Time-Based Maintenance (TBM) schedules equipment servicing at regular intervals to prevent unexpected failures and extend asset lifespan. This approach relies on historical data and manufacturer recommendations to optimize maintenance timing, ensuring reliable production and minimizing downtime. Explore the benefits and implementation strategies of Time-Based Maintenance in the rest of the article to enhance your maintenance program.
Table of Comparison
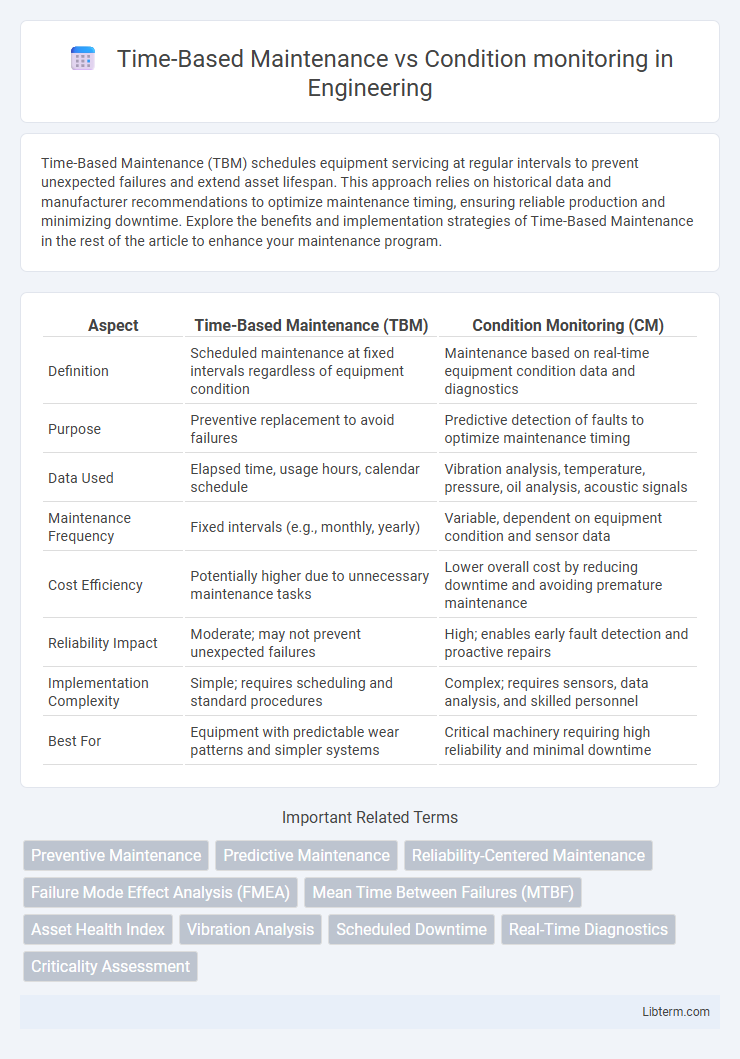
| Aspect | Time-Based Maintenance (TBM) | Condition Monitoring (CM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled maintenance at fixed intervals regardless of equipment condition | Maintenance based on real-time equipment condition data and diagnostics |
| Purpose | Preventive replacement to avoid failures | Predictive detection of faults to optimize maintenance timing |
| Data Used | Elapsed time, usage hours, calendar schedule | Vibration analysis, temperature, pressure, oil analysis, acoustic signals |
| Maintenance Frequency | Fixed intervals (e.g., monthly, yearly) | Variable, dependent on equipment condition and sensor data |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially higher due to unnecessary maintenance tasks | Lower overall cost by reducing downtime and avoiding premature maintenance |
| Reliability Impact | Moderate; may not prevent unexpected failures | High; enables early fault detection and proactive repairs |
| Implementation Complexity | Simple; requires scheduling and standard procedures | Complex; requires sensors, data analysis, and skilled personnel |
| Best For | Equipment with predictable wear patterns and simpler systems | Critical machinery requiring high reliability and minimal downtime |
Introduction to Maintenance Strategies
Time-Based Maintenance schedules service intervals based on predetermined time frames or usage cycles to prevent equipment failure. Condition Monitoring relies on real-time data collected from sensors to assess equipment health and predict maintenance needs, reducing unnecessary downtime. Selecting between these strategies depends on factors like asset criticality, operational costs, and failure patterns.
