O-ring seals are essential components used to prevent leaks in mechanical systems by creating a tight seal between two surfaces. Manufactured from various materials like rubber, silicone, or fluorocarbon, they offer durability and resistance to pressure, temperature, and chemicals. Discover how choosing the right O-ring seal can enhance your equipment's performance by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
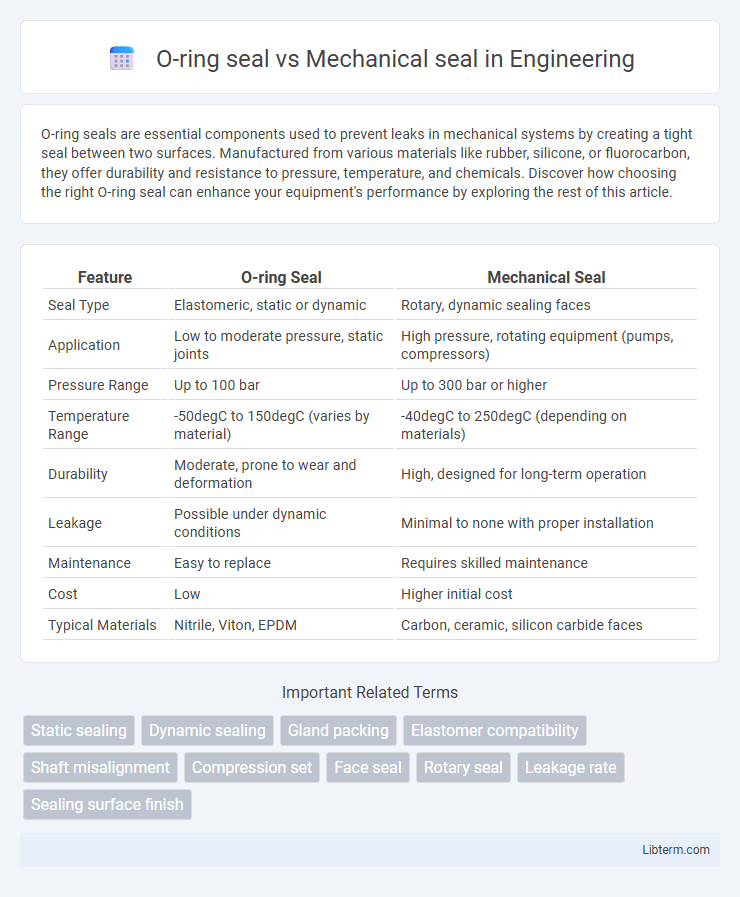
| Feature | O-ring Seal | Mechanical Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Seal Type | Elastomeric, static or dynamic | Rotary, dynamic sealing faces |
| Application | Low to moderate pressure, static joints | High pressure, rotating equipment (pumps, compressors) |
| Pressure Range | Up to 100 bar | Up to 300 bar or higher |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC (varies by material) | -40degC to 250degC (depending on materials) |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear and deformation | High, designed for long-term operation |
| Leakage | Possible under dynamic conditions | Minimal to none with proper installation |
| Maintenance | Easy to replace | Requires skilled maintenance |
| Cost | Low | Higher initial cost |
| Typical Materials | Nitrile, Viton, EPDM | Carbon, ceramic, silicon carbide faces |
Introduction to O-Ring Seal vs Mechanical Seal
O-ring seals are circular elastomer rings designed to fit into grooves and create a tight seal between two or more parts, commonly used in static or low-pressure dynamic applications. Mechanical seals consist of stationary and rotating components that maintain a seal in high-pressure and high-speed rotating equipment, preventing fluid leakage in pumps and compressors. The choice between O-ring seals and mechanical seals depends on factors like pressure, temperature, fluid type, and motion dynamics within the system.
Understanding O-Ring Seals
O-ring seals are circular elastomeric rings designed to fit into grooves and create a tight, reliable seal by compressing between two surfaces, commonly used in static and dynamic applications to prevent fluid or gas leakage. Their simple design, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation make them ideal for moderate pressure and temperature conditions, whereas mechanical seals provide enhanced sealing capabilities in high-pressure, high-speed, or abrasive environments. Understanding O-ring material compatibility with chemicals and temperature ranges is crucial for optimal sealing performance and longevity in various industrial applications.
