Roller bearings are essential mechanical components designed to reduce friction and support radial and axial loads in rotating machinery. Their cylindrical rolling elements improve performance and durability compared to plain bearings, making them invaluable in applications ranging from industrial machinery to automotive systems. Discover how selecting the right roller bearing can enhance your equipment's efficiency and lifespan in the full article.
Table of Comparison
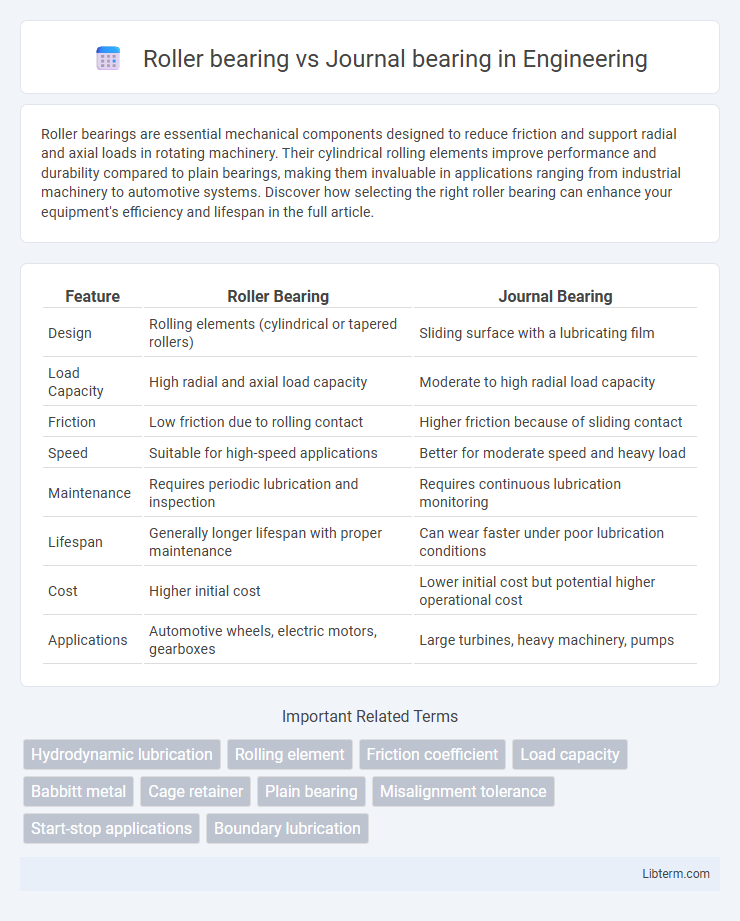
| Feature | Roller Bearing | Journal Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Rolling elements (cylindrical or tapered rollers) | Sliding surface with a lubricating film |
| Load Capacity | High radial and axial load capacity | Moderate to high radial load capacity |
| Friction | Low friction due to rolling contact | Higher friction because of sliding contact |
| Speed | Suitable for high-speed applications | Better for moderate speed and heavy load |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic lubrication and inspection | Requires continuous lubrication monitoring |
| Lifespan | Generally longer lifespan with proper maintenance | Can wear faster under poor lubrication conditions |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost but potential higher operational cost |
| Applications | Automotive wheels, electric motors, gearboxes | Large turbines, heavy machinery, pumps |
Introduction to Roller Bearings and Journal Bearings
Roller bearings use cylindrical or spherical rolling elements to reduce friction and support radial and axial loads, providing high load capacity and accuracy in mechanical systems. Journal bearings consist of a shaft rotating within a lubricated sleeve, relying on a thin film of lubricant to minimize direct metal-to-metal contact and absorb shock loads. Both bearing types are essential in applications requiring efficient load distribution and reduced wear, but differ in design, lubrication needs, and load handling characteristics.
