Finned tube heat exchangers enhance heat transfer efficiency by increasing the surface area through the addition of fins around the tubes, making them essential in HVAC and industrial applications. These exchangers are designed to handle both air-to-liquid and gas-to-liquid heat exchange processes, improving energy savings and system performance. Discover how finned tube heat exchangers can optimize your thermal management needs by exploring the detailed benefits and applications in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
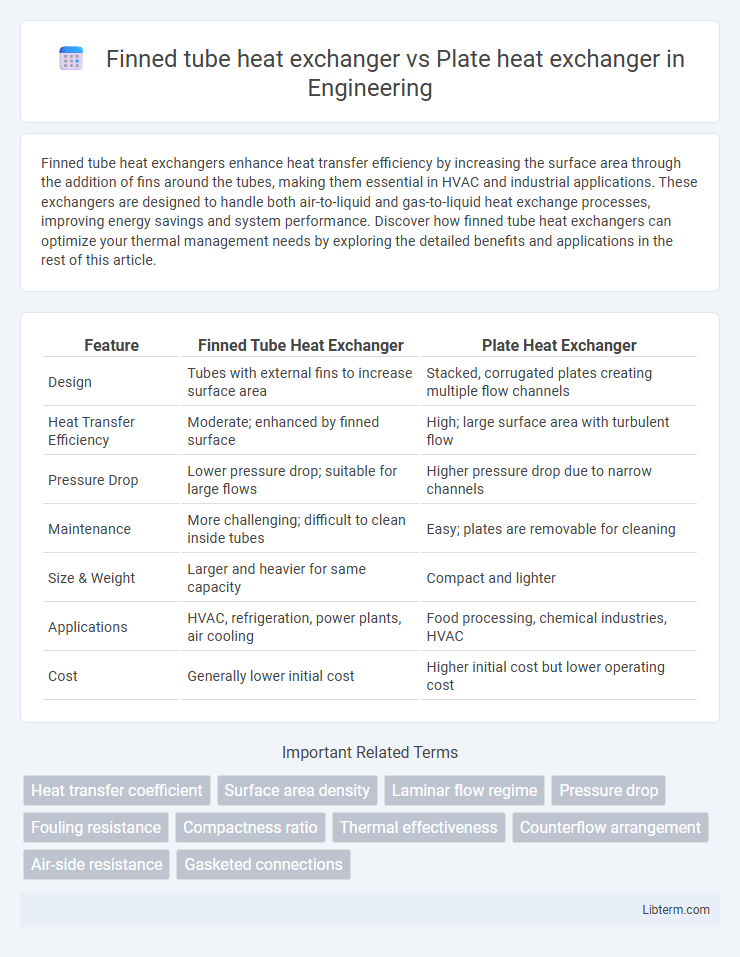
| Feature | Finned Tube Heat Exchanger | Plate Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Tubes with external fins to increase surface area | Stacked, corrugated plates creating multiple flow channels |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | Moderate; enhanced by finned surface | High; large surface area with turbulent flow |
| Pressure Drop | Lower pressure drop; suitable for large flows | Higher pressure drop due to narrow channels |
| Maintenance | More challenging; difficult to clean inside tubes | Easy; plates are removable for cleaning |
| Size & Weight | Larger and heavier for same capacity | Compact and lighter |
| Applications | HVAC, refrigeration, power plants, air cooling | Food processing, chemical industries, HVAC |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but lower operating cost |
Introduction to Heat Exchangers
Finned tube heat exchangers maximize heat transfer by increasing the surface area with extended fins, making them ideal for applications involving gas-to-liquid heat exchange and high-temperature environments. Plate heat exchangers consist of multiple thin, corrugated plates that create efficient heat transfer with compact size and ease of maintenance, commonly used in HVAC and food processing industries. Each type offers distinct advantages depending on the thermal requirements, space constraints, and fluid types involved in industrial and commercial heat transfer processes.
Overview of Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Finned tube heat exchangers consist of tubes with extended surfaces (fins) that enhance heat transfer by increasing the contact area between the tube and the surrounding fluid. They are commonly used in HVAC systems, power plants, and refrigeration for efficient heat exchange between air and fluids. The design allows for effective cooling or heating of gases and liquids, especially in applications with low fluid flow rates or high temperature differences.
