Robotic welding enhances precision and efficiency in manufacturing by automating complex welds with consistent accuracy. This technology reduces labor costs and minimizes human error, making it ideal for high-volume production environments. Explore the article to discover how robotic welding can transform your fabrication processes.
Table of Comparison
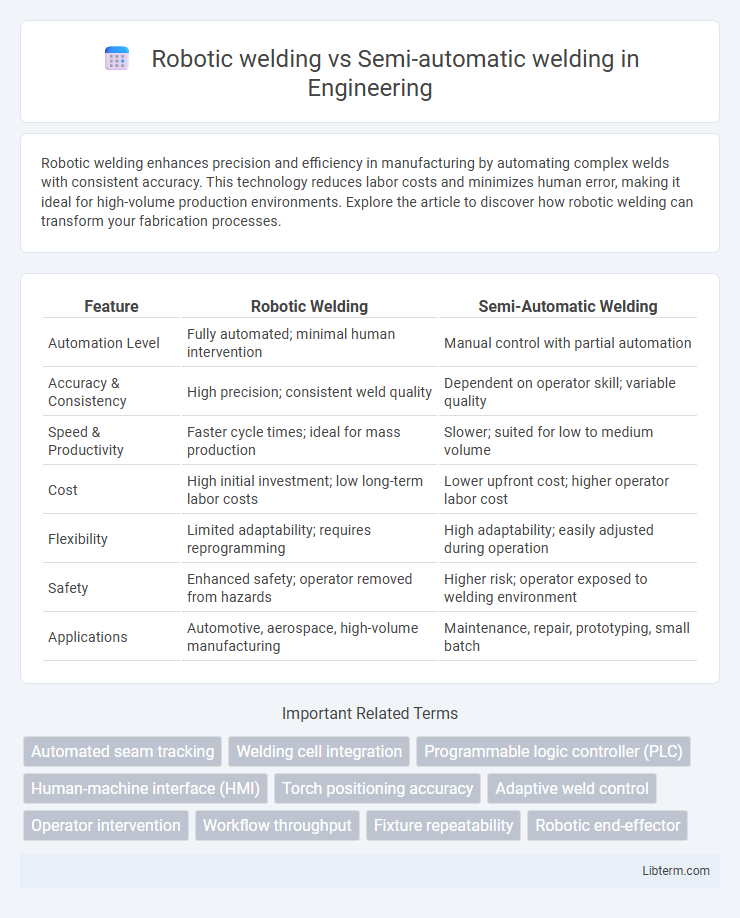
| Feature | Robotic Welding | Semi-Automatic Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Automation Level | Fully automated; minimal human intervention | Manual control with partial automation |
| Accuracy & Consistency | High precision; consistent weld quality | Dependent on operator skill; variable quality |
| Speed & Productivity | Faster cycle times; ideal for mass production | Slower; suited for low to medium volume |
| Cost | High initial investment; low long-term labor costs | Lower upfront cost; higher operator labor cost |
| Flexibility | Limited adaptability; requires reprogramming | High adaptability; easily adjusted during operation |
| Safety | Enhanced safety; operator removed from hazards | Higher risk; operator exposed to welding environment |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, high-volume manufacturing | Maintenance, repair, prototyping, small batch |
Introduction to Robotic and Semi-Automatic Welding
Robotic welding utilizes programmable automated machines to perform precise, consistent welds, ideal for high-volume production and complex tasks. Semi-automatic welding involves a human operator controlling the welding torch while a machine feeds the electrode or wire, offering flexibility and control for varied fabrication processes. Both technologies enhance efficiency and quality but differ in automation level, with robotic welding emphasizing full automation and semi-automatic welding combining human skill with mechanized assistance.
Key Differences Between Robotic and Semi-Automatic Welding
Robotic welding offers high precision, consistency, and increased production speed through automated processes, while semi-automatic welding relies on skilled operators controlling welding parameters manually. Robotic systems reduce human error and labor costs but require significant initial investment and programming expertise, whereas semi-automatic welding provides flexibility and lower setup costs ideal for smaller-scale or customized projects. The choice between these methods depends on factors like production volume, quality requirements, and budget constraints.