Basic Working Principles
Roller bearings use cylindrical or spherical rolling elements to reduce friction between rotating shafts and stationary supports by distributing the load over a larger surface area, enabling smooth motion with minimal resistance. Journal bearings operate on the principle of hydrodynamic or oil film lubrication, where a thin layer of lubricant creates a fluid film that separates the rotating shaft from the bearing surface, preventing direct metal-to-metal contact. Roller bearings are ideal for applications requiring precise alignment and higher load capacities, while journal bearings excel in high-speed or heavy-load environments due to their self-lubricating properties and ability to accommodate shaft misalignment.
Key Design Differences
Roller bearings use rolling elements such as cylinders or spheres to reduce friction, allowing higher load capacity and lower wear compared to journal bearings that rely on a thin lubricating film between a shaft and a bearing surface. Journal bearings typically have simpler construction, providing better damping and accommodating misalignment, but they require precise lubrication and operate efficiently within a narrow speed range. Material selection and heat dissipation strategies differ significantly, with roller bearings favoring hardened steel rollers and cages, whereas journal bearings use babbitt or bronze alloys with fluid film lubrication to minimize metal-to-metal contact.
Load Capacity Comparison
Roller bearings typically exhibit higher load capacity than journal bearings due to their rolling elements that reduce friction and evenly distribute loads across contact points. Journal bearings, relying on a thin lubricant film and fluid dynamic pressure, generally support lower loads but excel in applications requiring smooth, continuous rotation under moderate stress. Material composition and design geometry significantly influence the load-bearing performance of both bearing types in industrial machinery.
Friction and Efficiency
Roller bearings exhibit lower friction coefficients ranging from 0.001 to 0.004 due to rolling contact, enhancing mechanical efficiency in high-speed applications. Journal bearings operate on hydrodynamic lubrication principles, with friction coefficients typically between 0.001 and 0.02, where efficiency depends on maintaining a full lubricant film to minimize metal-to-metal contact. Efficiency in roller bearings generally surpasses journal bearings under dynamic loads, but journal bearings provide superior damping and load capacity in heavy-duty, low-speed machinery.
Maintenance and Lubrication
Roller bearings require less frequent maintenance due to their sealed design, which retains lubricant and prevents contamination, making them ideal for high-speed applications. Journal bearings demand regular lubrication checks and oil changes because they rely on a continuous oil film for operation, and inadequate lubrication can lead to metal-to-metal contact and wear. Proper lubrication in journal bearings typically involves oil pumps or circulating systems, while roller bearings commonly use grease or sealed oil lubricants that ensure longevity and lower maintenance costs.
Applications and Industry Usage
Roller bearings excel in heavy load and high-speed applications, making them ideal for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery where durability and precision are critical. Journal bearings, with their capability to support heavier radial loads and operate under lower speeds with fluid lubrication, are commonly used in large industrial equipment, turbines, and marine engines. The choice between roller and journal bearings hinges on specific operational requirements, including load capacity, speed, lubrication conditions, and environmental factors.
Advantages of Roller Bearings
Roller bearings offer higher load-carrying capacity and lower friction compared to journal bearings, which enhances efficiency and reduces wear in machinery. Their ability to support both radial and axial loads with minimal lubrication extends maintenance intervals and improves operational reliability. These bearings also provide precise shaft positioning and better performance at high speeds, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications.
Advantages of Journal Bearings
Journal bearings offer superior load-carrying capacity and enhanced durability due to their large surface area distributing forces evenly, reducing wear and extending service life. They provide better vibration damping and smoother operation in high-speed applications compared to roller bearings. Journal bearings also require less maintenance and are often more cost-effective for heavy industrial machinery and large-scale rotating equipment.
Choosing the Right Bearing for Your Application
Roller bearings offer high load capacity and lower friction, making them ideal for applications with heavy radial loads and high-speed rotation. Journal bearings excel in applications requiring smooth, quiet operation and can handle higher continuous loads due to their fluid film lubrication. Selecting the right bearing depends on factors like load type, speed, operating temperature, and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Roller bearing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com