Market discipline enforces financial stability by compelling institutions to manage risks prudently and maintain transparency with investors. It influences your investment decisions by reflecting the true risks and performance of financial entities, encouraging responsible behavior. Explore the article to understand how market discipline shapes economic resilience and impacts your financial choices.
Table of Comparison
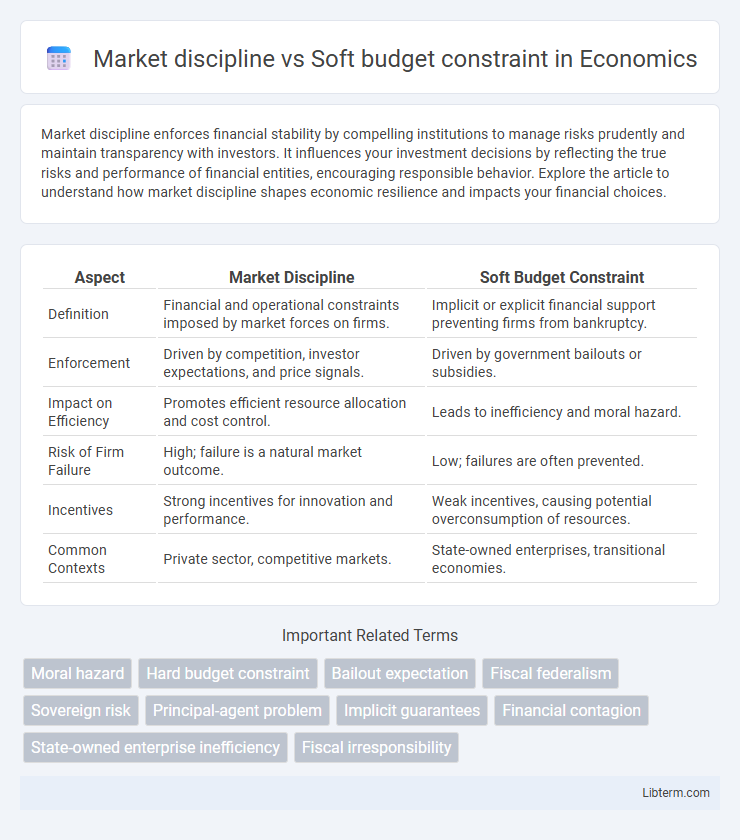
| Aspect | Market Discipline | Soft Budget Constraint |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial and operational constraints imposed by market forces on firms. | Implicit or explicit financial support preventing firms from bankruptcy. |
| Enforcement | Driven by competition, investor expectations, and price signals. | Driven by government bailouts or subsidies. |
| Impact on Efficiency | Promotes efficient resource allocation and cost control. | Leads to inefficiency and moral hazard. |
| Risk of Firm Failure | High; failure is a natural market outcome. | Low; failures are often prevented. |
| Incentives | Strong incentives for innovation and performance. | Weak incentives, causing potential overconsumption of resources. |
| Common Contexts | Private sector, competitive markets. | State-owned enterprises, transitional economies. |
Understanding Market Discipline: Definition and Importance
Market discipline refers to the mechanism by which market participants influence the behavior of firms, especially financial institutions, through investment decisions and pricing of risk. This concept is crucial in enforcing prudent management and preventing excessive risk-taking by aligning the interests of creditors and shareholders. Understanding market discipline helps regulators and stakeholders design policies that enhance accountability and financial stability in competitive markets.
What Is a Soft Budget Constraint? Key Concepts Explained
A soft budget constraint occurs when a firm or organization expects external financial support, leading to reduced incentives for cost control and efficiency. This concept contrasts with market discipline, which enforces financial accountability through competitive pressures and the risk of bankruptcy. Understanding soft budget constraints is crucial for analyzing behaviors in state-owned enterprises and sectors with government bailouts.
