N-Type semiconductors are essential in modern electronics due to their surplus of electrons, which enhance electrical conductivity. These materials are widely used in devices like transistors and diodes, where precise control of electron flow is crucial. Explore the rest of this article to understand how N-Type semiconductors can impact your technology solutions.
Table of Comparison
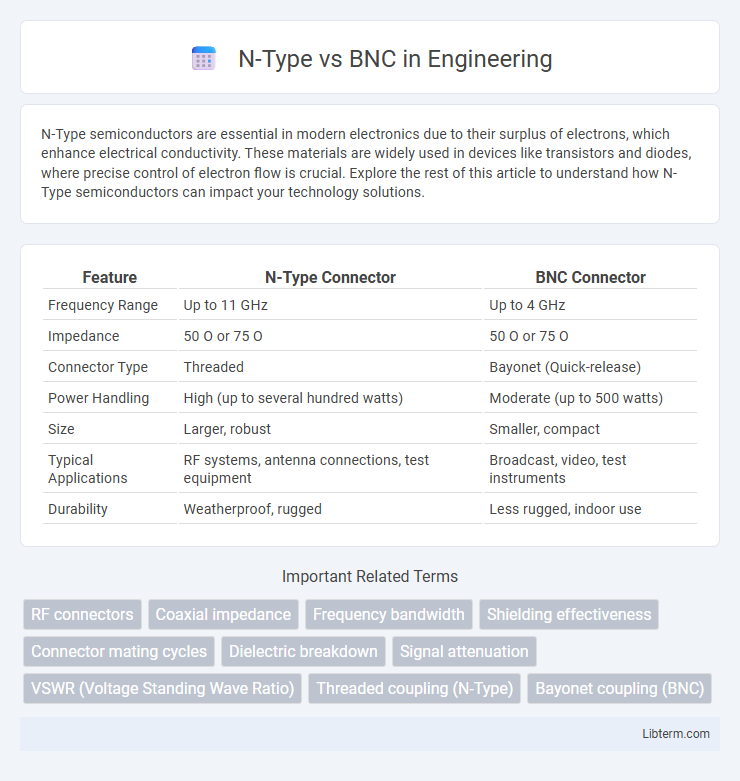
| Feature | N-Type Connector | BNC Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | Up to 11 GHz | Up to 4 GHz |
| Impedance | 50 O or 75 O | 50 O or 75 O |
| Connector Type | Threaded | Bayonet (Quick-release) |
| Power Handling | High (up to several hundred watts) | Moderate (up to 500 watts) |
| Size | Larger, robust | Smaller, compact |
| Typical Applications | RF systems, antenna connections, test equipment | Broadcast, video, test instruments |
| Durability | Weatherproof, rugged | Less rugged, indoor use |
Introduction to N-Type and BNC Connectors
N-Type connectors are weatherproof RF connectors designed for high-frequency applications up to 11 GHz, known for their rugged durability and low signal loss. BNC connectors are rapid-locking RF connectors primarily used in video and radio frequency applications, suitable for frequencies up to 4 GHz. Both connectors are widely used in telecommunications, test equipment, and networking, with N-Type favored for outdoor and high-power uses, and BNC for quick and reliable connections in indoor settings.
Historical Overview: N-Type vs BNC
N-Type connectors, developed in the 1940s by Paul Neill at Bell Labs, were designed to support high-frequency signals up to 11 GHz with enhanced durability for military and aerospace applications. BNC connectors, introduced by Bayonet Neill-Concelman in the late 1940s, became popular in radio, television, and test instrumentation due to their quick connect/disconnect bayonet coupling and reliable performance up to 4 GHz. Both connectors have evolved to address specific industry needs, with N-Type favored for robust outdoor and high-power applications, while BNC remains a standard for low-power, moderate-frequency RF connections.
Design and Structural Differences
N-Type connectors feature a threaded coupling mechanism that ensures a robust, weatherproof connection, ideal for outdoor and high-frequency applications. In contrast, BNC connectors utilize a bayonet locking system designed for quick connect and disconnect, commonly used in low-frequency signals and test equipment. Structurally, N-Type connectors have a larger, more durable metal body with a consistent impedance of 50 or 75 ohms, while BNC connectors are smaller, lightweight, and also available in 50 or 75-ohm versions but offer less durability for rugged environments.
Frequency Range and Performance
N-Type connectors support a frequency range up to 11 GHz, making them ideal for high-frequency applications such as wireless communications and RF testing. BNC connectors typically operate efficiently up to 4 GHz, suitable for lower-frequency applications like video signals and instrumentation. The N-Type offers superior performance in terms of signal integrity and durability at higher frequencies, while BNC connectors prioritize ease of use and quick connect-disconnect cycles.
Applications in Modern Electronics
N-Type connectors are widely used in high-frequency applications such as telecommunications, radar systems, and wireless networks due to their excellent performance up to 11 GHz and robust weatherproof design. BNC connectors are preferred for lower frequency applications like video signals, test equipment, and radio-frequency connections up to 4 GHz for their quick connect/disconnect mechanism and compact size. Modern electronics leverage N-Type connectors in outdoor and high-power scenarios, while BNC connectors dominate laboratory and broadcast environments requiring easy handling and moderate frequency range.
Advantages of N-Type Connectors
N-Type connectors offer superior durability and weather resistance, making them ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty applications compared to BNC connectors. Their threaded coupling mechanism ensures a secure, low-loss connection suitable for high-frequency signals up to 11 GHz. These advantages make N-Type connectors preferred in telecommunications, military, and aerospace sectors where reliability and signal integrity are critical.
Strengths of BNC Connectors
BNC connectors offer a compact and easy-to-use design ideal for quick connect and disconnect applications, facilitating efficient signal transmission in radio, video, and networking systems. Their bayonet locking mechanism ensures secure and reliable connections, minimizing signal loss and interference in high-frequency applications up to 4 GHz. BNC connectors are widely favored for their versatility, compatibility with coaxial cables, and cost-effectiveness in professional and consumer electronics environments.
Compatibility and Interchangeability
N-Type connectors offer superior weather resistance and are designed for use with larger coaxial cables, making them ideal for outdoor and high-frequency applications, while BNC connectors are commonly used with smaller cables in indoor or laboratory settings. Compatibility between N-Type and BNC connectors is limited by size and frequency range, as N-Type supports higher frequencies up to 11 GHz and higher power levels compared to BNC's typical range of DC to 4 GHz. Interchangeability requires adapters due to differences in mechanical design and impedance, with N-Type connectors typically having 50 or 75-ohm versions, whereas BNC connectors are widely available in both impedances but are more vulnerable to signal loss at higher frequencies.
Cost Considerations: N-Type vs BNC
N-Type connectors generally incur higher costs due to their superior durability and performance in high-frequency and outdoor applications compared to BNC connectors. BNC connectors are more budget-friendly and widely used for lower-frequency signals and indoor environments, making them suitable for cost-sensitive projects. Evaluating project demands and environmental conditions is essential to optimize spending when choosing between N-Type and BNC connectors.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your Project
N-Type connectors provide superior weather resistance and low signal loss, making them ideal for outdoor and high-frequency applications, whereas BNC connectors excel in quick connect/disconnect needs and are widely used in video and RF testing environments. Consider the operating frequency, environmental exposure, and mechanical durability when selecting between N-Type's robust design and BNC's convenient, compact form factor. Matching the connector type to your specific project requirements ensures optimal signal integrity and long-term reliability.
N-Type Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com