Bow-tie analysis visually maps out risk pathways by combining fault tree and event tree methodologies to identify causes and consequences of hazardous events. This method enhances your understanding of risk controls and mitigations by clearly illustrating preventive and recovery barriers. Explore the full article to master how bow-tie analysis can strengthen your risk management strategy.
Table of Comparison
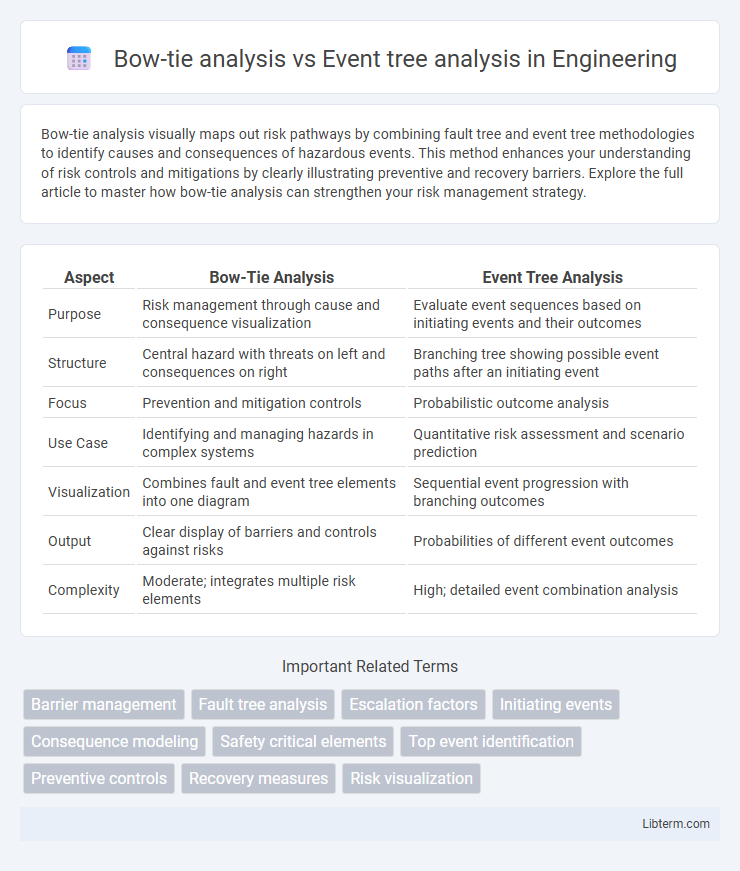
| Aspect | Bow-Tie Analysis | Event Tree Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Risk management through cause and consequence visualization | Evaluate event sequences based on initiating events and their outcomes |
| Structure | Central hazard with threats on left and consequences on right | Branching tree showing possible event paths after an initiating event |
| Focus | Prevention and mitigation controls | Probabilistic outcome analysis |
| Use Case | Identifying and managing hazards in complex systems | Quantitative risk assessment and scenario prediction |
| Visualization | Combines fault and event tree elements into one diagram | Sequential event progression with branching outcomes |
| Output | Clear display of barriers and controls against risks | Probabilities of different event outcomes |
| Complexity | Moderate; integrates multiple risk elements | High; detailed event combination analysis |
Introduction to Bow-Tie Analysis and Event Tree Analysis
Bow-Tie Analysis visually integrates fault tree and event tree methods to identify risk causes and consequences, highlighting barriers that manage hazard controls. Event Tree Analysis systematically explores possible event sequences following an initiating incident, quantifying probabilities and outcomes for risk assessment. Both techniques enhance safety management by providing structured frameworks for hazard identification and mitigation evaluation.
Fundamental Principles of Bow-Tie Analysis
Bow-tie analysis integrates fault tree and event tree methodologies to visually map risk pathways from causes to consequences, emphasizing hazard identification, preventive, and mitigative controls. Its fundamental principles center on a clear depiction of risk scenarios by linking potential causes (left side) to an undesired event (knot) and resulting consequences (right side), facilitating comprehensive risk management. This approach aids in understanding barrier effectiveness, enhancing safety measures, and supporting decision-making in complex systems.
