Financial resources are essential assets that enable individuals and organizations to fund their operations, investments, and growth strategies effectively. Proper management of these resources ensures stability, supports decision-making, and maximizes returns while minimizing risks. Explore the rest of the article to uncover strategies that can optimize your financial resources for long-term success.
Table of Comparison
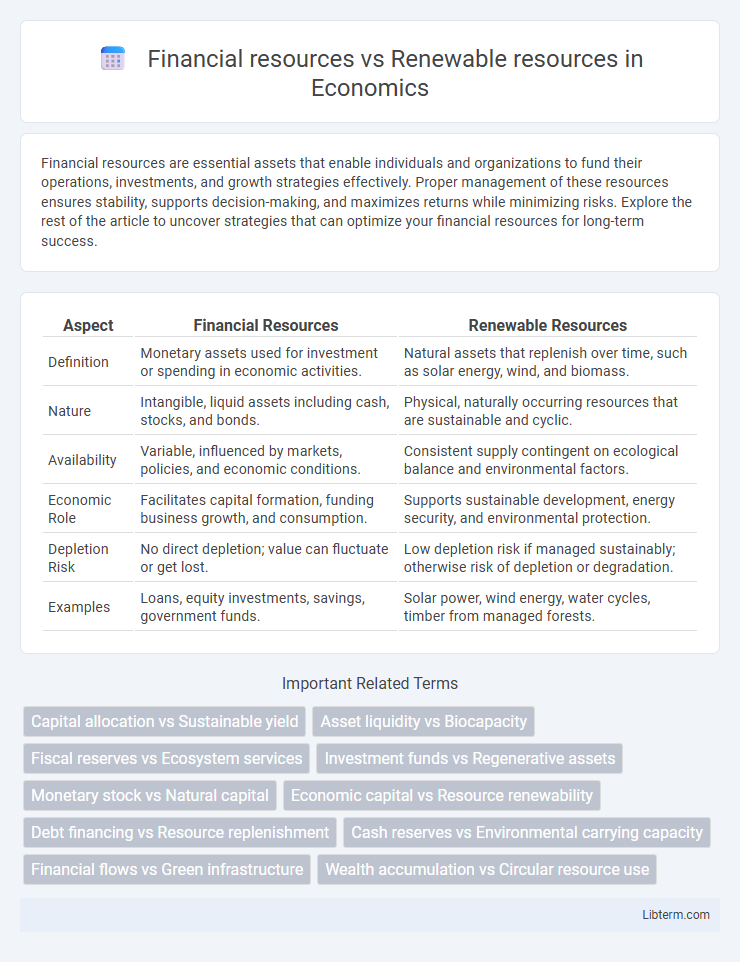
| Aspect | Financial Resources | Renewable Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monetary assets used for investment or spending in economic activities. | Natural assets that replenish over time, such as solar energy, wind, and biomass. |
| Nature | Intangible, liquid assets including cash, stocks, and bonds. | Physical, naturally occurring resources that are sustainable and cyclic. |
| Availability | Variable, influenced by markets, policies, and economic conditions. | Consistent supply contingent on ecological balance and environmental factors. |
| Economic Role | Facilitates capital formation, funding business growth, and consumption. | Supports sustainable development, energy security, and environmental protection. |
| Depletion Risk | No direct depletion; value can fluctuate or get lost. | Low depletion risk if managed sustainably; otherwise risk of depletion or degradation. |
| Examples | Loans, equity investments, savings, government funds. | Solar power, wind energy, water cycles, timber from managed forests. |
Understanding Financial Resources
Financial resources encompass assets such as capital, credit, and investments essential for funding projects and operations, enabling organizations to pursue growth and innovation. Understanding financial resources involves analyzing their availability, allocation, and management to ensure sustainable economic performance and risk mitigation. Effective utilization of financial resources supports long-term business stability and the ability to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Defining Renewable Resources
Renewable resources are natural assets that replenish through ecological processes at a rate comparable to their consumption, such as solar energy, wind power, and biomass. Unlike financial resources, which represent monetary capital used for investment and expenditures, renewable resources provide sustainable inputs that reduce environmental degradation. Emphasizing the regenerative capacity of renewable resources highlights their role in supporting long-term ecological balance and energy security.
Key Differences Between Financial and Renewable Resources
Financial resources refer to monetary assets such as cash, investments, and credit used to fund economic activities, while renewable resources are natural assets like solar energy, wind, and biomass that replenish over time. Unlike financial resources, which are intangible and can fluctuate with market conditions, renewable resources are tangible and sustainable, supporting long-term environmental balance. The key difference lies in their nature of availability and utilization: financial resources depend on economic factors and human management, whereas renewable resources depend on ecological cycles and natural regeneration.
Economic Importance of Financial Resources
Financial resources play a crucial role in economic development by enabling investments in infrastructure, technology, and human capital, which drive growth and productivity. Access to capital markets and credit facilities facilitates business expansion and innovation, directly impacting employment and income levels. Unlike renewable resources, which provide natural inputs, financial resources serve as the essential fuel for economic activities and sustainable development strategies.
Environmental Impact of Renewable Resources
Renewable resources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power generate significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to financial investments in fossil fuels, reducing air and water pollution that harms ecosystems. The environmental impact of renewable energy includes minimal habitat disruption and decreased reliance on finite resources, fostering sustainable development. These resources contribute to mitigating climate change effects by providing clean energy alternatives and supporting carbon footprint reduction goals worldwide.
Resource Sustainability: Financial vs. Renewable
Financial resources, such as capital and investments, provide essential funding for sustainable projects but are inherently finite and subject to market fluctuations. Renewable resources, including solar, wind, and biomass, offer long-term sustainability by replenishing naturally and reducing environmental impact. Prioritizing renewable resources enhances resource sustainability by ensuring continuous availability and mitigating the risks of resource depletion associated with financial dependency.
Investment Strategies for Financial and Renewable Resources
Investment strategies for financial resources prioritize diversification across stocks, bonds, and real estate to optimize risk-adjusted returns and liquidity. Renewable resource investments focus on funding sustainable projects such as solar, wind, and bioenergy infrastructure, leveraging government incentives and long-term growth potential in green energy markets. Balancing portfolios between traditional financial assets and renewable energy investments enhances resilience against market volatility and aligns with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria.
Global Trends in Resource Management
Global trends in resource management highlight a growing shift from financial resources toward renewable resources, driven by increasing environmental concerns and sustainability goals. Investments in renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind, and bioenergy have surged, reflecting a global commitment to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate climate change impacts. Governments and corporations worldwide are implementing policies and strategies to optimize renewable resource utilization while balancing economic growth and financial stability.
Challenges in Balancing Financial and Renewable Resources
Balancing financial resources with renewable resources presents challenges such as high initial investment costs and uncertain long-term returns, which can strain budgets and impact cash flow management. Integrating renewable energy infrastructure often requires significant capital expenditure, making it difficult for organizations to allocate funds without compromising other financial priorities. Furthermore, fluctuating market prices and regulatory changes create financial risks that complicate the sustainable scaling of renewable projects.
Future Outlook for Financial and Renewable Resource Utilization
The future outlook for financial and renewable resource utilization shows a significant shift towards increased investment in sustainable energy projects, driven by global climate goals and technological advancements in solar, wind, and bioenergy sectors. Financial resources are increasingly allocated to renewable infrastructure, with projections indicating a substantial rise in green bonds, climate finance, and government subsidies aimed at accelerating the transition to low-carbon economies. The integration of financial innovations such as impact investing and carbon trading markets is crucial for maximizing resource efficiency and ensuring long-term economic and environmental resilience.
Financial resources Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com