Labyrinth seals provide a non-contact method to prevent leakage of fluids or gases in rotating machinery, ensuring high efficiency and durability under challenging operating conditions. These seals use a series of intricate grooves to create a tortuous path that minimizes leakage without physical contact, reducing wear and maintenance costs. Discover how you can optimize the performance of your equipment by exploring the detailed functions and applications of labyrinth seals in the article below.
Table of Comparison
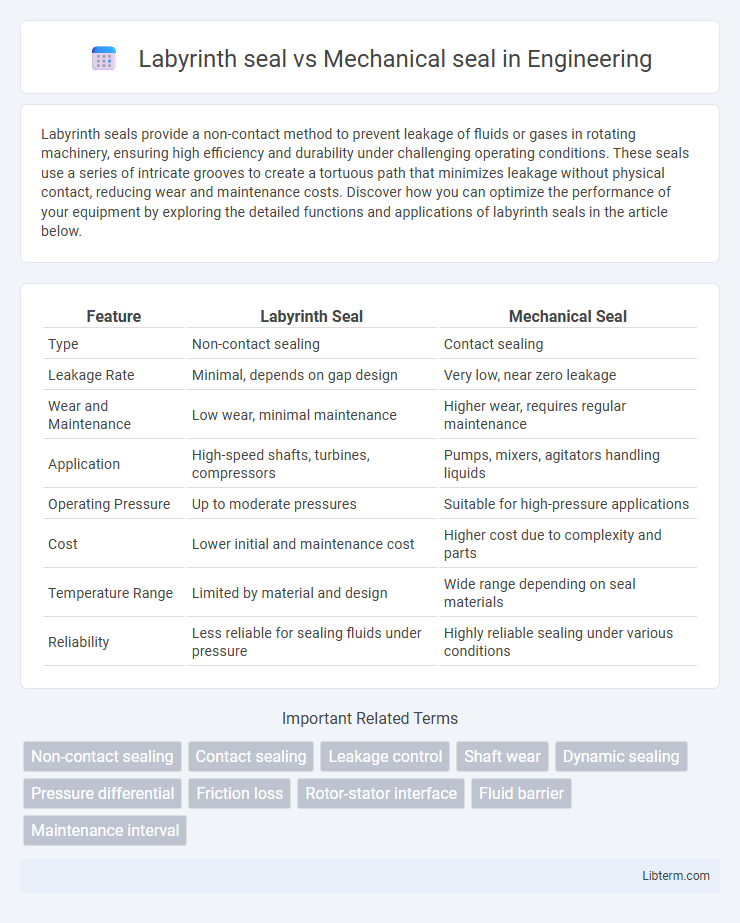
| Feature | Labyrinth Seal | Mechanical Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Non-contact sealing | Contact sealing |
| Leakage Rate | Minimal, depends on gap design | Very low, near zero leakage |
| Wear and Maintenance | Low wear, minimal maintenance | Higher wear, requires regular maintenance |
| Application | High-speed shafts, turbines, compressors | Pumps, mixers, agitators handling liquids |
| Operating Pressure | Up to moderate pressures | Suitable for high-pressure applications |
| Cost | Lower initial and maintenance cost | Higher cost due to complexity and parts |
| Temperature Range | Limited by material and design | Wide range depending on seal materials |
| Reliability | Less reliable for sealing fluids under pressure | Highly reliable sealing under various conditions |
Introduction to Sealing Technologies
Labyrinth seals provide non-contact sealing by creating a complex path to prevent fluid leakage, ideal for high-speed rotating shafts in turbines and compressors. Mechanical seals use contact sealing with elastomeric or metallic components to maintain a tight barrier against fluids, commonly employed in pumps and mixers where leakage control is critical. Understanding the fundamental differences in sealing mechanisms is essential for selecting the appropriate seal type based on operational speed, pressure, and fluid characteristics.
What is a Labyrinth Seal?
