Price flexibility allows businesses to adjust their prices quickly in response to market demand and competition, enhancing profitability and customer satisfaction. This adaptability helps manage inventory levels effectively and maintain a competitive edge in fluctuating markets. Discover how mastering price flexibility can transform Your pricing strategy and drive business growth in the full article.
Table of Comparison
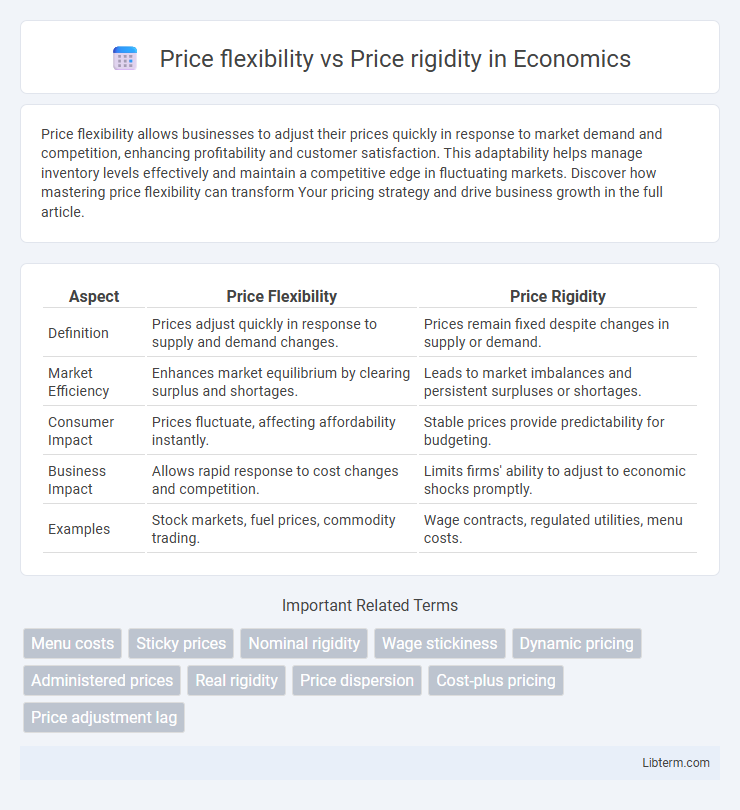
| Aspect | Price Flexibility | Price Rigidity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prices adjust quickly in response to supply and demand changes. | Prices remain fixed despite changes in supply or demand. |
| Market Efficiency | Enhances market equilibrium by clearing surplus and shortages. | Leads to market imbalances and persistent surpluses or shortages. |
| Consumer Impact | Prices fluctuate, affecting affordability instantly. | Stable prices provide predictability for budgeting. |
| Business Impact | Allows rapid response to cost changes and competition. | Limits firms' ability to adjust to economic shocks promptly. |
| Examples | Stock markets, fuel prices, commodity trading. | Wage contracts, regulated utilities, menu costs. |
Introduction to Price Flexibility and Price Rigidity
Price flexibility refers to a market condition where prices adjust quickly in response to changes in supply and demand, enabling efficient resource allocation and market equilibrium. Price rigidity occurs when prices remain fixed or change slowly due to menu costs, contracts, or regulatory constraints, often leading to imbalances such as shortages or surpluses. Understanding the causes and implications of price flexibility and rigidity is crucial for economic analysis and policy formulation.
Defining Price Flexibility
Price flexibility refers to a firm's ability to adjust prices quickly in response to market demand, supply changes, or competitive actions. It enables businesses to optimize revenue by aligning prices with real-time consumer willingness to pay and cost fluctuations. In contrast, price rigidity occurs when prices remain fixed despite changes in market conditions, often due to contracts, regulations, or strategic pricing decisions.
Understanding Price Rigidity
Price rigidity occurs when prices remain constant despite shifts in supply and demand, often due to menu costs, long-term contracts, or customer expectations. This inflexibility can lead to market inefficiencies, such as shortages or surpluses, as prices fail to adjust to changing economic conditions. Understanding the causes and implications of price rigidity is crucial for businesses seeking to navigate competitive markets and optimize revenue strategies.
Key Differences Between Flexible and Rigid Pricing
Price flexibility allows businesses to adjust prices frequently based on market demand, competition, and cost fluctuations, maximizing revenue and adapting to consumer behavior. Price rigidity involves maintaining consistent prices over time despite external changes, promoting customer trust and simplifying budgeting but potentially losing competitive advantage. Key differences include responsiveness to market changes, impact on profit margins, and consumer perception of fairness and stability.
Factors Influencing Price Flexibility
Price flexibility is influenced by factors such as market competition intensity, product differentiation, and consumer price sensitivity, which determine how easily prices can be adjusted without losing demand. Cost structures and supply chain responsiveness also play critical roles, with businesses experiencing lower variable costs typically showing greater ability to modify prices quickly. Regulatory environments and contract terms often impose price rigidity by restricting frequent or significant price changes despite market fluctuations.
Market Conditions Affecting Price Rigidity
Price rigidity often occurs in markets with high competition intensity, where firms avoid frequent price changes to prevent price wars. Markets characterized by strong consumer price sensitivity and prominent brand loyalty also exhibit price rigidity, as firms prefer non-price competition to maintain market share. Furthermore, in oligopolistic industries, strategic interdependence among firms leads to price rigidity to stabilize market equilibrium and avoid unpredictable reactions.
Advantages of Price Flexibility
Price flexibility enables businesses to respond swiftly to market demand fluctuations, optimizing revenue and competitiveness. It allows dynamic adjustments to consumer behavior, seasonal trends, and competitor pricing strategies, enhancing profit margins. This adaptability supports better inventory management and reduces the risk of overstock or stockouts.
Limitations of Price Rigidity
Price rigidity limits a firm's ability to respond to market fluctuations, reducing competitiveness in dynamic markets. Fixed prices can lead to inventory surpluses or shortages, impacting revenue and customer satisfaction. Inflexible pricing also hinders adaptation to cost changes, decreasing profit margins and market share over time.
Real-World Examples of Flexible and Rigid Pricing
Price flexibility is evident in industries like airlines and ride-sharing, where dynamic pricing adjusts in real-time based on demand, supply, and competition. Conversely, price rigidity appears in regulated sectors such as healthcare and utilities, where prices remain fixed due to government policies or long-term contracts. Retailers occasionally exhibit rigidity during sales periods by maintaining discount prices despite fluctuating supply costs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pricing Strategy
Selecting the ideal pricing strategy hinges on market conditions, customer behavior, and competitive dynamics. Price flexibility enables businesses to respond swiftly to demand fluctuations and optimize revenue, while price rigidity ensures stability and customer trust in markets sensitive to frequent changes. Balancing these approaches requires analyzing elasticity, cost structures, and long-term brand positioning to maximize profitability and sustainability.
Price flexibility Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com