Shaft drive systems offer a durable and low-maintenance alternative for transmitting power in motorcycles and bicycles, ensuring efficient energy transfer with minimal wear. These drives are known for their reliability in various weather conditions and reduced need for lubrication compared to chain drives. Explore the rest of this article to discover how a shaft drive could enhance your vehicle's performance and longevity.
Table of Comparison
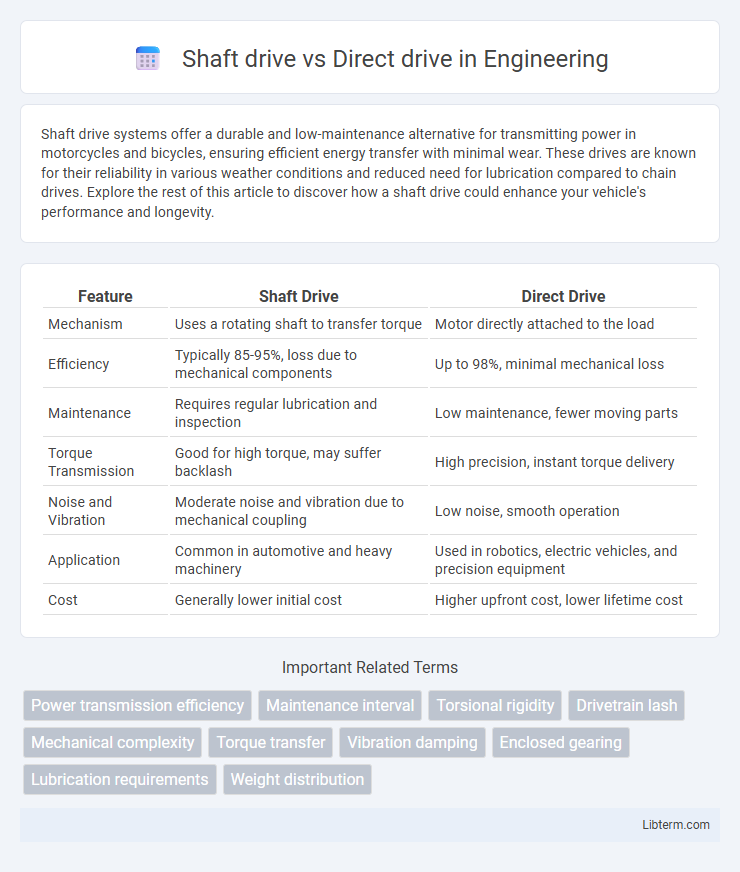
| Feature | Shaft Drive | Direct Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Uses a rotating shaft to transfer torque | Motor directly attached to the load |
| Efficiency | Typically 85-95%, loss due to mechanical components | Up to 98%, minimal mechanical loss |
| Maintenance | Requires regular lubrication and inspection | Low maintenance, fewer moving parts |
| Torque Transmission | Good for high torque, may suffer backlash | High precision, instant torque delivery |
| Noise and Vibration | Moderate noise and vibration due to mechanical coupling | Low noise, smooth operation |
| Application | Common in automotive and heavy machinery | Used in robotics, electric vehicles, and precision equipment |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost, lower lifetime cost |
Introduction to Shaft Drive and Direct Drive Systems
Shaft drive systems use a rotating shaft to transmit power from the motor to the wheels, commonly found in motorcycles and bicycles, offering durability and low maintenance. Direct drive systems connect the motor directly to the wheel or load, providing higher efficiency, reduced mechanical loss, and quieter operation, often utilized in electric vehicles and industrial applications. Understanding the fundamental difference in power transmission mechanisms helps in selecting the appropriate drive system for specific performance and maintenance requirements.
How Shaft Drive Works
Shaft drive systems transfer power from the engine to the rear wheel through a steel driveshaft and a series of gears, providing smooth and low-maintenance torque delivery. Unlike chain drives, the enclosed shaft drive requires minimal lubrication and reduces exposure to dirt and debris, enhancing durability. The mechanical complexity of shaft drives results in increased weight but offers consistent power transmission and longer service intervals.
How Direct Drive Works
Direct drive systems operate by connecting the motor rotor directly to the wheel or load, eliminating intermediary components like belts or gears, which reduces mechanical loss and increases efficiency. This direct connection allows for precise torque control and smoother acceleration because the motor's rotational power is transmitted without interruption or slack. The absence of additional transmission parts also leads to lower maintenance requirements and quieter operation compared to shaft drive systems.
Key Differences Between Shaft Drive and Direct Drive
Shaft drive systems use a rotating shaft to transfer power from the engine to the wheels, offering durability and low maintenance, while direct drive connects the motor directly to the wheel or load, maximizing efficiency by reducing power loss. Shaft drives typically provide smoother torque transmission and are commonly found in motorcycles and bicycles designed for long-distance use. In contrast, direct drive systems are favored in electric vehicles and precision machinery where immediate response and high efficiency are critical.
Performance Comparison: Efficiency and Power Transfer
Shaft drive systems typically exhibit lower efficiency due to increased mechanical resistance and energy loss through gears and chain links, resulting in less direct power transfer between the motor and wheels. Direct drive systems maximize efficiency by eliminating intermediate components, enabling near-instantaneous torque transfer and higher power output consistency. Performance data shows direct drives achieving efficiencies above 90%, while shaft drives often fall below 85%, significantly impacting acceleration and overall responsiveness in electric vehicles or bicycles.
Maintenance Requirements: Shaft vs Direct Drive
Shaft drive systems require regular maintenance, including lubrication of the shaft and checking for wear on the universal joints or gears, ensuring smooth power transmission over time. Direct drive systems have minimal maintenance needs because they eliminate components like chains or belts, reducing the risk of mechanical failures and eliminating the need for lubrication. Overall, direct drive offers a low-maintenance alternative to shaft drive, making it ideal for users who prioritize convenience and reliability.
Durability and Longevity
Shaft drive systems offer superior durability and longevity due to their enclosed design, which protects components from dirt, debris, and weather conditions, leading to reduced wear and maintenance. Direct drive mechanisms, while efficient and offering immediate power transfer, often rely on exposed components that can be more susceptible to environmental damage and wear over time. The robustness of shaft drives typically results in a longer service life and lower long-term upkeep costs compared to direct drive systems.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Shaft drives generally have higher initial costs due to complex engineering and robust materials but offer lower long-term maintenance expenses because of their durability and sealed design that reduces wear. Direct drives feature lower upfront costs with simpler construction but may incur higher long-term expenses due to increased maintenance needs and potential part replacements caused by direct exposure to elements and friction. Evaluating both drive systems requires analyzing the total cost of ownership, including initial investment and projected maintenance over the equipment's lifecycle.
Best Applications for Shaft Drive vs Direct Drive
Shaft drive systems excel in applications demanding durability and low maintenance, such as motorcycles used in long-distance touring and heavy-duty industrial machinery, where resilience to environmental factors is critical. Direct drive systems are ideal for high-precision equipment like electric bicycles and robotics, offering enhanced efficiency, reduced mechanical losses, and quieter operation by eliminating intermediary components. Selecting between shaft drive and direct drive hinges on balancing robustness and maintenance needs against efficiency and performance precision within the specific use case.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Drive System
Selecting the ideal drive system depends on factors such as maintenance preferences, efficiency, and riding style. Shaft drives offer low maintenance and durability suited for touring, while direct drives provide higher efficiency and responsiveness favored in performance cycling. Evaluating these attributes ensures a drive system aligns with individual needs and long-term cycling goals.
Shaft drive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com