A Transnational Corporation (TNC) operates in multiple countries, leveraging global resources and markets to maximize profits and efficiency. TNCs influence international trade, labor standards, and economic policies, shaping the global business landscape significantly. Explore this article to understand how your everyday life is impacted by the activities of TNCs worldwide.
Table of Comparison
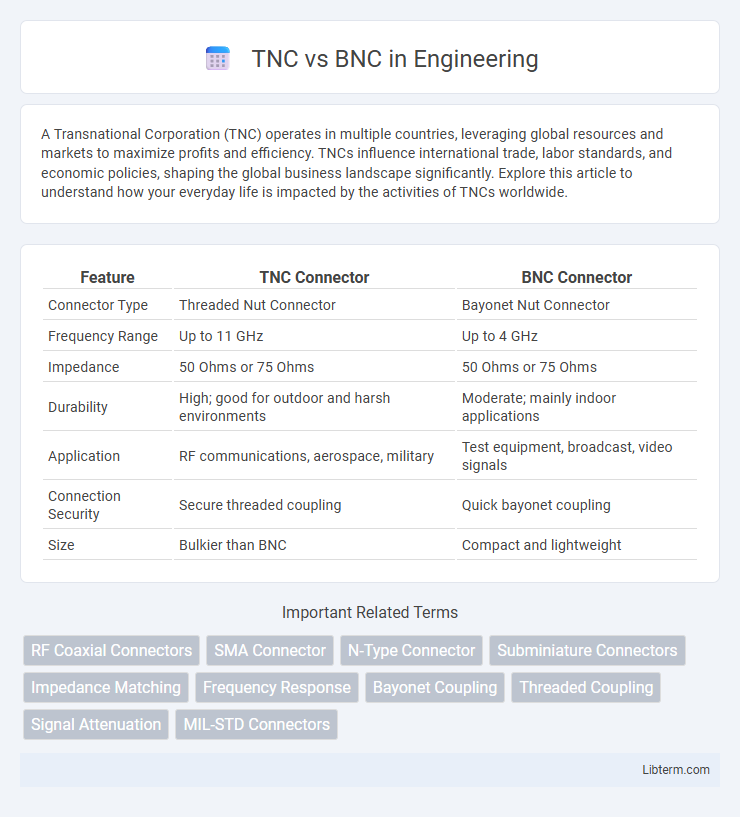
| Feature | TNC Connector | BNC Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Connector Type | Threaded Nut Connector | Bayonet Nut Connector |
| Frequency Range | Up to 11 GHz | Up to 4 GHz |
| Impedance | 50 Ohms or 75 Ohms | 50 Ohms or 75 Ohms |
| Durability | High; good for outdoor and harsh environments | Moderate; mainly indoor applications |
| Application | RF communications, aerospace, military | Test equipment, broadcast, video signals |
| Connection Security | Secure threaded coupling | Quick bayonet coupling |
| Size | Bulkier than BNC | Compact and lightweight |
Introduction to TNC and BNC Connectors
TNC and BNC connectors are widely used in RF and coaxial cable applications, designed to ensure secure and stable connections. TNC (Threaded Neill-Concelman) connectors feature a threaded coupling mechanism for enhanced vibration resistance and superior performance at higher frequencies, typically up to 11 GHz. BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman) connectors utilize a bayonet coupling system, providing quick connect/disconnect capabilities and reliable performance up to 4 GHz, commonly found in video and radio-frequency equipment.
Overview of TNC Connectors
TNC connectors feature a threaded coupling mechanism that provides superior vibration resistance and environmental sealing compared to BNC connectors, making them ideal for outdoor and high-frequency applications up to 11 GHz. They maintain a consistent 50-ohm impedance and support reliable RF signal transmission in demanding conditions such as military and telecommunications environments. The robust metal construction and precision design of TNC connectors ensure enhanced durability and stable performance in harsh settings.
Overview of BNC Connectors
BNC connectors are miniature quick connect/disconnect radio frequency connectors used primarily for coaxial cable connections in television, radio, and other RF applications. They feature a bayonet mount locking mechanism that provides secure and reliable connections, typically operating at frequencies up to 4 GHz. BNC connectors are widely favored for their ease of use, durability, and consistent impedance matching, making them ideal for professional video and networking equipment.
Key Differences Between TNC and BNC
TNC connectors feature a threaded coupling mechanism providing superior durability and resistance to vibration, ideal for outdoor and industrial applications, while BNC connectors use a bayonet-style coupling for quick and easy connections primarily in indoor environments. TNC connectors typically support higher frequency ranges up to 11 GHz, compared to BNC connectors which are generally limited to 4 GHz. The difference in design affects impedance options, with TNC connectors available in both 50 ohm and 75 ohm versions, whereas BNC connectors are commonly found in 50 ohm configurations.
Electrical Performance Comparison
TNC connectors provide better electrical performance than BNC connectors at higher frequencies, typically up to 500 MHz compared to BNC's limit of around 4 GHz, due to their threaded coupling mechanism which ensures a more secure connection and reduced signal loss. The impedance of TNC connectors is generally 50 ohms, making them ideal for RF applications requiring consistent impedance matching, whereas BNC connectors can be found in both 50 and 75 ohms but may suffer from signal reflection in high-frequency scenarios. TNC connectors exhibit lower voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) values, minimizing signal degradation and maintaining signal integrity in demanding electrical performance environments.
Applications and Use Cases
TNC connectors are widely used in outdoor and commercial wireless applications due to their superior weather resistance and secure threaded coupling, making them ideal for antenna connections in cellular networks and Wi-Fi systems. BNC connectors are common in low-frequency applications such as CCTV security cameras, test equipment, and broadcast video setups because of their quick bayonet coupling and reliable signal transmission up to 4 GHz. Both connectors serve distinct roles in RF and video systems, with TNC preferred for rugged environmental conditions and BNC favored for ease of use in laboratory and video environments.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
TNC connectors offer superior durability due to their threaded coupling, which provides a secure connection resistant to mechanical stresses and vibrations, making them suitable for harsh environments. BNC connectors, with their bayonet coupling design, are less robust under extreme conditions but provide quicker connect and disconnect capabilities for moderate environmental exposure. TNC connectors exhibit enhanced environmental resistance, including better sealing against moisture and dust, significantly improving performance in outdoor and industrial applications compared to BNC connectors.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
TNC connectors, featuring a threaded coupling mechanism, offer superior durability and secure connections ideal for outdoor and high-vibration environments, simplifying installation with their robust design. BNC connectors use a bayonet locking system that enables quick and easy installation but may require more frequent maintenance due to potential loosening in high-stress conditions. Maintenance of TNC connectors often involves less frequent retightening and better resistance to moisture ingress, whereas BNC connectors are more prone to wear and require regular inspection to ensure signal integrity.
Cost Analysis: TNC vs BNC
TNC connectors typically offer a lower initial cost compared to BNC connectors due to simpler manufacturing processes and widespread availability. However, BNC connectors provide better performance in high-frequency applications, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including durability and signal integrity, is essential when choosing between TNC and BNC connectors.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate connector between TNC and BNC hinges on frequency requirements and environmental factors. TNC connectors offer superior performance at frequencies up to 11 GHz and feature a threaded coupling mechanism ideal for outdoor or high-vibration environments. BNC connectors operate efficiently up to 4 GHz, making them suitable for lower-frequency applications and quick, tool-free connections in controlled settings.
TNC Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com