Core Concepts of Event Tree Analysis
Event Tree Analysis (ETA) focuses on systematically exploring possible sequences of events following an initiating incident by mapping event outcomes as branches leading to various consequences, emphasizing probabilities and path dependencies. Core concepts include the identification of the initiating event, subsequent intermediate events represented as binary outcomes (success or failure), and the calculation of conditional probabilities for each branch to quantify risk. Unlike Bow-tie analysis, which combines fault and event trees for comprehensive hazard modeling, ETA centers on forward-looking scenario development to evaluate and mitigate potential accident sequences.
Visual Structure Comparison: Bow-Tie vs Event Tree
Bow-tie analysis visually combines fault tree and event tree elements to present a clear cause-and-effect relationship centered around a single hazardous event, showing threats on the left and consequences on the right. Event tree analysis uses a branching, top-down structure starting from an initiating event, illustrating possible outcomes through sequential safety barriers or failures. Bow-tie diagrams emphasize prevention and mitigation controls around the hazard, while event trees focus on the progression and probabilities of event sequences.
Strengths and Limitations of Bow-Tie Analysis
Bow-tie analysis excels in visually connecting hazards, preventive barriers, and mitigation measures in a straightforward diagram, enhancing risk communication and clarity. Its main strength lies in integrating cause and consequence analysis within a single framework, facilitating comprehensive risk assessment and management. However, limitations include potential oversimplification of complex systems and reliance on expert judgment, which may introduce subjectivity and reduce quantitative precision compared to event tree analysis.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Event Tree Analysis
Event Tree Analysis (ETA) offers a systematic approach to evaluate potential outcomes following an initiating event, providing clear visualization of possible event sequences and their probabilities. The method excels in identifying multiple accident paths and supports quantitative risk assessment but can become complex and time-consuming for systems with numerous branching events. One drawback is its dependence on accurate input data and assumptions; incomplete or incorrect information can reduce the reliability of the analysis outcomes.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Bow-Tie or Event Tree
Bow-tie analysis excels in visualizing risk pathways and identifying preventive and mitigative barriers, making it ideal for high-hazard industries like oil and gas, chemical plants, and aviation safety where clear communication of complex risk scenarios is crucial. Event tree analysis is best suited for detailed quantitative assessment of system reliability and failure consequences, commonly applied in nuclear power, aerospace engineering, and safety-critical system design to model sequential event probabilities and outcomes. Use bow-tie analysis for risk management and communication, and event tree analysis for probabilistic risk modeling and failure analysis.
Integration Possibilities: Combining Bow-Tie and Event Tree
Bow-tie analysis and event tree analysis complement each other by integrating preventive and mitigative perspectives within risk management frameworks. Bow-tie diagrams visually map causal pathways and barriers leading to a central hazardous event, while event trees systematically explore possible outcomes following that event, enabling comprehensive scenario assessment. Combining these methods enhances the accuracy of risk evaluation and supports robust decision-making by linking preventive controls with consequence analysis.
Case Study Comparisons: Real-World Examples
Bow-tie analysis excels in visualizing risk pathways by combining fault tree and event tree methodologies, as demonstrated in chemical plant hazard assessments where prevention and mitigation barriers are clearly mapped. Event tree analysis provides detailed probabilistic outcomes following an initiating event, evident in nuclear power plant safety studies that quantify consequence sequences and system failures. Comparative case studies reveal that bow-tie analysis enhances communication and barrier management, while event tree analysis offers granular quantification for emergency response planning.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Analysis Method
Bow-tie analysis excels in visualizing risk pathways and integrating preventive and mitigative controls within a single diagram, making it ideal for comprehensive risk communication. Event tree analysis offers a detailed, quantitative approach to model the sequence of events following an initiating incident, providing probabilistic outcomes essential for safety-critical system evaluation. Selecting the appropriate method depends on the objective: use bow-tie analysis for simplified risk overview and stakeholder engagement, while event tree analysis suits in-depth failure progression modeling and precise risk quantification.
Bow-tie analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com