complex, requires modeling of preferences |
| Use Cases | Suitable when risk minimization is primary goal | Better for strategic hedging aligned with investor utility |
Introduction to Hedging Strategies
Minimum variance hedge aims to reduce the overall risk of a portfolio by minimizing the variance of returns through strategic asset allocation. Optimal hedge extends this by incorporating additional factors such as cost, market conditions, and expected future volatility to achieve the best risk-return trade-off. Both strategies serve as foundational approaches in financial risk management, focusing on protecting investments from adverse price movements.
Defining Minimum Variance Hedge
Minimum variance hedge minimizes the variance of portfolio returns by selecting hedge ratios that reduce exposure to price fluctuations, typically calculated through regression analysis of spot and futures price changes. Optimal hedge extends this concept by incorporating additional factors like transaction costs, risk preferences, and market liquidity to maximize overall financial performance. The defining attribute of minimum variance hedge lies in its focus on statistical variance minimization as the primary criterion for hedging effectiveness.
Understanding Optimal Hedge Ratio
The minimum variance hedge aims to reduce risk by minimizing the variance of the hedged position, but it does not necessarily maximize expected returns or consider market conditions. The optimal hedge ratio improves on this by incorporating the correlation between the spot and futures price changes, thus providing a more precise hedge that balances risk and return. Understanding the optimal hedge ratio involves calculating the ratio that minimizes the variance of the combined position, often derived from the covariance of spot and futures price changes divided by the variance of futures price changes.
Key Differences Between MVH and Optimal Hedge
Minimum variance hedge aims to reduce the overall risk by minimizing portfolio variance through selecting hedge ratios based on historical data, whereas optimal hedge incorporates both variance minimization and cost-efficiency, often using forward-looking models and additional constraints. MVH typically relies solely on covariance and variance metrics to determine the hedge ratio, while optimal hedge strategies integrate factors such as transaction costs, liquidity, and risk preferences. The key difference lies in MVH's exclusive focus on risk reduction, contrasted with optimal hedge's broader objective of balancing risk reduction with economic practicality and real-world market considerations.
Calculation Methods for Hedge Ratios
Minimum variance hedge ratio calculation relies on minimizing the variance of the hedged portfolio by estimating the covariance between the asset and the hedge instrument divided by the variance of the hedge instrument. Optimal hedge ratio calculation, often using utility maximization, incorporates risk preferences and expected returns to balance risk reduction with potential gains. Both methods require historical price data, but the minimum variance approach is purely statistical, while the optimal hedge integrates economic factors and individual risk tolerance.
Pros and Cons of Minimum Variance Hedge
Minimum variance hedge minimizes portfolio risk by reducing variance in asset returns, making it highly effective for firms seeking risk reduction without speculative gains. Its simplicity and ease of implementation are significant advantages, but it may not achieve perfect hedging due to ignoring expected returns and market dynamics. The trade-off involves potential suboptimal hedge ratios and residual risk compared to the more complex optimal hedge, which considers both risk and return for maximizing economic value.
Advantages and Limitations of Optimal Hedge
Optimal hedge maximizes expected utility by considering risk preferences and portfolio variance, providing a tailored risk management strategy compared to the Minimum Variance Hedge that solely minimizes variance. Advantages include the ability to account for risk-aversion levels and potential returns, leading to more efficient hedging decisions under uncertainty. Limitations involve increased computational complexity and the requirement for precise estimation of utility functions and market parameters, which can result in model risk and reduced practicality in volatile markets.
Practical Applications in Financial Markets
Minimum variance hedge minimizes the variance of portfolio returns by selecting hedge ratios based on historical price data, widely used in commodity markets to reduce risk exposure. Optimal hedge extends this by incorporating factors like transaction costs, market liquidity, and time horizon, improving hedging efficiency for complex assets such as derivatives and foreign exchange positions. Financial institutions apply these strategies to balance risk and cost, enhancing portfolio stability and achieving tailored risk management goals.
Factors Influencing Hedge Effectiveness
Minimum variance hedge effectiveness depends heavily on the correlation between the asset and the hedging instrument, as a stronger correlation reduces basis risk and enhances hedge performance. Optimal hedge effectiveness considers additional factors such as transaction costs, risk tolerance, and market liquidity, optimizing hedge ratios beyond simple variance minimization. Both strategies require careful analysis of price volatility and forecasting accuracy to maximize protection against unfavorable price movements.
Selecting the Right Hedging Strategy
Minimum variance hedge minimizes the variance of the hedged portfolio by selecting hedge ratios that reduce risk exposure to price fluctuations. Optimal hedge considers both risk reduction and cost efficiency, balancing expected returns against potential losses for improved overall performance. Selecting the right hedging strategy depends on risk tolerance, market conditions, and the specific asset's volatility to achieve desired financial protection.
Minimum variance hedge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com