A roots blower is a type of positive displacement compressor that moves air or gas by trapping a fixed volume between rotating lobes and the casing. Its efficient design ensures a steady flow rate, making it ideal for applications requiring constant air delivery such as pneumatic conveying and wastewater treatment. Explore this article to understand how a roots blower can enhance your system's performance and efficiency.
Table of Comparison
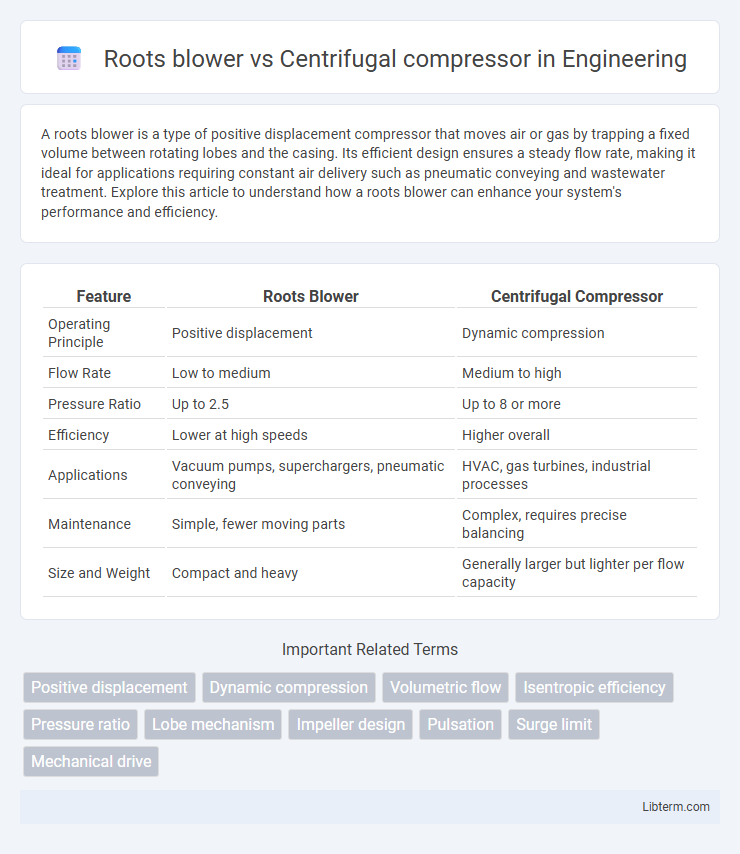
| Feature | Roots Blower | Centrifugal Compressor |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Positive displacement | Dynamic compression |
| Flow Rate | Low to medium | Medium to high |
| Pressure Ratio | Up to 2.5 | Up to 8 or more |
| Efficiency | Lower at high speeds | Higher overall |
| Applications | Vacuum pumps, superchargers, pneumatic conveying | HVAC, gas turbines, industrial processes |
| Maintenance | Simple, fewer moving parts | Complex, requires precise balancing |
| Size and Weight | Compact and heavy | Generally larger but lighter per flow capacity |
Introduction to Roots Blower and Centrifugal Compressor
Roots blowers operate using two meshing lobed rotors that trap and transfer air without internal compression, delivering a constant volume flow ideal for low-pressure applications. Centrifugal compressors utilize high-speed impellers to accelerate air radially, converting kinetic energy into pressure, enabling efficient compression at higher pressure ratios. The mechanical simplicity of Roots blowers contrasts with the aerodynamic complexity of centrifugal compressors, influencing their respective operational efficiencies and application scopes.
Basic Working Principles
A Roots blower operates by trapping a fixed volume of air between two meshing lobes and the casing, then mechanically pushing it to the outlet without internal compression, resulting in a constant flow at relatively low pressure. In contrast, a centrifugal compressor imparts velocity to the air using a rotating impeller, converting kinetic energy into pressure through a diffuser, leading to significant pressure increase in the airflow. The fundamental difference lies in the Roots blower's positive displacement mechanism versus the centrifugal compressor's dynamic energy transfer, affecting their efficiency and pressure capabilities.
Key Design Differences
Roots blowers operate using two meshing lobes that trap and move fixed volumes of air without internal compression, resulting in pulsating airflow and limited pressure rise. Centrifugal compressors employ a rotating impeller to accelerate air outward through centrifugal force, converting velocity to pressure in a diffuser, enabling higher pressure ratios and continuous smooth airflow. The key design difference lies in the Roots blower's positive displacement mechanism versus the centrifugal compressor's dynamic compression process.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Roots blowers provide consistent air flow at lower pressures with high volumetric efficiency but generally exhibit lower pressure ratios and energy efficiency compared to centrifugal compressors. Centrifugal compressors achieve higher pressure ratios and efficiencies by converting kinetic energy to pressure with dynamic compression, making them ideal for high-pressure, continuous applications. Efficiency in centrifugal compressors improves with higher operating speeds and optimized impeller design, while Roots blowers excel in applications requiring steady, low-pressure air delivery.
Applications in Industry
Roots blowers are commonly used in wastewater treatment, pneumatic conveying, and combustion air supply due to their ability to deliver constant, high-volume airflow at low pressures. Centrifugal compressors are preferred in petrochemical plants, gas processing, and HVAC systems where high-pressure, high-capacity air or gas compression is required with greater efficiency. Industry applications favor Roots blowers for low-pressure, high-flow needs and centrifugal compressors for high-pressure, variable-flow scenarios.
Advantages of Roots Blower
Roots blowers offer high volumetric efficiency and reliable performance at low to medium pressure ranges, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent airflow. Their simple design ensures low maintenance costs and robust operation under dusty or dirty conditions, outperforming centrifugal compressors in durability. Roots blowers deliver immediate pressure rise with minimal pulsation, which benefits processes demanding stable and steady air delivery.
Benefits of Centrifugal Compressor
Centrifugal compressors offer higher efficiency and greater pressure capabilities compared to Roots blowers, making them ideal for industrial processes requiring consistent airflow and higher pressure ratios. Their ability to handle large volumes of gas with minimal pulsation reduces vibration and noise, enhancing operational stability in HVAC, chemical, and petrochemical applications. Moreover, centrifugal compressors provide better energy savings due to advanced aerodynamic design, resulting in lower operational costs and reduced maintenance requirements.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Roots blowers require regular inspection of lobes and bearings due to their positive displacement design, ensuring minimal wear and optimal performance. Centrifugal compressors demand frequent monitoring of impeller balance and clearance to prevent efficiency loss and mechanical failures under variable flow conditions. Operationally, Roots blowers excel in low-pressure, constant flow applications, while centrifugal compressors are preferred for high-pressure, variable flow systems requiring precise control.
Cost Analysis and Lifecycle
Roots blowers typically have lower initial costs and simpler maintenance requirements compared to centrifugal compressors, making them suitable for budget-sensitive applications with moderate performance needs. Centrifugal compressors, while more expensive upfront, offer higher energy efficiency and longer operational lifespans, reducing total lifecycle costs in high-capacity or continuous-duty scenarios. Lifecycle cost analysis often favors centrifugal compressors in industrial settings due to their durability, lower energy consumption, and advanced materials reducing wear and downtime.
Choosing the Right Equipment for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate equipment between Roots blowers and centrifugal compressors depends on specific application requirements such as pressure range, airflow capacity, and efficiency. Roots blowers excel in low-pressure, high-volume situations and provide steady airflow with minimal pulsation. Centrifugal compressors are better suited for higher pressure applications and greater efficiency at variable flow rates, making them ideal for industrial processes demanding precise control and energy savings.
Roots blower Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com