Project Portfolio Management (PPM) and Product Configuration Processes (PCP) streamline organizational workflows by prioritizing projects and customizing products to meet specific customer needs. Effective integration of PPM and PCP enhances resource allocation, decision-making, and product quality, directly impacting business success. Explore the full article to discover how optimizing these processes can transform your project outcomes and customer satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
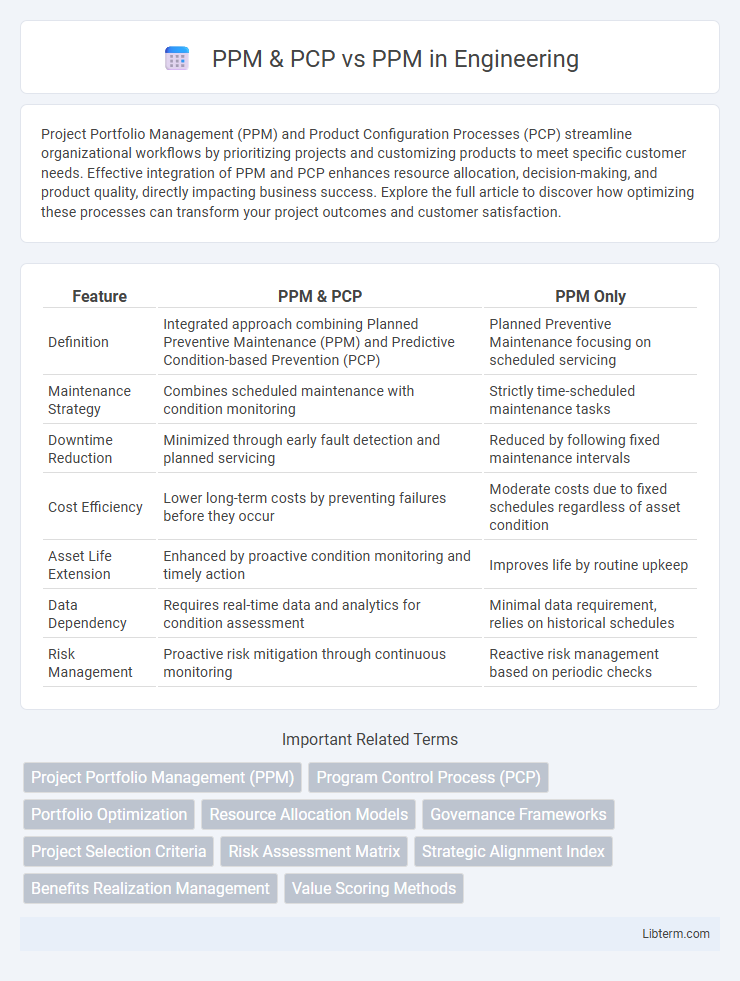
| Feature | PPM & PCP | PPM Only |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated approach combining Planned Preventive Maintenance (PPM) and Predictive Condition-based Prevention (PCP) | Planned Preventive Maintenance focusing on scheduled servicing |
| Maintenance Strategy | Combines scheduled maintenance with condition monitoring | Strictly time-scheduled maintenance tasks |
| Downtime Reduction | Minimized through early fault detection and planned servicing | Reduced by following fixed maintenance intervals |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower long-term costs by preventing failures before they occur | Moderate costs due to fixed schedules regardless of asset condition |
| Asset Life Extension | Enhanced by proactive condition monitoring and timely action | Improves life by routine upkeep |
| Data Dependency | Requires real-time data and analytics for condition assessment | Minimal data requirement, relies on historical schedules |
| Risk Management | Proactive risk mitigation through continuous monitoring | Reactive risk management based on periodic checks |
Introduction to PPM & PCP vs PPM
PPM (Project Portfolio Management) and PCP (Project Control Process) are critical methodologies in project management, with PPM focusing on aligning projects with strategic business goals by prioritizing, selecting, and managing a portfolio of projects. PCP enhances PPM by introducing structured control mechanisms to monitor project performance, manage risks, and ensure compliance with project objectives. Understanding the distinction between PPM alone and the integrated approach of PPM & PCP is essential for organizations seeking optimized resource allocation, improved project visibility, and enhanced decision-making in complex project environments.
