Needle roller bearings offer high load capacity and compact design, making them ideal for applications with limited radial space but significant load requirements. These bearings use long, thin cylindrical rollers to distribute the load efficiently, reducing friction and enhancing machine performance. Discover how needle roller bearings can improve Your machinery's reliability and lifespan by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
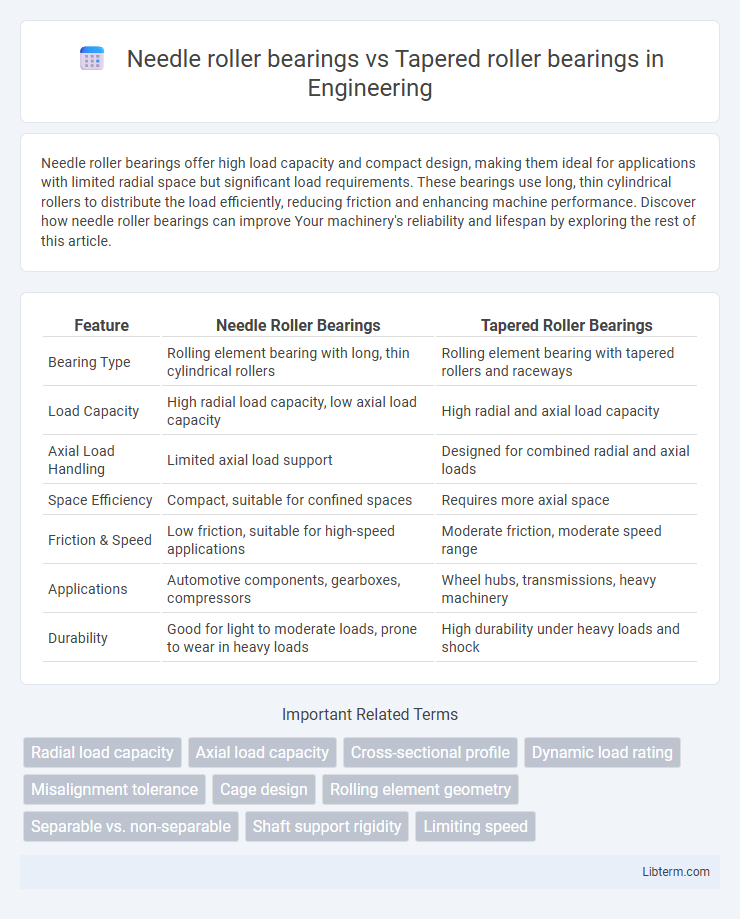
| Feature | Needle Roller Bearings | Tapered Roller Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Bearing Type | Rolling element bearing with long, thin cylindrical rollers | Rolling element bearing with tapered rollers and raceways |
| Load Capacity | High radial load capacity, low axial load capacity | High radial and axial load capacity |
| Axial Load Handling | Limited axial load support | Designed for combined radial and axial loads |
| Space Efficiency | Compact, suitable for confined spaces | Requires more axial space |
| Friction & Speed | Low friction, suitable for high-speed applications | Moderate friction, moderate speed range |
| Applications | Automotive components, gearboxes, compressors | Wheel hubs, transmissions, heavy machinery |
| Durability | Good for light to moderate loads, prone to wear in heavy loads | High durability under heavy loads and shock |
Introduction to Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings feature long, thin cylindrical rollers that provide high load capacity in compact spaces, making them ideal for applications with limited radial space. Tapered roller bearings use conical rollers designed to handle combined radial and axial loads, offering excellent durability in automotive and industrial machinery. Both types of roller bearings optimize load distribution and reduce friction, enhancing the performance and lifespan of rotating equipment.
What Are Needle Roller Bearings?
Needle roller bearings are specialized bearings that utilize long, thin cylindrical rollers resembling needles, providing a high load-carrying capacity within a compact design. These bearings excel in applications requiring reduced cross-sectional height while supporting heavy radial loads, making them ideal for automotive transmissions, gearboxes, and industrial machinery. Their unique design allows for efficient operation in limited space with minimal friction and wear compared to tapered roller bearings, which handle combined radial and axial loads but generally require more space.
What Are Tapered Roller Bearings?
Tapered roller bearings are designed to handle combined radial and axial loads due to their conical geometry and tapered inner and outer ring raceways. These bearings provide high load capacity and durability by distributing stresses over a larger surface area, making them suitable for automotive wheel hubs, gearboxes, and heavy machinery. Unlike needle roller bearings, tapered roller bearings accommodate both thrust and radial forces, enhancing stability in applications with misalignment and varying load directions.
Key Design Differences
Needle roller bearings feature long, thin cylindrical rollers that provide high load capacity with minimal radial space, making them ideal for compact designs and applications requiring high rotational speeds. Tapered roller bearings use conical rollers that handle combined radial and axial loads, offering superior alignment and thrust resistance in heavy-duty machinery. The primary design distinction lies in the roller shape, with needle rollers promoting compactness and speed, while tapered rollers excel in durability and multi-directional load support.
Load Capacity Comparison
Needle roller bearings have a higher load capacity for radial loads due to their smaller diameter rollers that increase surface contact area, making them ideal for applications with limited radial space. Tapered roller bearings excel in handling combined axial and radial loads, thanks to their conical geometry that distributes stress efficiently across the raceways. Load capacity depends on design factors such as roller diameter, length, and bearing arrangement, with tapered roller bearings generally providing better axial load support while needle roller bearings offer superior radial load performance.
Applications of Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings are predominantly used in applications requiring high load capacity and compact design, such as automotive transmissions, gearboxes, and two-stroke engines. Their slender rollers provide excellent resistance to radial loads while occupying minimal radial space, making them ideal for aerospace, industrial machinery, and agriculture equipment. Unlike tapered roller bearings, which accommodate both radial and axial loads, needle roller bearings excel in applications with limited radial space and primarily radial load demands.
Applications of Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings excel in automotive wheel hubs, gearboxes, and heavy machinery due to their ability to handle combined axial and radial loads efficiently. Their conical geometry allows them to support high thrust loads and moderate radial loads, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and precision under varying load conditions. These bearings are commonly found in construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and industrial gear reducers where reliability and load capacity are critical.
Performance Under Various Operating Conditions
Needle roller bearings excel in high-speed applications with limited radial space due to their small diameter rollers, offering excellent load capacity in compact designs. Tapered roller bearings provide superior performance in handling combined radial and axial loads, making them ideal for applications involving heavy thrust and shock loads. Under varying operating conditions, tapered roller bearings maintain better alignment and durability, while needle roller bearings are more efficient in minimizing friction and wear in lighter radial load scenarios.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Needle roller bearings require regular lubrication and contamination control to prevent premature wear due to their high load capacity and thin rollers, which are more susceptible to damage from debris. Tapered roller bearings, designed to handle combined axial and radial loads, benefit from proper adjustment and periodic inspection to maintain optimal preload and alignment, significantly extending service life. Both bearing types demand consistent maintenance schedules to ensure longevity, but tapered roller bearings generally offer greater durability in harsh operating conditions.
Choosing the Right Roller Bearing for Your Needs
Needle roller bearings offer high load capacity and compact design ideal for limited radial space applications, while tapered roller bearings excel in handling combined radial and axial loads, making them suitable for automotive and heavy machinery. Selecting the right roller bearing depends on factors like load type, space constraints, speed, and alignment requirements. Assessing operational conditions ensures optimal performance, durability, and efficiency in mechanical systems.
Needle roller bearings Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com