Ball valves provide reliable flow control by using a spherical disc to start, stop, or regulate fluid movement within pipelines. Known for their durability and tight sealing, they are essential in various industrial and residential applications. Explore the full article to understand how a ball valve can enhance your system's efficiency.
Table of Comparison
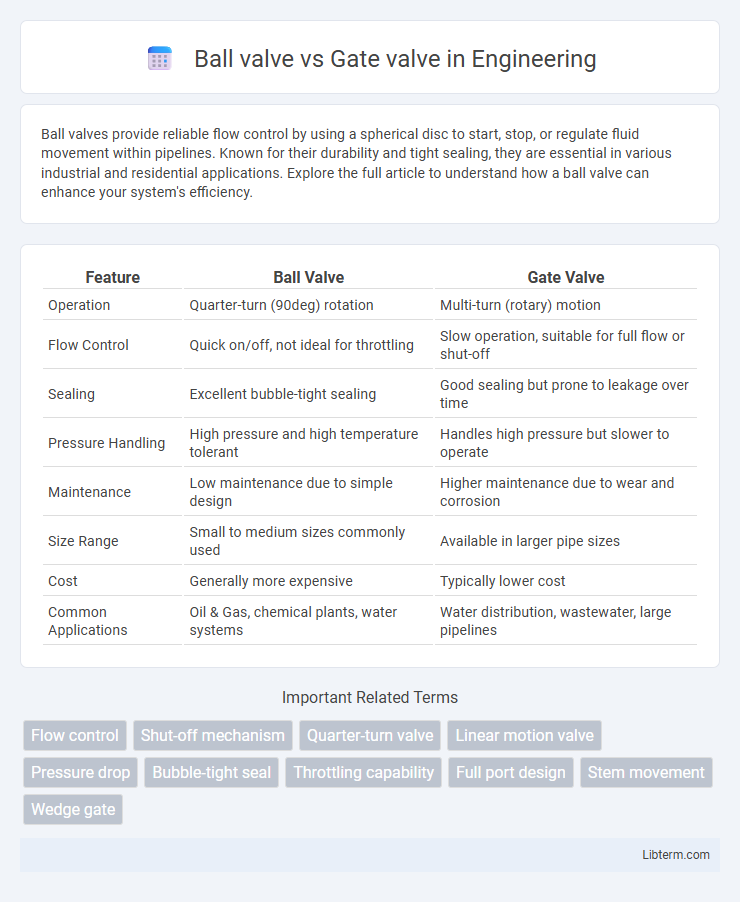
| Feature | Ball Valve | Gate Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Quarter-turn (90deg) rotation | Multi-turn (rotary) motion |
| Flow Control | Quick on/off, not ideal for throttling | Slow operation, suitable for full flow or shut-off |
| Sealing | Excellent bubble-tight sealing | Good sealing but prone to leakage over time |
| Pressure Handling | High pressure and high temperature tolerant | Handles high pressure but slower to operate |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to simple design | Higher maintenance due to wear and corrosion |
| Size Range | Small to medium sizes commonly used | Available in larger pipe sizes |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Typically lower cost |
| Common Applications | Oil & Gas, chemical plants, water systems | Water distribution, wastewater, large pipelines |
Introduction: Understanding Valve Types
Ball valves provide precise flow control and quick shutoff with a spherical disc that rotates 90 degrees, making them ideal for fast operations and tight sealing. Gate valves use a wedge-shaped gate that lifts to allow flow, suited for fully open or closed positions but less effective for throttling. Both valve types are essential in pipeline systems, chosen based on application needs such as pressure, flow control, and maintenance requirements.
What Is a Ball Valve?
A ball valve is a quarter-turn valve that uses a hollow, perforated, and pivoting ball to control fluid flow, providing tight shutoff and durability in high-pressure applications. It offers quick operation, minimal pressure drop, and reliable sealing, making it ideal for systems requiring frequent on/off control. Ball valves are commonly used in oil, gas, water, and chemical industries due to their robustness and low maintenance needs.
What Is a Gate Valve?
A gate valve is a type of valve used to control the flow of liquids by lifting a rectangular or round gate out of the flow path. It is designed for fully open or fully closed positions, minimizing pressure drop when open and providing a tight seal when closed. Commonly used in pipelines transporting water, oil, and gas, gate valves are ideal for applications requiring infrequent operation and low-pressure loss.
Key Design Differences
Ball valves feature a spherical disc that rotates 90 degrees to control flow, offering quick operation and reliable sealing, ideal for on/off control. Gate valves use a flat or wedge-shaped gate that moves vertically to start or stop flow, providing minimal pressure drop but slower operation. The ball valve's compact design suits frequent use and tight shutoff, while the gate valve's linear motion is better for applications requiring full flow or isolation.
Flow Control: Ball vs Gate Valve
Ball valves offer precise flow control with quick quarter-turn operation, enabling rapid shutoff and minimal pressure drop. Gate valves provide gradual flow regulation by lifting a gate out of the flow path, ideal for applications requiring full flow or complete shutoff but less suited for throttling. The robust sealing of ball valves ensures reliable flow control in high-pressure systems, while gate valves excel in low-pressure settings with less frequent operation.
Durability and Maintenance
Ball valves offer superior durability due to their robust construction and resistance to wear from frequent operation, making them ideal for high-cycle applications. Gate valves, while effective for on/off control, tend to experience more wear on the seating surfaces, leading to higher maintenance requirements over time. Regular inspection and lubrication are crucial for gate valves to prevent stem corrosion and ensure longevity, whereas ball valves typically require less maintenance due to their simpler sealing mechanism.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Ball valves are widely used in industries requiring quick shut-off and precise flow control, such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment facilities due to their reliable sealing and ease of operation. Gate valves are preferred in applications involving high pressure and temperature, commonly found in power plants, wastewater management, and pipeline systems where full flow and minimal pressure drop are critical. Both valves play essential roles in manufacturing, petrochemical, and HVAC sectors, with ball valves excelling in on/off services and gate valves suited for isolation purposes.
Cost Comparison
Ball valves typically have a higher initial cost than gate valves due to their complex design and precision components. Gate valves offer a more budget-friendly option for large diameter pipelines but may incur higher maintenance costs over time. Evaluating long-term operational expenses alongside upfront investment is critical for cost-effective valve selection.
Pros and Cons of Each Valve
Ball valves offer quick shut-off with a 90-degree turn and provide reliable sealing, making them ideal for high-pressure applications; however, they are generally more expensive and not suitable for throttling. Gate valves excel in regulating flow by allowing gradual opening and closing, and they offer less pressure drop when fully open, but they tend to be slower to operate and can suffer from valve seat wear. Choosing between ball and gate valves depends on the specific needs for flow control, durability, and maintenance frequency.
Choosing the Right Valve for Your System
Selecting the right valve for your system depends on factors such as flow control precision, pressure requirements, and maintenance needs. Ball valves provide quick shutoff and excellent sealing, making them ideal for applications requiring reliable isolation under high pressure. Gate valves offer minimal pressure drop and are suitable for fully open or fully closed positions in systems where flow needs to be unobstructed.
Ball valve Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com