Defining Time-Based Maintenance
Time-Based Maintenance (TBM) is a proactive maintenance strategy that schedules equipment servicing at predetermined intervals based on elapsed time or operating hours, regardless of the current condition of the asset. This approach helps prevent unexpected failures by replacing or overhauling components before wear and tear significantly impact performance. TBM contrasts with Condition Monitoring, which relies on real-time data and diagnostics to trigger maintenance activities only when actual degradation or faults are detected.
Understanding Condition Monitoring
Condition monitoring involves continuously assessing equipment performance through real-time data collection and analysis, enabling predictive maintenance based on actual asset condition. This proactive approach reduces unplanned downtime and optimizes maintenance schedules by detecting early signs of wear or failure. Unlike time-based maintenance, which relies on fixed intervals, condition monitoring leverages sensors and diagnostic tools to ensure maintenance actions are performed only when necessary.
Key Differences Between Time-Based and Condition Monitoring
Time-Based Maintenance schedules equipment servicing at predetermined intervals, regardless of the actual equipment condition, ensuring routine checks but potentially causing unnecessary maintenance or unexpected failures. Condition Monitoring relies on real-time data gathered from sensors and diagnostic tools to assess equipment health, enabling targeted interventions only when indicators show wear or risk of failure. Key differences include reliance on fixed schedules in Time-Based Maintenance versus dynamic, data-driven decisions in Condition Monitoring, leading to optimized resource use and reduced downtime with the latter.
Advantages of Time-Based Maintenance
Time-Based Maintenance offers predictable scheduling and budgeting by performing maintenance tasks at fixed intervals, reducing unexpected equipment failures. This proactive approach simplifies planning and resource allocation, enhancing overall operational efficiency. Regularly timed maintenance also extends equipment lifespan by preventing wear and tear before critical issues arise.
Benefits of Condition Monitoring
Condition monitoring improves maintenance efficiency by enabling real-time tracking of equipment health, reducing unexpected failures and downtime. This approach extends asset lifespan and optimizes resource allocation through early detection of potential issues. Predictive insights from condition monitoring enhance safety and lower operational costs compared to traditional time-based maintenance schedules.
Limitations of Time-Based Maintenance
Time-Based Maintenance (TBM) often results in unnecessary part replacements due to fixed schedules that do not account for actual equipment condition. This approach can lead to increased maintenance costs and unexpected failures because it ignores real-time operational data. In contrast, Condition Monitoring provides data-driven insights to optimize maintenance intervals and enhance asset reliability.
Challenges of Implementing Condition Monitoring
Implementing condition monitoring faces challenges such as high initial investment costs for advanced sensors and data analytics platforms, which can limit adoption in resource-constrained environments. Accurate interpretation of sensor data requires skilled personnel and sophisticated algorithms to avoid false alarms or missed detections, complicating maintenance decision-making processes. Integration of condition monitoring systems with existing maintenance workflows and legacy equipment poses compatibility and standardization issues that hinder seamless implementation.
Choosing the Right Maintenance Approach
Choosing the right maintenance approach depends on equipment type, operational criticality, and failure patterns. Time-Based Maintenance schedules inspections and replacements at fixed intervals, ideal for predictable wear components, while Condition Monitoring uses real-time data and sensors to detect early signs of failure, optimizing resource allocation and reducing downtime. Integrating both strategies can enhance asset reliability and maintenance efficiency by combining proactive scheduling with reactive diagnostics.
Future Trends in Maintenance Practices
Future trends in maintenance practices emphasize the integration of Time-Based Maintenance (TBM) with advanced Condition Monitoring (CM) techniques leveraging IoT sensors and AI analytics. Predictive maintenance models increasingly utilize real-time data to optimize maintenance schedules, reducing downtime and operational costs compared to traditional TBM approaches. The convergence of machine learning and CM technologies is set to drive smarter, more adaptive maintenance strategies across industries.
Time-Based Maintenance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com