Exploring Mechanical Seals
Mechanical seals provide superior leakage prevention compared to O-ring seals by utilizing advanced sealing faces and dynamic components, ensuring reliable performance in high-pressure and high-temperature environments. Their design incorporates rotating and stationary elements with precision-engineered materials like carbon, ceramic, and silicon carbide, enhancing durability and resistance to wear. Mechanical seals are essential in pumps, compressors, and mixers where fluid containment and longevity are critical.
Key Differences Between O-Ring and Mechanical Seals
O-ring seals provide a simple, cost-effective solution primarily for static sealing applications, using a flexible elastomer ring compressed between two surfaces to prevent fluid leakage. Mechanical seals, consisting of rotating and stationary components with precise mating surfaces, are designed for dynamic applications such as pumps and mixers, offering superior sealing performance under high pressure and temperature conditions. Key differences include the O-ring's limited resistance to wear and temperature compared to mechanical seals, which deliver enhanced durability, leak prevention, and suitability for complex rotating shaft assemblies.
Performance Comparison: O-Ring vs Mechanical Seal
O-ring seals provide effective sealing in low-pressure and static applications with simplicity and cost efficiency, but they may experience wear and leakage under high pressure or dynamic conditions. Mechanical seals offer superior performance in high-pressure, high-speed, and aggressive fluid environments by minimizing leakage through precise sealing faces and advanced materials like silicon carbide or tungsten carbide. While mechanical seals require higher initial investment and maintenance, their durability and reliability make them preferable for demanding industrial applications compared to O-ring seals.
Common Applications of O-Ring Seals
O-ring seals are commonly used in hydraulic cylinders, pneumatic systems, and automotive engines due to their simple design and effective sealing capabilities under static and low-pressure dynamic conditions. These seals perform well in applications requiring resistance to fluids, gases, and chemicals, making them ideal for pumps, valves, and compressors. Their cost-efficiency and ease of installation further drive widespread use in household appliances and industrial machinery where moderate pressure sealing is needed.
Typical Uses of Mechanical Seals
Mechanical seals are primarily used in high-pressure and high-speed rotating equipment such as pumps, compressors, and mixers where reliable sealing against fluid leakage is critical. They are essential in industries like chemical processing, oil and gas, and power generation, where harsh operating conditions demand durable and maintenance-friendly sealing solutions. Mechanical seals provide superior leakage control compared to O-ring seals, making them ideal for handling hazardous or abrasive fluids.
Maintenance and Durability Factors
O-ring seals offer easier maintenance due to their simple design and quick replacement process, but they are generally less durable under high pressure and temperature conditions compared to mechanical seals. Mechanical seals provide superior longevity and resistance to wear, benefiting applications requiring high durability and minimal leakage over extended periods. Maintenance frequency for O-ring seals tends to be higher, while mechanical seals often demand specialized servicing but result in longer operational life.
Cost Analysis: O-Ring Seal vs Mechanical Seal
O-ring seals generally offer a lower initial cost compared to mechanical seals, making them a cost-effective choice for applications with moderate pressure and temperature requirements. Mechanical seals, while more expensive upfront due to complex design and materials, provide greater durability and reduced maintenance costs over time in high-pressure, high-temperature, or chemically aggressive environments. Total cost of ownership favors mechanical seals in demanding applications despite their higher initial investment, whereas O-ring seals are economical for simpler, low-stress sealing needs.
Choosing the Right Seal for Your Application
Choosing the right seal for your application depends on factors such as operating pressure, temperature, and fluid compatibility. O-ring seals offer cost-effective, simple solutions for low to moderate pressure and temperature environments, while mechanical seals provide superior performance for high-pressure, high-temperature, and dynamic sealing applications. Evaluating the specific requirements of your system ensures optimal durability, leak prevention, and maintenance efficiency.
O-ring seal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com