Isometric projection is a method of visually representing three-dimensional objects in two dimensions, where the three axes appear equally foreshortened and the angle between any two axes is 120 degrees. This technique preserves the scale along each axis, allowing for accurate measurements and clear visualization of complex designs without perspective distortion. Explore the rest of this article to understand how isometric projection can enhance your drawings and technical illustrations.
Table of Comparison
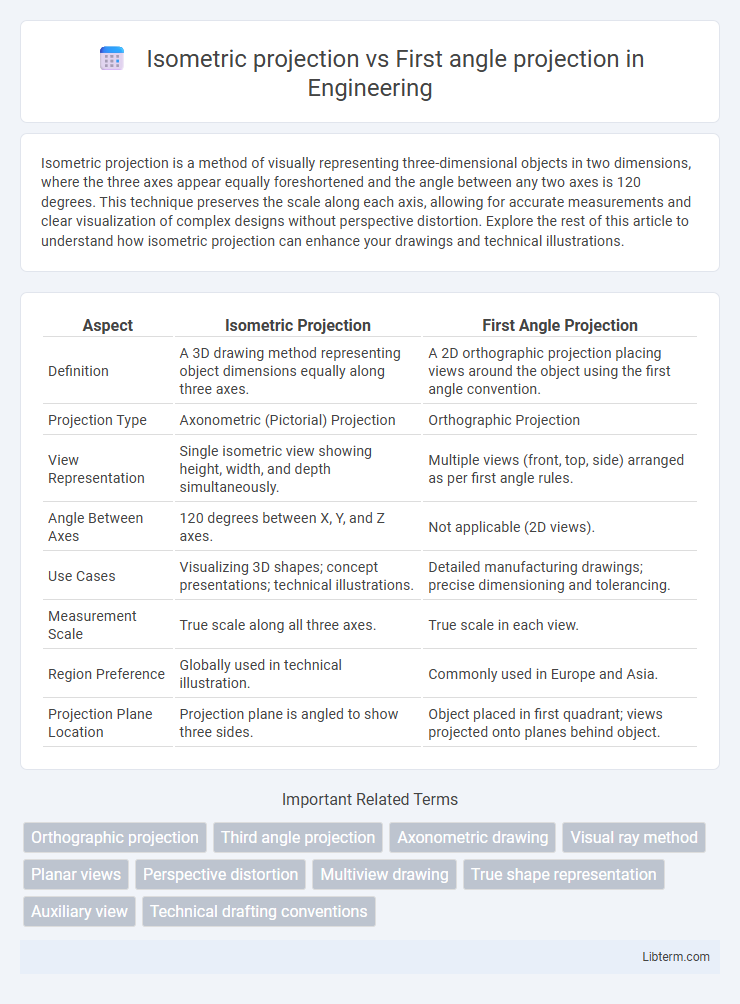
| Aspect | Isometric Projection | First Angle Projection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A 3D drawing method representing object dimensions equally along three axes. | A 2D orthographic projection placing views around the object using the first angle convention. |
| Projection Type | Axonometric (Pictorial) Projection | Orthographic Projection |
| View Representation | Single isometric view showing height, width, and depth simultaneously. | Multiple views (front, top, side) arranged as per first angle rules. |
| Angle Between Axes | 120 degrees between X, Y, and Z axes. | Not applicable (2D views). |
| Use Cases | Visualizing 3D shapes; concept presentations; technical illustrations. | Detailed manufacturing drawings; precise dimensioning and tolerancing. |
| Measurement Scale | True scale along all three axes. | True scale in each view. |
| Region Preference | Globally used in technical illustration. | Commonly used in Europe and Asia. |
| Projection Plane Location | Projection plane is angled to show three sides. | Object placed in first quadrant; views projected onto planes behind object. |
Introduction to Projection Methods
Isometric projection represents a 3D object where the three principal axes are foreshortened equally, preserving scale and angles for a visually balanced view, commonly used in technical and engineering drawings. First angle projection is a standardized orthographic projection method primarily used in Europe, where the object is imagined to be placed in the first quadrant, projecting views onto planes behind the object to create accurate 2D representations of each side. Both projection methods are fundamental in engineering graphics, facilitating the interpretation of complex geometries through systematic visualization techniques.