Workflow and Automation Levels
Robotic welding offers fully automated workflow with precise, repeatable motions controlled by programmable robots, enhancing consistency and throughput in high-volume production environments. Semi-automatic welding requires operator intervention to guide the welding torch and manage the process, resulting in lower automation levels and greater dependence on skilled labor. The workflow difference significantly impacts productivity, with robotic welding streamlining operations through integration with production lines, while semi-automatic welding remains flexible but less efficient for large-scale manufacturing.
Equipment and Setup Requirements
Robotic welding requires sophisticated machinery with programmable robotic arms, sensors, and automated control systems that demand significant initial investment and technical expertise for setup and calibration. Semi-automatic welding involves handheld welding guns and simpler power sources, offering greater flexibility and lower setup costs but requiring skilled operators for consistent results. Equipment for robotic welding emphasizes precision and repeatability, while semi-automatic setups prioritize operator control and adaptability in varying work environments.
Precision and Welding Quality
Robotic welding consistently delivers higher precision by utilizing advanced sensors and programmed movements to maintain exact control over weld parameters, resulting in uniform and repeatable weld quality. Semi-automatic welding relies heavily on operator skill, leading to greater variability in weld consistency and potential defects such as porosity or incomplete fusion. The automation in robotic welding significantly reduces human error, ensuring superior weld integrity, especially crucial in high-demand industries like automotive and aerospace manufacturing.
Production Speed and Efficiency
Robotic welding significantly enhances production speed by enabling continuous, high-precision operations without fatigue, resulting in consistent weld quality and reduced cycle times. Semi-automatic welding depends on operator skill, leading to variable speeds and potential downtime for adjustments, which can decrease overall efficiency in high-volume production environments. Integrating robotic welding systems often leads to improved throughput and lower labor costs, making it the preferred choice for industries demanding rapid, repeatable welding processes.
Cost Analysis and ROI Considerations
Robotic welding systems require higher initial investments, typically ranging between $150,000 and $400,000, but offer significant long-term cost savings through increased precision and reduced labor expenses, leading to a faster ROI within 1 to 3 years. Semi-automatic welding incurs lower upfront costs, generally around $20,000 to $50,000, yet involves higher labor costs and inconsistent weld quality, which can extend ROI timelines beyond 3 years. Analyzing operational scale and production volume is critical, as robotic welding delivers higher throughput and efficiency in large-scale manufacturing, optimizing cost per unit and maximizing capital return.
Flexibility and Adaptability for Various Projects
Robotic welding offers high precision and repeatability but tends to have limited flexibility for small-batch or complex custom projects due to programming constraints. Semi-automatic welding provides greater adaptability for diverse tasks, allowing welders to easily adjust techniques and parameters on-the-fly for varying material thicknesses and joint configurations. In dynamic production environments requiring frequent changes, semi-automatic systems excel by enabling skilled operators to handle diverse project requirements efficiently.
Operator Involvement and Skill Requirements
Robotic welding significantly reduces operator involvement by automating the welding process, requiring operators primarily to program and monitor machines rather than perform manual welding tasks. In contrast, semi-automatic welding demands higher operator skill, as the welder must control the welding torch and adjust parameters in real-time to ensure quality welds. The automation in robotic welding enhances consistency and precision, while semi-automatic welding relies on operator expertise for adaptability in complex or variable welding conditions.
Choosing the Right Welding Solution for Your Needs
Robotic welding offers unparalleled precision and consistent quality, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing environments requiring repeatability and speed. Semi-automatic welding provides greater flexibility and control for complex or customized projects, allowing welders to adapt techniques to specific material types and geometries. Choosing the right welding solution depends on factors such as production volume, budget constraints, desired welding accuracy, and the complexity of weld joints.
Robotic welding Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com