Double pipe heat exchangers offer efficient heat transfer by allowing fluids to flow through two concentric pipes, optimizing thermal exchange in a compact design. Their simplicity and ease of maintenance make them ideal for industries requiring precise temperature control in limited spaces. Discover how this effective system can enhance your process efficiency by exploring the detailed insights in the rest of the article.
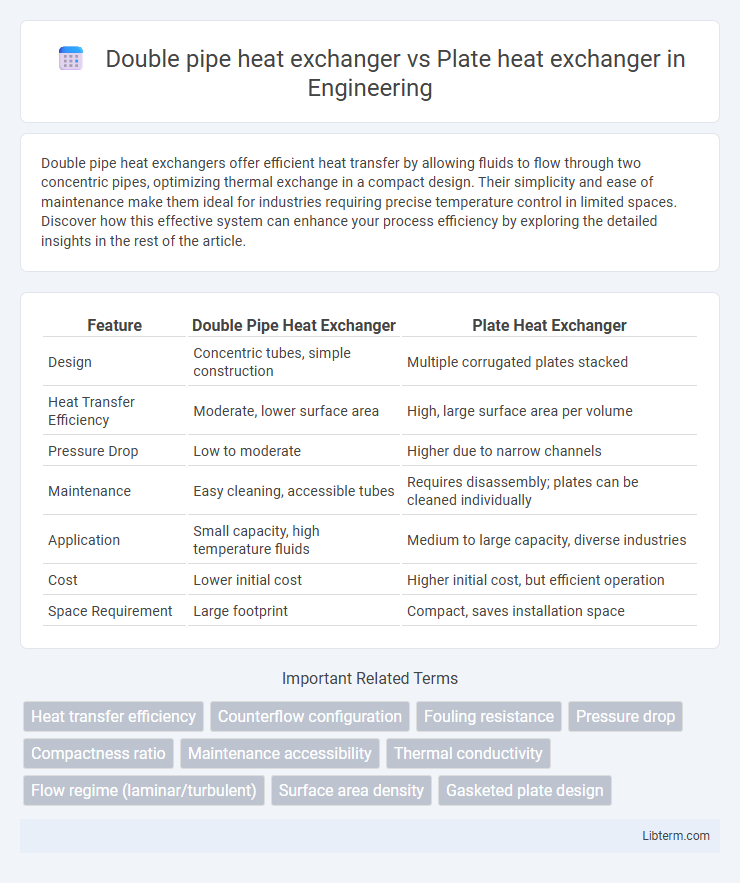
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Double Pipe Heat Exchanger | Plate Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Concentric tubes, simple construction | Multiple corrugated plates stacked |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | Moderate, lower surface area | High, large surface area per volume |
| Pressure Drop | Low to moderate | Higher due to narrow channels |
| Maintenance | Easy cleaning, accessible tubes | Requires disassembly; plates can be cleaned individually |
| Application | Small capacity, high temperature fluids | Medium to large capacity, diverse industries |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, but efficient operation |
| Space Requirement | Large footprint | Compact, saves installation space |
Introduction to Heat Exchangers
Double pipe heat exchangers consist of two concentric tubes allowing fluid flow in either parallel or counterflow, ideal for small-scale applications and fluids with high pressure or temperature. Plate heat exchangers utilize multiple thin, corrugated plates stacked together, offering a large surface area for efficient heat transfer and easy maintenance, making them suitable for larger systems. Both types are fundamental in transferring heat between fluids without mixing, optimizing energy use in various industries such as HVAC, chemical processing, and power generation.
Overview of Double Pipe Heat Exchangers
Double pipe heat exchangers consist of one pipe inside another, enabling hot and cold fluids to flow through the inner and outer pipes respectively, facilitating efficient heat transfer between them. They are ideal for applications requiring small heat transfer areas, handle high pressures and temperatures well, and allow easy maintenance due to their simple construction. Compared to plate heat exchangers, double pipe units exhibit lower heat transfer coefficients but offer greater durability and resistance to fouling in harsh industrial environments.
Overview of Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers consist of multiple thin, corrugated metal plates stacked together, creating channels for fluids to flow and transfer heat efficiently. These exchangers exhibit a high heat transfer coefficient due to the enhanced turbulence generated by the plate design, making them ideal for applications requiring compact size and high thermal performance. Compared to double pipe heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers allow easier maintenance and cleaning through plate disassembly, supporting versatile operational conditions.
Heat Transfer Efficiency Comparison
Double pipe heat exchangers exhibit lower heat transfer efficiency due to limited surface area and primarily laminar flow conditions within concentric pipes. Plate heat exchangers provide superior heat transfer efficiency by maximizing surface area through multiple thin plates, promoting turbulent flow and enhanced thermal conductivity. The overall heat transfer coefficient of plate heat exchangers can be up to four times higher than that of double pipe designs, making them ideal for processes requiring compact and efficient heat exchange.
Space and Design Considerations
Double pipe heat exchangers require more space due to their elongated cylindrical design, making them less suitable for compact installations. Plate heat exchangers offer a compact footprint with a modular design, enabling easy scalability and maintenance in limited space environments. The design of plate heat exchangers facilitates higher heat transfer efficiency with greater surface area per unit volume compared to double pipe exchangers.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Double pipe heat exchangers feature simple construction with fewer components, resulting in easier access for maintenance and cleaning, particularly effective for handling fluids with high fouling tendencies. Plate heat exchangers require regular disassembly to clean multiple thin plates that can trap residues, demanding more time and skilled labor for thorough maintenance. The design of double pipe units allows straightforward mechanical cleaning, while plate heat exchangers benefit from chemical cleaning methods due to tighter plate spacing and gasket sensitivity.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Operation
Double pipe heat exchangers generally have lower initial installation costs due to their simple design and ease of fabrication. Plate heat exchangers, although more expensive upfront, offer higher thermal efficiency and compactness, leading to reduced operational costs and energy savings over time. Maintenance expenses for double pipe units tend to be higher because fouling is more challenging to manage compared to the easily cleanable plates in plate heat exchangers.
Application Suitability and Industry Use
Double pipe heat exchangers excel in high-pressure, high-temperature applications and are commonly used in chemical processing, oil refining, and power generation industries due to their robust design and ease of maintenance. Plate heat exchangers offer superior heat transfer efficiency and compactness, making them ideal for HVAC systems, food and beverage processing, and pharmaceutical manufacturing where space-saving and hygienic conditions are critical. Selection between the two depends on factors such as fluid properties, operating conditions, and required heat transfer rates specific to industry demands.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Double pipe heat exchangers offer simplicity, easy maintenance, and suitability for high-pressure applications but have lower heat transfer efficiency and larger space requirements compared to plate heat exchangers. Plate heat exchangers provide high heat transfer surface area, compact design, and easy scalability, yet they are prone to fouling and are less suitable for handling high-pressure fluids. Selecting between the two depends on factors like fluid types, pressure conditions, maintenance needs, and installation space.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Heat Exchanger
Selecting between a double pipe heat exchanger and a plate heat exchanger depends on application-specific factors such as heat transfer efficiency, space constraints, and maintenance requirements. Double pipe heat exchangers are ideal for high-pressure, small-flow scenarios with straightforward construction, while plate heat exchangers provide higher heat transfer rates and compact design suited for larger, variable flow processes. Evaluating thermal performance, installation space, and operational costs ensures optimal heat exchanger selection for industrial or HVAC systems.
Double pipe heat exchanger Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com