Investing without a hedge exposes your portfolio to significant market volatility and potential losses during downturns. Without protective strategies, adverse price movements can directly impact your returns and financial stability. Discover effective ways to manage these risks and protect your investments by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
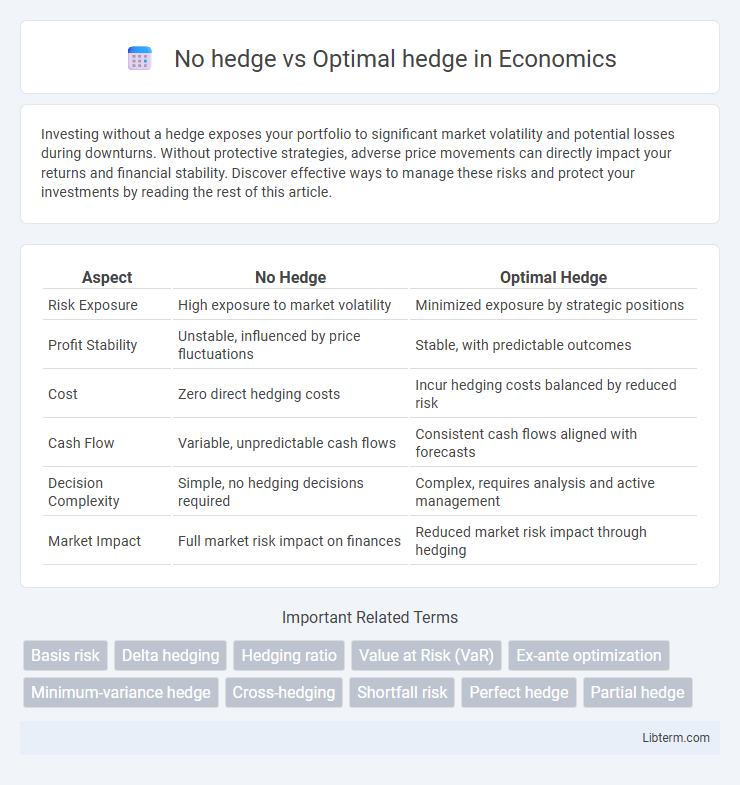
| Aspect | No Hedge | Optimal Hedge |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Exposure | High exposure to market volatility | Minimized exposure by strategic positions |
| Profit Stability | Unstable, influenced by price fluctuations | Stable, with predictable outcomes |
| Cost | Zero direct hedging costs | Incur hedging costs balanced by reduced risk |
| Cash Flow | Variable, unpredictable cash flows | Consistent cash flows aligned with forecasts |
| Decision Complexity | Simple, no hedging decisions required | Complex, requires analysis and active management |
| Market Impact | Full market risk impact on finances | Reduced market risk impact through hedging |
Understanding Hedging: An Overview
No hedge strategy exposes investors to full market risk, potentially leading to significant losses or gains depending on price fluctuations. Optimal hedge uses derivatives like futures or options to minimize risk by aligning hedge ratios with the asset's volatility and market conditions. Understanding hedging involves analyzing risk tolerance, asset correlation, and cost efficiency to determine the best approach for portfolio protection.
Defining No Hedge and Optimal Hedge Strategies
No hedge strategies involve leaving positions fully exposed to market risk, accepting potential price fluctuations without risk mitigation. Optimal hedge strategies use financial instruments like futures, options, or swaps to minimize risk by aligning hedging positions closely with underlying exposures. The effectiveness of optimal hedging lies in balancing cost, risk reduction, and market variability to achieve desired financial protection.
Risk Exposure: Unhedged vs. Optimally Hedged
Unhedged positions expose firms to significant market risk, including price volatility and adverse currency fluctuations, which can lead to unpredictable financial outcomes. Optimal hedging strategies utilize financial instruments like futures, options, and swaps to minimize risk exposure and stabilize cash flows. This approach enhances risk management by aligning hedging activities with the company's risk tolerance and market conditions, ultimately improving financial predictability.
Cost Implications: Saving or Spending with Hedging
No hedge strategies expose firms to full market volatility, potentially increasing unexpected costs due to unfavorable price movements in commodities, currencies, or interest rates. Optimal hedging minimizes cost fluctuations by strategically locking in prices or rates, thereby saving money through risk reduction and enhanced budget predictability. Firms adopting optimal hedging often experience improved financial stability and avoid the spending spikes associated with adverse market changes.
Impact on Portfolio Performance
No hedge leaves portfolios exposed to adverse currency fluctuations, resulting in increased volatility and potential losses in international investments. Optimal hedge strategies minimize foreign exchange risk by using financial instruments like forwards or options, leading to more stable returns and improved risk-adjusted performance. By reducing currency exposure, optimal hedging enhances portfolio diversification benefits and protects capital from unpredictable market movements.
Volatility Management: No Hedge Versus Optimal Hedge
No hedge strategies expose portfolios directly to market volatility, resulting in higher risk and potential for large losses during price fluctuations. Optimal hedge techniques utilize derivatives like futures or options to minimize exposure, effectively stabilizing asset values and reducing volatility impact. Implementing an optimal hedge improves risk-adjusted returns by systematically managing price variability and protecting against adverse market movements.
Real-world Scenarios: When No Hedge Works
No hedge strategies can be cost-effective in stable markets where currency fluctuations are minimal, allowing businesses to save on hedging fees while maintaining profit margins. Companies with natural hedges, such as balanced foreign revenues and expenses, often benefit from no hedge approaches since their exposure to currency risk is inherently reduced. Small firms or start-ups with limited capital may prefer no hedge strategies due to the complexity and cost of implementing optimal hedges in volatile international markets.
Case Studies: Optimal Hedge in Action
Case studies on optimal hedge strategies reveal significant reductions in financial risk and enhanced portfolio stability compared to no hedge scenarios. Firms employing optimal hedging techniques demonstrate measurable improvements in earnings volatility control, often achieving up to 30% lower exposure to commodity price fluctuations and currency risks. These real-world examples highlight optimized hedge ratios tailored to specific market conditions, driving superior risk-adjusted returns and increased corporate value.
Decision Criteria: When to Choose No Hedge or Optimal Hedge
Choosing between no hedge and optimal hedge depends on risk tolerance, market volatility, and cost considerations. No hedge suits firms with high risk tolerance or when hedging costs outweigh potential losses, while optimal hedge balances minimizing risk exposure and hedging expenses by determining optimal hedge ratios. Decision criteria prioritize financial objectives, market forecasts, and the firm's ability to absorb risk shocks to select the appropriate strategy.
Future Outlook: Trends in Hedging Strategies
No hedge strategies expose firms to full market volatility, often leading to unpredictable financial outcomes and increased risk during economic uncertainty. Optimal hedge approaches leverage advanced analytics and dynamic risk assessment to tailor hedging proportions, improving cost efficiency and resilience against market fluctuations. Emerging trends favor integrating artificial intelligence and real-time data for adaptive hedging, enhancing precision in mitigating exposure and supporting strategic financial planning.
No hedge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com