Mesh topology ensures robust network connectivity by directly linking every device to multiple others, providing high redundancy and fault tolerance. This setup minimizes communication delays and enhances data transmission reliability, ideal for critical applications requiring uninterrupted performance. Explore the following article to understand how mesh topology can optimize your network infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
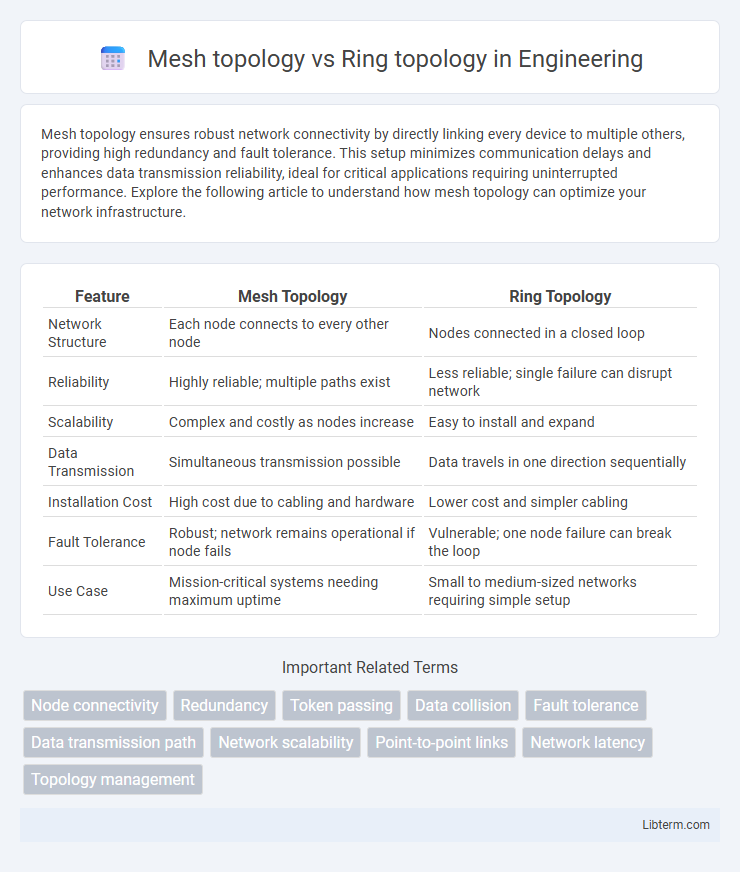
| Feature | Mesh Topology | Ring Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Network Structure | Each node connects to every other node | Nodes connected in a closed loop |
| Reliability | Highly reliable; multiple paths exist | Less reliable; single failure can disrupt network |
| Scalability | Complex and costly as nodes increase | Easy to install and expand |
| Data Transmission | Simultaneous transmission possible | Data travels in one direction sequentially |
| Installation Cost | High cost due to cabling and hardware | Lower cost and simpler cabling |
| Fault Tolerance | Robust; network remains operational if node fails | Vulnerable; one node failure can break the loop |
| Use Case | Mission-critical systems needing maximum uptime | Small to medium-sized networks requiring simple setup |
Introduction to Network Topologies
Mesh topology offers robust network architecture with direct connections between all nodes, ensuring high fault tolerance and efficient data transmission. In contrast, ring topology connects nodes in a circular sequence, where each device links to exactly two others, facilitating orderly data flow but posing challenges if one node fails. Understanding the fundamental differences between mesh and ring topologies is crucial for designing resilient and efficient computer networks.
What is Mesh Topology?
Mesh topology is a network configuration where each device connects directly to every other device, providing multiple paths for data transmission. This design ensures high reliability and fault tolerance, as the failure of one link does not disrupt overall network communication. Mesh topology is commonly used in environments requiring robust and redundant connections, such as wireless networks and critical data centers.
What is Ring Topology?
Ring topology is a network configuration where each device connects to exactly two other devices, forming a circular data path. Data travels in one direction around the ring until it reaches the intended recipient, ensuring orderly communication and reducing collision risks. Unlike mesh topology, which offers multiple redundant paths, ring topology relies on a single loop, making network performance dependent on the ring's integrity.
Key Characteristics of Mesh Topology
Mesh topology features direct point-to-point connections between all nodes, ensuring high redundancy and fault tolerance with multiple data pathways available. This design supports continuous network operation despite individual link failures, making it highly reliable for mission-critical systems. The complexity and cost increase significantly with the number of nodes due to the extensive cabling and configuration required.
Key Characteristics of Ring Topology
Ring topology features a network configuration where each device connects to exactly two other devices, forming a circular data path. Data travels in one or both directions around the ring, reducing collisions and ensuring orderly communication. This topology offers predictable performance but can be vulnerable to a single point of failure unless dual-ring or fault-tolerant mechanisms are implemented.
Mesh vs Ring Topology: Performance Comparison
Mesh topology offers superior network resilience and fault tolerance compared to ring topology due to its multiple redundant paths, ensuring continuous data transmission even if one node fails. Ring topology relies on a single closed loop, where a failure in any node or connection disrupts the entire network, leading to potential data loss and higher downtime. Performance in mesh topology is typically enhanced through parallel data transfers and reduced latency, whereas ring topology may experience delays caused by token passing and limited pathways.
Scalability in Mesh and Ring Topologies
Mesh topology offers superior scalability by allowing the addition of nodes without disrupting existing connections, supporting large and dynamic networks efficiently. In contrast, ring topology exhibits limited scalability since each new node requires reconfiguring the entire ring, increasing latency and potential points of failure. Mesh networks maintain performance and reliability as the network grows, whereas ring networks may face bottlenecks and reduced fault tolerance with expansion.
Fault Tolerance and Reliability
Mesh topology offers superior fault tolerance and reliability by providing multiple redundant paths between nodes, allowing network traffic to reroute automatically when a connection fails. In contrast, ring topology has limited fault tolerance because a single break in the ring can disrupt the entire network unless dual rings or fault-tolerant mechanisms are implemented. Mesh networks are commonly used in environments demanding high availability, such as data centers and mission-critical communication systems, due to their robust reliability and minimal downtime.
Cost and Implementation Considerations
Mesh topology generally incurs higher costs due to extensive cabling and numerous network interfaces required for direct device connections, making implementation complex and expensive in large-scale networks. Ring topology reduces cabling expenses and simplifies installation by connecting each device to exactly two others, forming a closed loop, which limits hardware requirements but can risk entire network failure if a single connection breaks. Cost-efficiency and implementation feasibility often lead organizations to prefer ring topology for smaller or less critical networks, while mesh topology suits environments demanding high redundancy and fault tolerance despite the increased investment.
Choosing the Right Topology for Your Network
Mesh topology offers robust redundancy and fault tolerance by connecting each node to multiple others, ensuring optimal data transmission and minimal downtime, ideal for mission-critical networks requiring high availability. Ring topology, with its circular data flow and equal access, suits smaller or less complex networks where cost-efficiency and simplicity are prioritized over redundancy. Network designers should evaluate factors such as scalability, fault tolerance, cost, and maintenance complexity to choose between the comprehensive reliability of mesh topology and the straightforward efficiency of ring topology.
Mesh topology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com