Overview of Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers consist of multiple thin, corrugated plates that create large surface areas for efficient heat transfer between fluids. They are highly favored for their compact design, ease of maintenance, and ability to handle varying temperatures and pressures with minimal fluid volume. Compared to finned tube heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers offer superior heat transfer efficiency and flexibility in configuration, making them ideal for HVAC, refrigeration, and process industries.
Design and Construction Differences
Finned tube heat exchangers utilize tubes with extended surfaces or fins to increase the heat transfer area and are typically constructed with metal fins mechanically or hydraulically attached to the tubes, optimizing performance in air-to-fluid or fluid-to-fluid applications with high thermal resistance. Plate heat exchangers consist of multiple thin, corrugated metal plates assembled in a frame with alternating flow channels, promoting high heat transfer efficiency and compact design, ideal for liquid-to-liquid heat exchange. The design differences emphasize finned tubes for enhanced surface area in gaseous flows, whereas plate exchangers focus on maximizing heat transfer through turbulent flow between plates with minimal fluid volume.
Heat Transfer Efficiency Comparison
Finned tube heat exchangers excel in applications requiring effective heat transfer with air or gas due to their extended surface area enhancing convective heat transfer rates. Plate heat exchangers offer superior heat transfer efficiency in liquid-to-liquid applications by providing a large surface area with turbulent flow channels that maximize thermal exchange and minimize fouling. Comparing heat transfer coefficients, plate heat exchangers typically achieve higher rates, often ranging from 5000 to 10000 W/m2K, whereas finned tube designs generally achieve lower values depending on fin density and airflow conditions.
Applications and Suitability
Finned tube heat exchangers excel in applications requiring efficient heat transfer between air and fluids, such as HVAC systems, power plants, and industrial cooling, due to their enhanced surface area and ability to handle high temperatures and pressures. Plate heat exchangers are ideal for processes involving liquid-to-liquid heat transfer with minimal space requirements, commonly used in food processing, chemical industries, and refrigeration because of their high thermal efficiency and ease of maintenance. Suitability depends on operational conditions: finned tube heat exchangers perform better in air and gas cooling, while plate heat exchangers are preferred for compact installations and fluids with low fouling tendencies.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Finned tube heat exchangers require regular inspection and cleaning to prevent fouling and corrosion, with maintenance involving wire brushing or chemical cleaning to remove deposits from tubes and fins. Plate heat exchangers offer easier maintenance due to their design, allowing quick disassembly for manual cleaning, gasket replacement, and visual inspection, reducing downtime significantly. Both types demand routine monitoring, but plate heat exchangers typically provide more straightforward cleaning, especially in applications with high fouling risk.
Cost Analysis and Lifespan
Finned tube heat exchangers typically have lower initial costs compared to plate heat exchangers due to simpler design and materials, making them cost-effective for applications involving high temperatures and pressures. Plate heat exchangers, although generally more expensive upfront, offer superior thermal efficiency and easier maintenance, potentially reducing operational costs over time. Lifespan of finned tube heat exchangers ranges from 10 to 20 years depending on operating conditions, while plate heat exchangers often last 15 to 25 years with proper maintenance, influencing long-term investment decisions.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Finned tube heat exchangers offer high heat transfer efficiency in air-cooled applications due to their extended surface area, making them ideal for handling large temperature differences and dirty fluids; however, they can be bulky and require more maintenance. Plate heat exchangers provide compact design and easy cleaning with excellent thermal performance for clean fluids, but they are less effective with highly viscous or particulate-laden fluids and susceptible to gasket wear. Selecting between these heat exchangers depends on specific application needs such as space constraints, fluid cleanliness, and maintenance capabilities.
Choosing the Right Heat Exchanger for Your Needs
Finned tube heat exchangers excel in applications requiring high thermal efficiency and handling of gases with particulate matter, offering robust performance in HVAC systems and power plants. Plate heat exchangers provide superior heat transfer efficiency in liquid-to-liquid processes, compact design, and ease of maintenance, ideal for food processing and chemical industries. Selecting the right heat exchanger depends on factors such as fluid type, temperature ranges, space constraints, and maintenance requirements to optimize operational performance and cost-effectiveness.
Finned tube heat exchanger Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com