A chain drive is a reliable mechanical system used to transfer power between rotating shafts through interconnected links of a chain. Its efficiency and durability make it ideal for applications such as bicycles, motorcycles, and industrial machinery, ensuring consistent motion and torque transmission. Explore the article to understand how a chain drive can enhance your mechanical projects and why it remains a preferred choice.
Table of Comparison
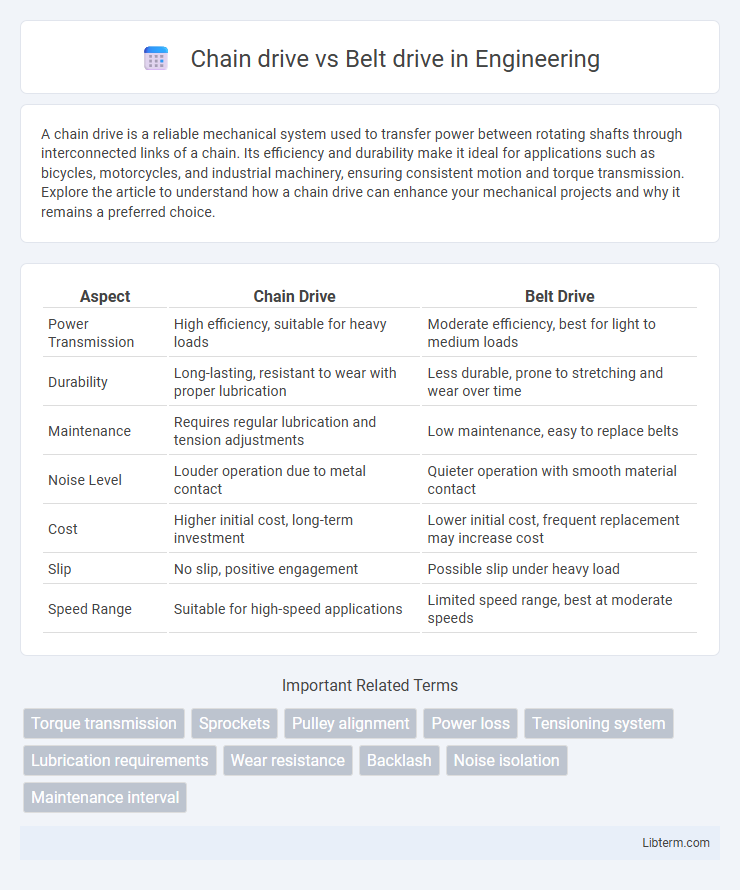
| Aspect | Chain Drive | Belt Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Power Transmission | High efficiency, suitable for heavy loads | Moderate efficiency, best for light to medium loads |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resistant to wear with proper lubrication | Less durable, prone to stretching and wear over time |
| Maintenance | Requires regular lubrication and tension adjustments | Low maintenance, easy to replace belts |
| Noise Level | Louder operation due to metal contact | Quieter operation with smooth material contact |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, long-term investment | Lower initial cost, frequent replacement may increase cost |
| Slip | No slip, positive engagement | Possible slip under heavy load |
| Speed Range | Suitable for high-speed applications | Limited speed range, best at moderate speeds |
Introduction to Chain Drive and Belt Drive
Chain drive transmits mechanical power through a series of interconnected metal links that engage with sprockets, offering high torque capacity and reliable performance under heavy loads. Belt drive utilizes flexible belts made of rubber, polymer, or composite materials running over pulleys, providing smooth and quiet operation with efficient power transfer for moderate load applications. Both systems serve critical roles in machinery, with chain drives favored for durability and strength, while belt drives excel in reducing vibration and maintenance requirements.
Key Differences Between Chain and Belt Drives
Chain drives offer higher torque transmission and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications, while belt drives provide quieter operation and require less maintenance, suited for lighter, high-speed tasks. Chain drives exhibit minimal slippage due to positive engagement with sprockets, whereas belt drives rely on friction, resulting in potential slip under heavy loads. Belt drives typically have better shock absorption and flexibility, whereas chain drives demand precise alignment and regular lubrication to prevent wear.
Construction and Design Features
Chain drives feature interlocking metal links that provide high durability and precise power transmission, suitable for heavy-duty applications and environments requiring minimal slippage. Belt drives utilize flexible rubber or synthetic belts running over pulleys, offering quieter operation and absorbing shock loads but generally experiencing more stretching and wear over time. The rigid, metallic construction of chain drives contrasts with the elastic, smooth surfaces of belt drives, influencing maintenance needs and efficiency in various mechanical systems.
Efficiency and Power Transmission
Chain drives offer superior efficiency, typically around 95-98%, due to minimal slippage and direct metal-to-metal contact, making them ideal for high power transmission applications. Belt drives, with efficiency ranging from 88-95%, provide smoother operation and noise reduction but tend to experience slip and stretch under heavy loads, reducing power transfer reliability. For maximum power transmission and efficiency in demanding environments, chain drives are generally preferred over belt drives.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Chain drives offer superior durability due to their metal construction, making them ideal for heavy-duty and high-torque applications, but they require regular lubrication and tension adjustments to prevent wear and elongation. Belt drives, typically made from rubber or synthetic materials, have lower maintenance demands since they do not need lubrication and can absorb shock loads better, yet they tend to wear out faster and may need periodic replacement. Both systems require monitoring, but chain drives generally demand more frequent, hands-on maintenance to ensure long-term reliability.
Cost Comparison: Chain vs Belt Drive
Chain drives generally have a higher initial cost due to the use of metal components and precise manufacturing requirements, but they offer longer durability and lower maintenance costs over time. Belt drives are typically less expensive upfront with simpler installation and quieter operation, but they may incur higher replacement and maintenance expenses due to wear and stretch. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors chain drives in high-load, long-term applications, while belt drives are cost-effective for low to moderate loads and intermittent use.
Noise and Vibration Levels
Chain drives generate higher noise and vibration levels due to metal-on-metal contact and link articulation during operation, making them less suitable for noise-sensitive environments. Belt drives, typically made from rubber or synthetic materials, operate more quietly and with reduced vibration because of their flexible, continuous surface and inherent damping properties. Selecting belt drive systems enhances overall noise control and vibration reduction in mechanical applications.
Common Applications of Each Drive System
Chain drives are commonly used in motorcycles, bicycles, and industrial machinery where high torque transmission and durability are essential. Belt drives find frequent applications in automotive engines, HVAC systems, and light machinery due to their smooth, quiet operation and ability to absorb shock loads. Each drive system suits specific roles based on load capacity, maintenance needs, and environmental conditions.
Pros and Cons Summary Table
Chain drives offer high durability and efficient power transmission, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications, but they require regular lubrication and can be noisy. Belt drives provide quieter operation and require less maintenance, with smooth motion suitable for light to medium loads, though they may slip under heavy load and have limited lifespan compared to chains. The summary table highlights chain drives' strength in load capacity and longevity versus belt drives' advantages in cost-effectiveness and noise reduction.
How to Choose the Right Drive System
Choosing the right drive system depends on factors such as load capacity, maintenance requirements, and efficiency needs. Chain drives offer high strength and durability for heavy-duty applications but require regular lubrication and tension adjustments. Belt drives provide quiet operation and lower maintenance for lighter loads but may slip under high torque conditions, making the choice critical based on specific performance demands.
Chain drive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com