A labyrinth seal is a non-contact sealing mechanism designed to prevent leakage of fluids by creating a complex path through interlocking ridges and grooves, which disrupts the flow and reduces pressure. Commonly used in rotating machinery such as turbines, compressors, and pumps, labyrinth seals offer high durability and minimal wear since they do not rely on direct surface contact. Unlike mechanical seals that use sealing faces and secondary seals, labyrinth seals prioritize leakage control through geometric design and pressure drop.
What is a Mechanical Seal?
A mechanical seal is a device used to prevent leakage between a rotating shaft and its housing by creating a tight seal using precisely machined surfaces and elastomeric components. Unlike labyrinth seals, which rely on a tortuous path to reduce leakage, mechanical seals provide a more reliable and efficient seal by directly controlling fluid flow through contact faces. This technology is commonly used in pumps, compressors, and mixers to enhance performance and reduce maintenance requirements.
Key Differences Between Labyrinth and Mechanical Seals
Labyrinth seals rely on a series of intricate grooves and a tortuous path to minimize leakage by restricting fluid flow, while mechanical seals use a pair of precisely machined sealing faces pressed together to prevent fluid escape. Labyrinth seals are preferred for applications with high rotational speeds and moderate leakage tolerance due to their non-contact design, whereas mechanical seals provide superior leakage control and are suited for high-pressure and hazardous fluid scenarios. The main differences lie in their sealing mechanism, leakage performance, maintenance frequency, and suitability for varying operational conditions.
Performance Efficiency: Labyrinth Seal vs Mechanical Seal
Labyrinth seals offer moderately high performance efficiency through reduced friction and minimal wear, making them ideal for high-speed applications with lower leakage tolerance. Mechanical seals provide superior sealing efficiency by maintaining a tight barrier against fluids under high pressure and temperature, significantly reducing leakage and improving overall equipment reliability. Performance efficiency in mechanical seals generally surpasses labyrinth seals due to their precise design, enabling extended maintenance intervals and enhanced operational stability.
Typical Applications for Each Seal Type
Labyrinth seals are typically used in high-speed rotating equipment like turbines, compressors, and pumps where leakage control and contamination prevention are critical without physical contact. Mechanical seals are preferred in applications requiring robust sealing under high pressure and temperature conditions, such as chemical processing, oil refining, and marine propulsion systems. Both seal types serve crucial roles in maintaining equipment reliability and efficiency across various industrial sectors.
Maintenance and Longevity Comparison
Labyrinth seals require minimal maintenance due to their non-contact design, reducing wear and extending service intervals, whereas mechanical seals demand regular inspection and replacement because of their contact surfaces prone to wear and leakage. Mechanical seals, while offering superior sealing performance and reduced leakage, tend to have shorter operational lifespans and higher maintenance costs compared to labyrinth seals. Longevity of labyrinth seals can exceed mechanical seals in abrasive or contaminated environments, making them preferable for heavy-duty applications with infrequent maintenance opportunities.
Cost Considerations: Labyrinth vs Mechanical Seals
Labyrinth seals generally offer a lower initial cost compared to mechanical seals due to simpler design and easier manufacturing processes. Mechanical seals involve higher upfront expenses because of precision engineering, specialized materials, and intricate assembly requirements. Over time, mechanical seals can offer cost savings through improved leak prevention and reduced maintenance frequency, while labyrinth seals may incur higher operational costs due to leakage and wear.
Seal Selection Guidelines for Engineers
Engineers selecting between labyrinth seals and mechanical seals must consider operational conditions such as pressure, temperature, and fluid type to ensure optimal performance. Labyrinth seals are ideal for applications requiring low friction and minimal leakage under moderate pressure, while mechanical seals provide superior sealing in high-pressure or hazardous environments. Critical factors like shaft speed, maintenance intervals, and cost-effectiveness guide the decision to achieve durability and reliability in rotating equipment.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Seal for Your Operation
Labyrinth seals provide effective non-contact sealing ideal for high-speed and high-temperature applications with minimal wear and maintenance needs. Mechanical seals offer superior leakage control and reliability in demanding environments where fluid containment is critical. Selecting the right seal depends on operating conditions, fluid type, pressure, and maintenance capabilities to ensure optimal equipment performance and longevity.
Labyrinth seal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com