Round belts offer superior flexibility and efficient power transmission in various industrial applications, making them ideal for machinery requiring quiet and smooth operation. Their durable design reduces wear and extends the lifespan of your equipment, ensuring consistent performance under diverse conditions. Discover how round belts can optimize your machinery by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
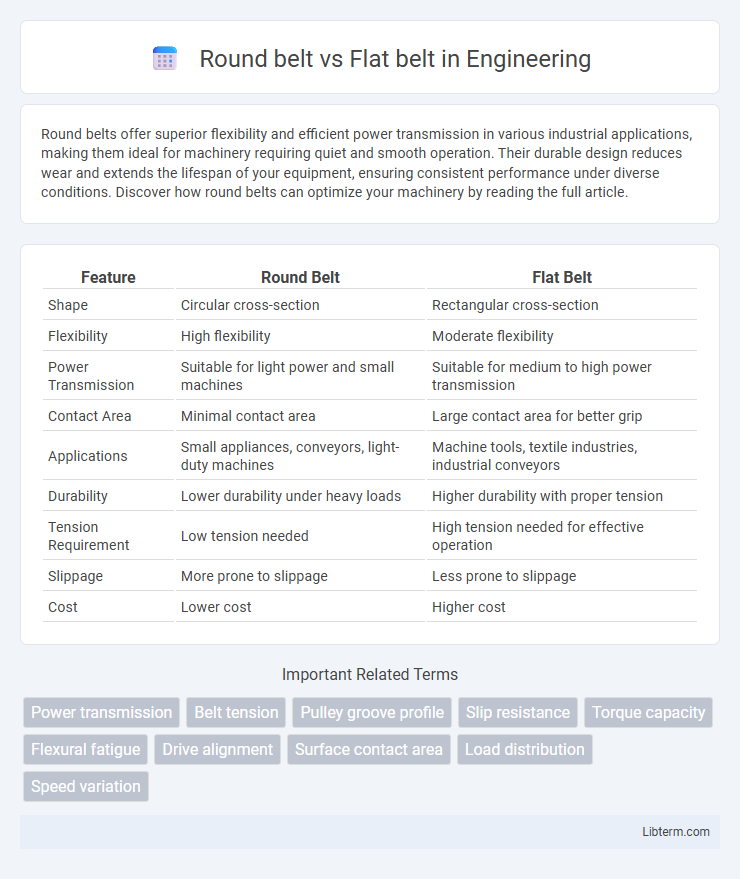
| Feature | Round Belt | Flat Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Circular cross-section | Rectangular cross-section |
| Flexibility | High flexibility | Moderate flexibility |
| Power Transmission | Suitable for light power and small machines | Suitable for medium to high power transmission |
| Contact Area | Minimal contact area | Large contact area for better grip |
| Applications | Small appliances, conveyors, light-duty machines | Machine tools, textile industries, industrial conveyors |
| Durability | Lower durability under heavy loads | Higher durability with proper tension |
| Tension Requirement | Low tension needed | High tension needed for effective operation |
| Slippage | More prone to slippage | Less prone to slippage |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Belt Types
Round belts are typically made of rubber or synthetic materials with a circular cross-section, providing flexibility and suited for power transmission in light-duty applications. Flat belts consist of a wide, flat strip of leather, fabric, or polymer, designed for high-speed and long-distance power transmission with better grip and efficiency. Both types serve specific industrial purposes based on load capacity, tension, and pulley compatibility.
What is a Round Belt?
A round belt is a continuous loop of flexible material with a circular cross-section, primarily used in light-duty power transmission applications and conveyor systems. Made from materials like rubber, polyurethane, or leather, round belts offer high flexibility and resistance to wear, making them ideal for small pulley drives and low-torque situations. Compared to flat belts, round belts provide reduced slippage and require less maintenance in compact, precise mechanical operations.
What is a Flat Belt?
A flat belt is a flexible, continuous loop made from materials like leather, rubber, or synthetic compounds, designed to transmit power between pulleys in mechanical systems. It offers high speed capabilities and smooth operation with minimal slip when properly tensioned, often used in industrial machinery and conveyor systems. Compared to round belts, flat belts provide greater surface contact, resulting in efficient power transmission and reduced wear.
Key Differences Between Round and Flat Belts
Round belts offer high flexibility and are ideal for light-duty power transmission in small machinery, while flat belts provide greater surface contact and are suited for high-speed, heavy-load applications. The key difference lies in their shape and contact area: round belts have a circular cross-section that fits well in V-groove pulleys, whereas flat belts have a rectangular cross-section providing better grip and less slippage on flat pulleys. Material composition also varies, with round belts often made from polyurethane or rubber for elasticity, and flat belts commonly constructed from leather or synthetic fabrics for durability and strength.
Material Options for Round and Flat Belts
Round belts are commonly made from polyurethane, neoprene, or rubber, offering flexibility and resistance to wear, ideal for light to medium power transmission. Flat belts typically utilize materials like leather, rubber, or synthetic fabrics such as polyester and nylon, providing high tensile strength and smooth surface contact for efficient power transfer. Material selection depends on application requirements including load capacity, environmental conditions, and durability needs.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Round belts offer higher flexibility and better resistance to twisting, making them suitable for applications with small pulley diameters, but they typically generate more friction and heat, reducing overall efficiency. Flat belts provide superior power transmission efficiency due to greater surface contact reducing slippage and energy loss, which enhances performance in high-speed, long-distance drives. In terms of durability, flat belts tend to have a longer service life, while round belts require less precise alignment, balancing maintenance needs and operational efficiency.
Typical Applications and Industries
Round belts are commonly used in light-duty applications such as small machinery, household appliances, and office equipment due to their flexibility and ability to handle lower power transmission. Flat belts dominate in industrial applications requiring high-speed and high-power transmission, including textile manufacturing, automotive assembly lines, and conveyor systems. Industries such as agriculture, packaging, and printing heavily rely on flat belts for their durability and efficient power transfer in large-scale machinery.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Round belts require less precise alignment during installation and are easier to replace due to their smaller contact area, making them ideal for applications with variable load conditions. Flat belts demand precise pulley alignment and tension adjustments to prevent slippage and uneven wear, increasing installation complexity and maintenance frequency. Regular inspection of round belts focuses on checking for wear and cracks, while flat belts require monitoring for fraying edges and proper tension to ensure longevity.
Cost Analysis: Round Belt vs Flat Belt
Round belts typically cost less initially due to simpler manufacturing and lower material use, making them ideal for budget-sensitive applications. Flat belts, while often more expensive upfront, provide longer service life and better efficiency, which can result in lower total cost of ownership over time. Maintenance expenses for round belts can be higher due to increased wear and the need for more frequent replacements compared to durable flat belts.
Which Belt is Best for Your Needs?
Choosing the best belt depends on the application requirements: round belts offer excellent flexibility and power transmission for small pulleys and misaligned shafts, making them ideal for light to medium loads in agricultural and industrial machinery. Flat belts provide higher speed capabilities, smoother operation, and are suited for high-power applications with precise alignment, commonly used in conveyor systems and automotive engines. Assess factors such as load capacity, speed, pulley design, and environmental conditions to determine whether a round belt or flat belt aligns best with your operational needs.
Round belt Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com