Rack and pinion systems convert rotational motion into linear motion, making them essential in steering mechanisms and various machinery. This gear arrangement offers precise control and efficient power transmission, improving your equipment's performance. Explore the article to understand how rack and pinion technology can enhance your mechanical applications.
Table of Comparison
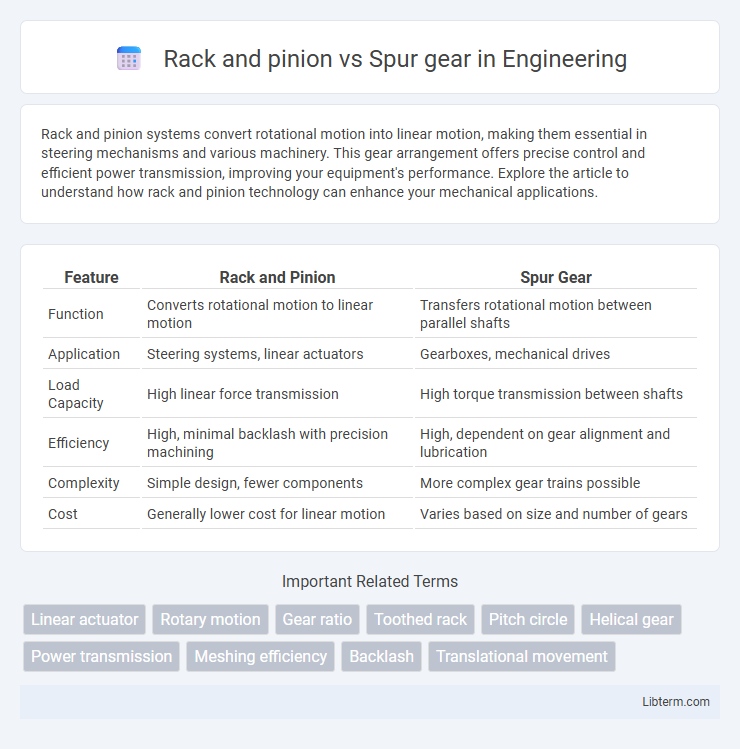
| Feature | Rack and Pinion | Spur Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts rotational motion to linear motion | Transfers rotational motion between parallel shafts |
| Application | Steering systems, linear actuators | Gearboxes, mechanical drives |
| Load Capacity | High linear force transmission | High torque transmission between shafts |
| Efficiency | High, minimal backlash with precision machining | High, dependent on gear alignment and lubrication |
| Complexity | Simple design, fewer components | More complex gear trains possible |
| Cost | Generally lower cost for linear motion | Varies based on size and number of gears |
Introduction to Rack and Pinion and Spur Gear Mechanisms
Rack and pinion mechanisms convert rotational motion into linear motion through a circular gear (pinion) engaging a flat, toothed component (rack), commonly used in steering systems and linear actuators. Spur gears consist of parallel cylindrical gears with straight teeth that mesh directly to transmit rotational motion and torque efficiently in machinery like gearboxes. Both systems rely on precise tooth geometry for smooth operation, but rack and pinion offer linear displacement, whereas spur gears provide rotational power transmission.
Fundamental Principles of Rack and Pinion Systems
Rack and pinion systems convert rotational motion into linear motion through meshing of a circular gear (pinion) with a linear gear (rack) featuring evenly spaced teeth. This mechanism allows precise control of position and speed, making it ideal for steering systems and linear actuators. Unlike spur gears that transmit rotational motion between parallel shafts, rack and pinion setups enable direct translation of rotational input into straight-line output.
Understanding Spur Gear Operation
Spur gears operate by transmitting rotary motion and torque between parallel shafts through meshing straight-cut teeth, providing efficient power transfer with minimal axial thrust. Their design enables high precision in speed and position control, making them ideal for applications requiring simple, reliable gear stages. Unlike rack and pinion systems that convert rotary motion into linear motion, spur gears focus solely on rotational power transmission within compact mechanical assemblies.
Key Differences Between Rack and Pinion vs Spur Gear
Rack and pinion systems convert rotational motion into linear motion, utilizing a straight bar (rack) and a circular pinion, while spur gears involve two parallel gears transferring rotational motion without linear displacement. Rack and pinion setups are ideal for steering mechanisms and linear actuators, offering precise control over linear positioning, whereas spur gears excel in torque transmission between parallel shafts with high efficiency. Load capacity, application type, and motion output (linear vs. rotational) are primary distinctions defining their use in mechanical systems.
Applications of Rack and Pinion Mechanisms
Rack and pinion mechanisms are widely used in steering systems of automobiles and railways due to their ability to convert rotational motion into precise linear motion. These mechanisms are essential in CNC machinery and automation for accurate positioning and controlled linear movement. Their applications also extend to lifting devices, such as jacks and elevators, where efficient force transmission and reliability are critical.
Typical Uses of Spur Gears in Industry
Spur gears are widely used in industrial applications such as conveyor systems, machine tools, and automotive transmissions due to their simple design and high efficiency in transmitting power between parallel shafts. They are favored for their ability to handle high loads and maintain precise speed ratios in equipment like conveyor belts, gear pumps, and milling machines. Typical uses highlight spur gears' role in ensuring reliable, low-noise, and cost-effective power transmission across diverse manufacturing and mechanical systems.
Advantages of Rack and Pinion Over Spur Gear
Rack and pinion systems provide linear motion with high precision and simplicity, making them ideal for applications requiring straight-line movement, unlike spur gears designed primarily for rotational motion. They offer a compact design with fewer components, reducing maintenance needs and improving reliability in steering mechanisms and CNC machines. The ability to easily convert rotational force into linear force gives rack and pinion systems superior load distribution and smoother operation compared to spur gears.
Benefits of Spur Gear Compared to Rack and Pinion
Spur gears offer higher precision and smoother operation in rotary motion applications compared to rack and pinion systems, which excel in linear movement. The compact design of spur gears allows for efficient power transmission with minimal backlash and noise, making them ideal for high-speed and high-torque environments. Their durability and ease of manufacturing contribute to lower maintenance costs and longer service life in mechanical systems.
Selection Criteria: When to Choose Rack and Pinion or Spur Gear
Rack and pinion systems are ideal for applications requiring linear motion with high precision and simple construction, often found in steering mechanisms and CNC machinery. Spur gears are preferred for transmitting rotary motion between parallel shafts with high efficiency and load capacity, commonly used in gearboxes and mechanical clocks. Selection depends on the motion type (linear vs. rotary), load requirements, space constraints, and desired mechanical advantage.
Future Trends and Innovations in Gear Mechanisms
Future trends in gear mechanisms emphasize the integration of advanced materials like carbon fiber composites and additive manufacturing to enhance durability and reduce weight in rack and pinion and spur gear systems. Innovations include the development of smart gears equipped with embedded sensors for real-time condition monitoring and predictive maintenance, improving efficiency and lifespan. Research also focuses on improving the precision and noise reduction capabilities of these gear types for applications in electric vehicles and robotics.
Rack and pinion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com