Market transparency ensures that accurate and timely information about prices, demand, and supply is readily available to all participants, reducing uncertainty and fostering fair competition. Enhanced transparency improves decision-making for investors, businesses, and consumers, driving efficiency and confidence in the marketplace. Explore the rest of the article to understand how market transparency impacts your financial decisions and market dynamics.
Table of Comparison
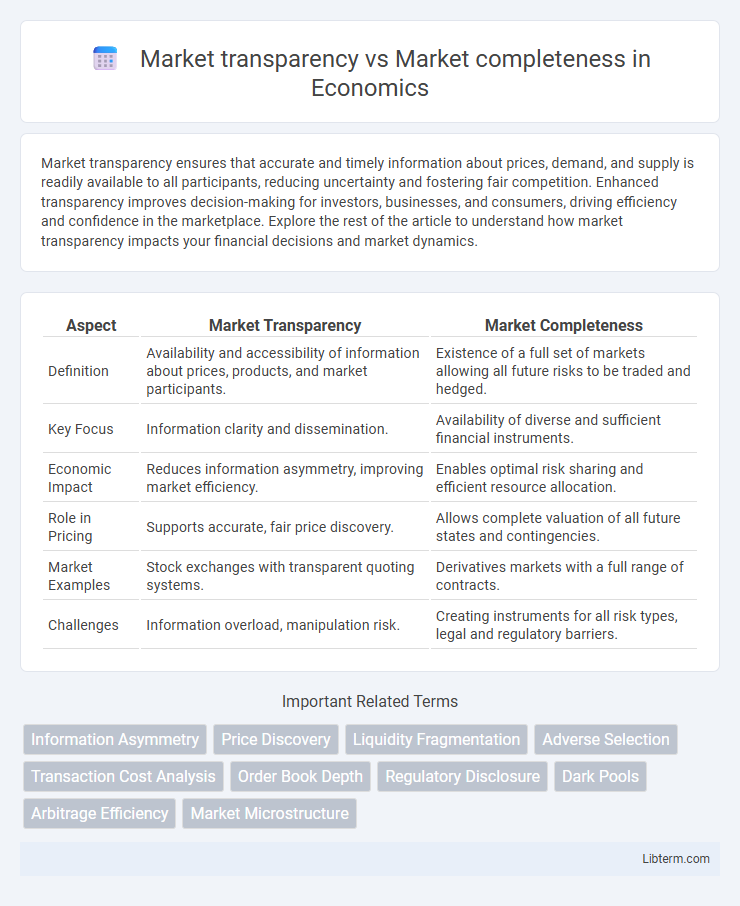
| Aspect | Market Transparency | Market Completeness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Availability and accessibility of information about prices, products, and market participants. | Existence of a full set of markets allowing all future risks to be traded and hedged. |
| Key Focus | Information clarity and dissemination. | Availability of diverse and sufficient financial instruments. |
| Economic Impact | Reduces information asymmetry, improving market efficiency. | Enables optimal risk sharing and efficient resource allocation. |
| Role in Pricing | Supports accurate, fair price discovery. | Allows complete valuation of all future states and contingencies. |
| Market Examples | Stock exchanges with transparent quoting systems. | Derivatives markets with a full range of contracts. |
| Challenges | Information overload, manipulation risk. | Creating instruments for all risk types, legal and regulatory barriers. |
Defining Market Transparency
Market transparency refers to the degree to which buyers and sellers have access to accurate, timely, and comprehensive information about prices, product quality, and market conditions. It enhances efficient decision-making by reducing information asymmetry and enabling participants to predict market trends accurately. High market transparency supports fair competition and helps prevent market manipulation by making critical data openly available to all stakeholders.
Understanding Market Completeness
Market completeness refers to a financial market's ability to allow every contingent claim to be replicated or hedged through available securities, ensuring that all possible future states of the world are accounted for. Understanding market completeness is crucial for evaluating the efficiency and risk management potential of the market, as it determines whether investors can construct portfolios to achieve any desired payoff structure. Unlike market transparency, which concerns the availability and accessibility of information, market completeness emphasizes the structural capacity of financial instruments to span all outcomes and thus facilitate optimal risk-sharing.
Key Differences Between Transparency and Completeness
Market transparency involves the availability and clarity of information about prices, transactions, and market conditions, enabling participants to make informed decisions. Market completeness refers to a market's ability to offer a full set of securities or contracts that allow agents to fully insure against all possible future contingencies. The key difference lies in transparency emphasizing information flow and clarity, while completeness focuses on the range of traded instruments that facilitate risk-sharing and hedging opportunities.
The Role of Information in Market Operations
Market transparency enables participants to make informed decisions by providing accessible and accurate information about prices, supply, and demand, reducing information asymmetry. Market completeness depends on the availability of a full set of contingent claims, allowing all possible future states to be insured or traded, which requires robust information flows. Efficient market operations rely on transparent information dissemination to ensure that incomplete markets can still function effectively by mitigating uncertainty and facilitating optimal resource allocation.
Effects of Transparency on Market Efficiency
Market transparency significantly enhances market efficiency by reducing information asymmetry, allowing investors to make well-informed decisions and improving price accuracy. Higher transparency leads to increased liquidity and lower transaction costs, facilitating smoother market operations. However, excessive transparency might deter market participants due to concerns over strategic information exposure, potentially affecting market completeness.
Impact of Completeness on Pricing and Liquidity
Market completeness significantly enhances pricing accuracy by ensuring all possible contingent claims can be traded, allowing prices to fully reflect underlying risks and information. This completeness reduces informational asymmetries and market frictions, thus improving liquidity as traders can hedge and diversify more effectively. Consequently, markets with higher completeness exhibit tighter bid-ask spreads and increased trading volumes, bolstering efficient resource allocation.
Case Studies: Transparent but Incomplete Markets
Transparent but incomplete markets reveal crucial pricing data yet lack comprehensive coverage of all assets or participants, limiting their informational efficiency. Case studies such as peer-to-peer lending platforms demonstrate how transparency in loan terms and borrower histories enhances trust, but incomplete participation restricts market liquidity and risk diversification. Regulatory interventions in carbon trading schemes highlight transparency successes in emissions data while underscoring challenges from gaps in market coverage and verification processes.
Case Studies: Complete but Opaque Markets
Case studies of complete but opaque markets reveal significant challenges in achieving market transparency, as all assets may be available for trade yet information asymmetry persists. For instance, the housing market often exhibits completeness through diverse asset availability, but opacity arises from undisclosed property defects or insider knowledge, impeding efficient price discovery. These scenarios highlight the importance of transparency measures alongside market completeness to ensure fair valuation and optimal resource allocation.
Enhancing Both Transparency and Completeness
Market transparency involves the clear, accessible disclosure of price, volume, and transaction data, enabling informed decision-making by participants. Market completeness refers to the availability of a full range of financial instruments that cover all possible states of the world, ensuring efficient risk allocation. Enhancing both transparency and completeness improves market efficiency, reduces information asymmetry, and fosters greater investor confidence by providing accurate data and diverse trading options.
Future Trends in Market Transparency and Completeness
Future trends in market transparency emphasize the integration of blockchain technology and AI-driven analytics to enhance real-time data accessibility and reduce information asymmetry. Market completeness is evolving through advanced financial instruments and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms that enable a broader range of risk-sharing and asset diversification options. These innovations collectively drive more efficient price discovery and improved market participation across global financial ecosystems.
Market transparency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com