Historical Context: The Evolution of Market Discipline and Soft Budget Constraints
Market discipline emerged prominently during the 1980s as governments and financial institutions sought to reduce inefficiencies in state-owned enterprises through increased accountability and risk-sensitive pricing. The concept of soft budget constraints was extensively studied by economist Janos Kornai in the 1970s, highlighting how socialist economies allowed enterprises to operate with financial leniency, leading to persistent inefficiencies and moral hazard. Over time, the global shift toward market-oriented reforms in the late 20th century underscored the tension between enforcing hard budget constraints through market discipline and the legacy of soft budget constraints in transition economies.
Causes and Drivers of Soft Budget Constraints in Modern Economies
Soft budget constraints arise primarily from government interventions and expectations of bailouts that reduce financial discipline among firms, particularly in state-owned enterprises and heavily regulated industries. These constraints are driven by political motives, such as preserving employment and social stability, as well as institutional factors like weak bankruptcy laws and insufficient market competition. Market discipline encourages firms to operate efficiently through financial accountability, but soft budget constraints undermine this by enabling recurrent financial support despite poor performance.
Core Differences: Market Discipline vs Soft Budget Constraint
Market discipline enforces financial responsibility through external pressures like investor demands, regulatory oversight, and competition, ensuring firms operate efficiently and allocate resources effectively. Soft budget constraints occur when organizations receive bailouts or financial support despite poor performance, weakening incentives to control costs and triggering inefficiencies. The core difference lies in market discipline promoting accountability and sustainability, whereas soft budget constraints encourage dependency and moral hazard.
Effects on Organizational Behavior and Efficiency
Market discipline enforces strict budget adherence by subjecting organizations to competitive pressures and financial accountability, driving efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Soft budget constraints reduce the urgency for cost control by allowing organizations to expect external bailouts or financial support, often resulting in inefficient resource allocation and riskier organizational behavior. The contrasting effects shape how entities prioritize innovation, operational discipline, and responsiveness to market signals.
Case Studies: Market Discipline in Developed vs Emerging Markets
Market discipline operates more effectively in developed markets where transparency, regulatory enforcement, and financial infrastructure facilitate timely information dissemination and risk assessment by investors. In emerging markets, weak institutions, limited access to reliable financial data, and government interventions often result in soft budget constraints, undermining market discipline and encouraging inefficient capital allocation. Case studies from countries like the US and Germany show robust market responses to fiscal mismanagement, whereas emerging economies such as India and Brazil reveal persistent reliance on state support and bailout expectations.
Consequences of Soft Budget Constraints for Public and Private Sectors
Soft budget constraints often lead to inefficiencies in both public and private sectors by diminishing incentives for fiscal discipline and effective resource allocation. In the public sector, this results in persistent budget deficits and reliance on government bailouts, undermining accountability and long-term sustainability. Private firms facing soft budget constraints may engage in excessive risk-taking and overinvestment, knowing that losses will likely be absorbed by external support, which distorts market competition and innovation.
Policy Approaches: Strengthening Market Discipline and Reducing Soft Budget Constraints
Policy approaches to strengthening market discipline emphasize enhancing transparency, accountability, and financial performance monitoring to ensure firms operate under real economic constraints. Reducing soft budget constraints involves limiting government bailouts and subsidies, fostering competitive environments, and implementing strict regulatory frameworks to prevent chronic financial dependency. These strategies collectively promote efficient resource allocation and sustainable economic growth by aligning incentives with market realities.
Future Outlook: Balancing Market Discipline and Financial Flexibility
Balancing market discipline and financial flexibility requires integrating robust credit evaluation systems with adaptive budget frameworks to ensure firms remain accountable while preserving growth potential. Future trends emphasize leveraging data analytics and real-time monitoring to enforce market discipline without triggering rigid soft budget constraints that hinder innovation. Effective policies will focus on dynamic regulatory mechanisms that incentivize prudent financial behavior and allow strategic flexibility in resource allocation.
Market discipline Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com