What is Isometric Projection?
Isometric projection is a type of axonometric drawing used in technical and engineering fields to represent three-dimensional objects on two-dimensional surfaces, where the three principal axes are equally foreshortened at 120-degree angles. This method maintains the scale along each axis, allowing accurate measurements without distortion, making it ideal for visualizing complex parts and assemblies. Unlike first angle projection, which is a planar orthographic method based on multiple views, isometric projection provides a single, visually comprehensive perspective enhancing spatial understanding.
What is First Angle Projection?
First Angle Projection is a method of orthographic projection primarily used in Europe and Asia for technical drawings, where the object is positioned between the observer and the plane of projection. It represents the views by projecting the image onto planes behind the object, resulting in a specific arrangement of front, top, and side views that differ from the Third Angle Projection standard. This technique facilitates clear communication in engineering and manufacturing by providing standardized, consistent views of complex objects.
Key Differences Between Isometric and First Angle Projection
Isometric projection displays a three-dimensional object on a two-dimensional plane where all three axes are equally angled at 120 degrees, providing a clear volumetric view without distortion of scale. First angle projection, predominantly used in Europe, represents a 3D object by projecting views onto planes located between the observer and the object, resulting in specific view placements such as the top view below the front view. The key differences lie in their projection methods--Isometric offers a pictorial 3D representation with equal measurements along each axis, while First angle projection delivers orthographic 2D views arranged around the object's principal planes, emphasizing dimension accuracy over visual realism.
Applications of Isometric Projection
Isometric projection is widely used in engineering and architecture for visualizing complex 3D objects on 2D planes, enabling accurate measurements and design clarity. It facilitates technical drawing, CAD modeling, and assembly instructions where spatial relationships must be clearly understood without perspective distortion. Unlike first angle projection, which is primarily used for orthographic views in mechanical drawings, isometric projection provides a more intuitive representation for conceptual design and client presentations.
Applications of First Angle Projection
First angle projection is widely used in European countries and is essential for manufacturing industries requiring clear, standardized orthographic views to interpret technical drawings accurately. This projection method aids in producing precise engineering blueprints for mechanical parts, ensuring compatibility with ISO standards and facilitating international collaboration. Its application is crucial in automotive design, aerospace engineering, and construction, where exact dimensions and relationships between components must be conveyed unambiguously.
Advantages of Isometric Projection
Isometric projection offers a clear advantage in visualizing three-dimensional objects by maintaining equal scale along all three axes, which simplifies measurements and representation for designers and engineers. This projection eliminates distortion caused by perspective, enabling accurate and consistent dimensioning that aids in precise manufacturing and assembly processes. Unlike the first angle projection, isometric views provide a more intuitive spatial understanding, reducing interpretation errors in technical drawings.
Advantages of First Angle Projection
First Angle Projection offers clearer visualization of object views by placing the top view below the front view and the right side view to the left, which aligns with traditional European drafting standards. This method reduces confusion in interpreting drawings, particularly for manufacturing and technical communication across international teams. It also simplifies dimensioning and measurement by maintaining consistent orientation between views, enhancing accuracy and ease of understanding.
Isometric vs First Angle Projection: Which to Choose?
Isometric projection provides a three-dimensional view where all axes are equally foreshortened, making it ideal for visualizing complex objects with clear spatial relationships. First angle projection is a two-dimensional orthographic technique primarily used in Europe and Asia, organizing views in a specific layout for detailed engineering drawings. Choose isometric projection for intuitive 3D visualization, while first angle projection suits precise technical documentation and standardized communication in manufacturing.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Isometric projection offers a clear, three-dimensional view by maintaining equal scales along all three axes, which is ideal for visualizing objects in engineering and design. First angle projection, commonly used in Europe and Asia, provides multiple orthographic views that emphasize true dimensions and relationships between object features. Choosing between these projection methods depends on the purpose: isometric for intuitive spatial understanding, and first angle for precise technical documentation.
Isometric projection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com