Simulation teaching enhances experiential learning by immersing students in realistic scenarios that develop problem-solving and critical thinking skills. This method bridges theory and practice, ensuring learners gain hands-on experience in a controlled environment. Discover how simulation teaching can transform your educational approach in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
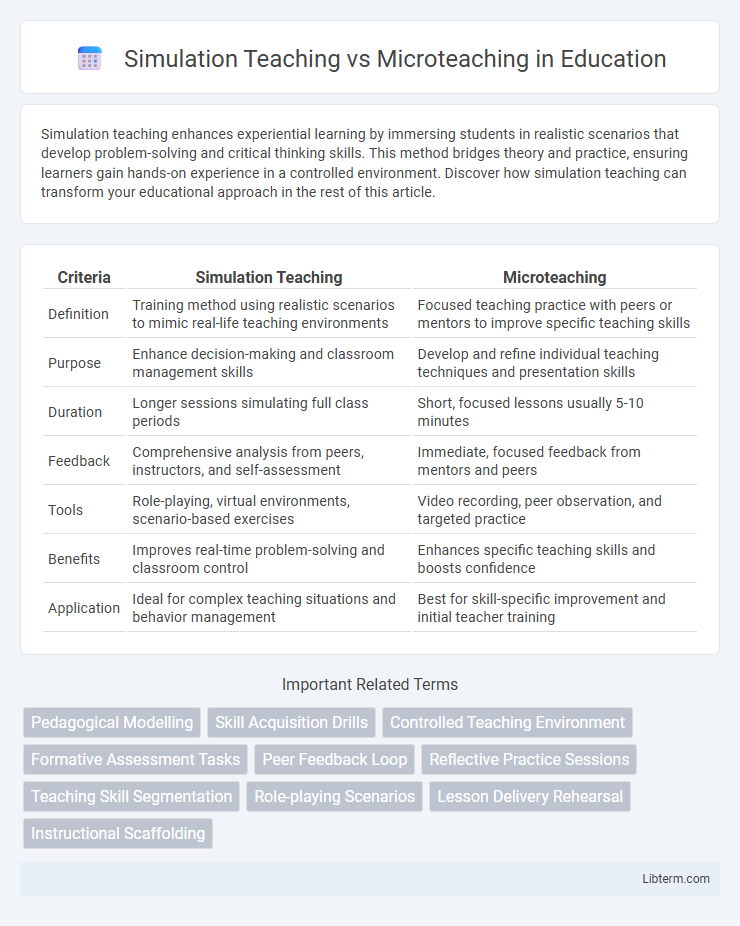
| Criteria | Simulation Teaching | Microteaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Training method using realistic scenarios to mimic real-life teaching environments | Focused teaching practice with peers or mentors to improve specific teaching skills |
| Purpose | Enhance decision-making and classroom management skills | Develop and refine individual teaching techniques and presentation skills |
| Duration | Longer sessions simulating full class periods | Short, focused lessons usually 5-10 minutes |
| Feedback | Comprehensive analysis from peers, instructors, and self-assessment | Immediate, focused feedback from mentors and peers |
| Tools | Role-playing, virtual environments, scenario-based exercises | Video recording, peer observation, and targeted practice |
| Benefits | Improves real-time problem-solving and classroom control | Enhances specific teaching skills and boosts confidence |
| Application | Ideal for complex teaching situations and behavior management | Best for skill-specific improvement and initial teacher training |
Introduction to Simulation Teaching and Microteaching
Simulation teaching uses realistic scenarios and technology to replicate real-life environments, enabling learners to practice and refine skills in a controlled setting. Microteaching breaks down teaching into small, focused sessions where educators practice specific techniques and receive immediate feedback. Both methods enhance teaching effectiveness but differ in scope, with simulation offering immersive practice and microteaching emphasizing targeted skill development.
Defining Simulation Teaching
Simulation teaching involves creating realistic, controlled environments where learners practice skills and decision-making without real-world consequences, enhancing experiential learning. It uses advanced technologies such as virtual reality, mannequins, or role-playing scenarios to mimic authentic situations for medical, technical, or educational training. This method improves competency, critical thinking, and confidence by allowing repetitive practice and immediate feedback in a risk-free setting.
Key Features of Microteaching
Microteaching emphasizes a scaled-down, practice-based approach where teachers conduct short, focused lessons to sharpen specific teaching skills within a controlled environment. Key features include video recording for self-review, peer and mentor feedback, and repeated practice of targeted teaching strategies in brief sessions, typically lasting 5-10 minutes. This method contrasts with simulation teaching by prioritizing skill refinement over complex, scenario-based role-playing, fostering confidence and competence in essential instructional techniques.
Differences Between Simulation Teaching and Microteaching
Simulation teaching involves creating lifelike scenarios using technology or role-play to mimic real classroom challenges, enabling teachers to practice decision-making and classroom management. Microteaching focuses on refining specific teaching skills by having educators teach short lessons to a small group, often peers or a coach, followed by detailed feedback and reflection. The key difference lies in simulation teaching's broader, immersive environment versus microteaching's skill-specific, controlled practice sessions.
Benefits of Simulation Teaching in Education
Simulation teaching enhances experiential learning by providing realistic scenarios that foster critical thinking and decision-making skills in a risk-free environment. It allows students to practice complex procedures repeatedly, leading to improved retention and confidence before real-world application. This method also supports immediate feedback and adaptive learning, which accelerates skill acquisition and promotes deeper understanding in education.
Advantages of Microteaching for Teacher Development
Microteaching offers targeted practice in a controlled environment, allowing teachers to refine specific skills such as questioning, feedback, and classroom management with immediate constructive feedback. This technique enhances self-confidence and reduces anxiety by enabling repeated rehearsals of teaching segments before applying them in real classrooms. Microteaching's focused sessions facilitate personalized improvement, making it a highly effective tool for professional growth and competency development in educators.
Challenges of Simulation Teaching and Microteaching
Simulation teaching faces challenges such as high costs for realistic equipment, limited flexibility in replicating complex real-life scenarios, and the need for extensive technical support. Microteaching struggles with constraints like reduced class size that may not represent actual classroom dynamics, limited feedback scope, and the difficulty of addressing diverse learner behaviors in a controlled environment. Both methods require significant time investment from educators to design, implement, and evaluate effective teaching practices.
Implementation Strategies for Both Methods
Simulation teaching employs realistic scenarios and virtual environments to enhance experiential learning, requiring advanced technological tools and structured role-playing exercises for effective implementation. Microteaching focuses on delivering concise, targeted teaching sessions within a controlled setting, emphasizing feedback mechanisms and iterative practice to refine instructional skills. Implementing both methods involves tailoring lesson objectives, selecting appropriate participant groups, and integrating performance assessments to optimize teaching competence and learner engagement.
Case Studies: Successful Applications
Case studies highlight Simulation Teaching's effectiveness in medical education, where virtual patient scenarios enhance clinical decision-making skills. Microteaching has proven successful in teacher training programs by allowing educators to practice and refine specific teaching techniques through recorded sessions and peer feedback. Both methods demonstrate significant improvements in participant confidence and mastery of targeted skills within controlled learning environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Simulation teaching offers immersive, realistic practice environments ideal for developing complex decision-making skills, while microteaching emphasizes focused skill refinement through brief, controlled teaching sessions. Selecting the right approach depends on the educator's objectives, whether aiming for comprehensive experiential learning or targeted pedagogical improvement. Integrating both methods can enhance overall teaching effectiveness by combining practical application with precise instructional feedback.
Simulation Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com