Defining PPM (Planned Preventive Maintenance)
PPM (Planned Preventive Maintenance) involves scheduled inspections and servicing of equipment to prevent unexpected failures and extend asset lifespan. PCP (Planned Corrective Maintenance) vs PPM highlights the difference where PCP addresses repairs after issues arise, while PPM emphasizes proactive measures to avoid downtime. Effective PPM relies on detailed maintenance schedules, historical data analysis, and condition monitoring to optimize operational efficiency.
Understanding PCP (Planned Corrective Maintenance)
Planned Corrective Maintenance (PCP) involves scheduling repairs based on identified equipment faults to prevent unplanned downtime, distinguishing it from traditional Planned Preventive Maintenance (PPM), which focuses on routine inspections and servicing to avoid failures. PCP targets specific maintenance tasks triggered by condition monitoring or fault detection, optimizing resource allocation and reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns. Integrating PCP with PPM enhances asset reliability by combining proactive inspections with timely corrective actions.
Differences Between PPM & PCP
PPM (Parts Per Million) measures concentration by indicating the number of units of a substance per million units of the total, while PCP (Process Control Plan) is a structured document used in manufacturing to monitor and control processes to ensure quality standards. The key difference lies in their application: PPM quantifies substance concentration, often in chemistry or environmental science, whereas PCP focuses on quality management in production environments. PPM is a measurement unit, whereas PCP is a strategic framework for process stability and product consistency.
PPM & PCP vs Traditional PPM: Key Contrasts
PPM & PCP integrates Portfolio Project Management with Product Cycle Planning to enhance resource allocation and project prioritization compared to Traditional PPM, which often emphasizes task management and linear workflows. This hybrid approach leverages data-driven insights and continuous product lifecycle monitoring to optimize project outcomes, ensuring alignment with strategic business goals. Emphasizing adaptive planning and iterative feedback loops, PPM & PCP facilitates more dynamic and responsive project execution than the static, schedule-focused methods typically seen in Traditional PPM.
Advantages of Integrating PPM & PCP
Integrating Project Portfolio Management (PPM) with Production Capacity Planning (PCP) enhances resource allocation accuracy and aligns project execution with manufacturing capabilities, improving overall operational efficiency. This integration provides real-time visibility into capacity constraints, enabling more effective prioritization and risk management across projects. Businesses gain a competitive advantage by reducing delays and optimizing throughput while maintaining strategic alignment between project goals and production capacity.
Common Challenges in PPM & PCP Implementation
Common challenges in PPM & PCP implementation include aligning project portfolios with strategic business goals, managing resource constraints effectively, and ensuring consistent communication across teams for transparency. Difficulty in integrating data from diverse systems often hinders accurate portfolio analysis and decision-making. Resistance to change and lack of stakeholder buy-in further complicate the successful adoption of PPM & PCP frameworks compared to standalone PPM.
Best Practices for Optimizing PPM & PCP
Effective optimization of Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) and Production Control Planning (PCP) hinges on rigorous documentation, early supplier involvement, and thorough process validation to ensure consistent quality and compliance. Implementing automated workflow systems and leveraging real-time data analytics enhances visibility and accelerates decision-making in both PPM and PCP phases. Continuous training and cross-functional collaboration further solidify best practices by fostering proactive risk management and continuous improvement throughout the product lifecycle.
Case Studies: Success Stories with PPM & PCP
Case studies demonstrate that integrating Project Portfolio Management (PPM) with Product Cycle Planning (PCP) significantly boosts organizational efficiency and project success rates. Companies leveraging PPM and PCP together report enhanced resource allocation, improved risk management, and accelerated product development timelines compared to utilizing PPM alone. This combined approach fosters strategic alignment between project execution and product lifecycle objectives, driving measurable business growth and competitive advantage.
Future Trends in Maintenance: Moving Beyond PPM
Future trends in maintenance emphasize the integration of Predictive Condition-Based Maintenance (PCP) with traditional Planned Preventive Maintenance (PPM) to enhance asset reliability and reduce downtime. Advanced data analytics and IoT sensors enable proactive fault detection and adaptive scheduling, surpassing the limitations of static PPM frameworks. The shift towards smart maintenance strategies leverages machine learning algorithms for real-time condition monitoring, optimizing maintenance costs and operational efficiency in industrial environments.
PPM & PCP Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com