Fiber optic connectors play a crucial role in ensuring high-quality signal transmission by precisely aligning the fiber cores for minimal loss and reflection. Choosing the right connector type, such as LC, SC, or ST, directly impacts your network's performance and reliability. Explore the rest of the article to discover how to select, install, and maintain fiber optic connectors for optimal connectivity.
Table of Comparison
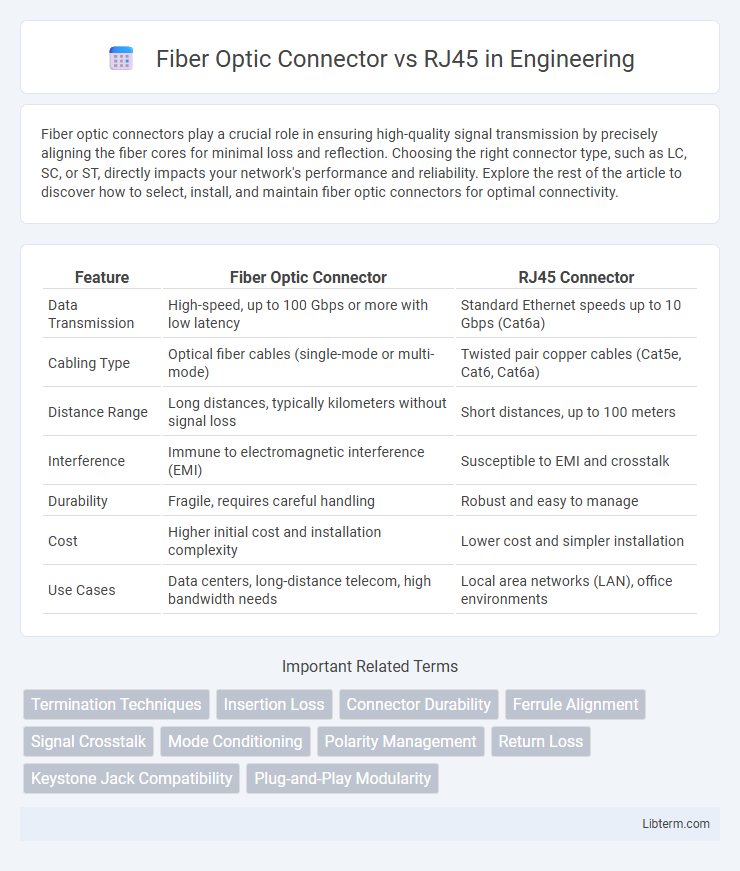
| Feature | Fiber Optic Connector | RJ45 Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transmission | High-speed, up to 100 Gbps or more with low latency | Standard Ethernet speeds up to 10 Gbps (Cat6a) |
| Cabling Type | Optical fiber cables (single-mode or multi-mode) | Twisted pair copper cables (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a) |
| Distance Range | Long distances, typically kilometers without signal loss | Short distances, up to 100 meters |
| Interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) | Susceptible to EMI and crosstalk |
| Durability | Fragile, requires careful handling | Robust and easy to manage |
| Cost | Higher initial cost and installation complexity | Lower cost and simpler installation |
| Use Cases | Data centers, long-distance telecom, high bandwidth needs | Local area networks (LAN), office environments |
Overview of Fiber Optic Connectors
Fiber optic connectors, designed for high-speed data transmission, utilize glass or plastic fibers to carry light signals, offering significantly higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances compared to RJ45 connectors, which rely on copper cables. Common types of fiber optic connectors include SC, LC, ST, and MTP/MPO, each optimized for specific applications and environments, ensuring minimal signal loss and robust physical connections. These connectors are essential in modern telecommunications, data centers, and network infrastructures, where speed, reliability, and reduced electromagnetic interference are critical.
Introduction to RJ45 Connectors
RJ45 connectors are widely used for Ethernet networking, featuring an 8-pin modular plug designed to connect twisted-pair copper cables. These connectors support speeds up to 10 Gbps over Cat6a cables and are standard in LAN environments, providing reliable data transmission for local networks. Unlike fiber optic connectors that use light signals, RJ45 operates through electrical signals, making it cost-effective and simpler to install for short to medium distances.
Key Differences Between Fiber Optic and RJ45 Connectors
Fiber optic connectors transmit data using light signals through glass or plastic fibers, enabling high-speed, long-distance communication with minimal signal loss, while RJ45 connectors use copper wires for electrical signal transmission primarily in Ethernet networks. Fiber connectors, such as SC, LC, or ST types, support higher bandwidths and immunity to electromagnetic interference compared to RJ45 connectors, which rely on twisted pair cables like Cat5e or Cat6. The installation processes and durability requirements differ significantly, with fiber optic connectors demanding precise cleaning and alignment, contrasted by the simpler plug-and-play nature of RJ45 connectors.
Transmission Speed and Bandwidth Comparison
Fiber optic connectors support significantly higher transmission speeds, often reaching 10 Gbps to 100 Gbps and beyond, compared to RJ45 connectors used in Ethernet cables, which typically max out at 1 Gbps for Cat5e and 10 Gbps for Cat6a standards. The bandwidth capacity of fiber optic connectors far exceeds that of RJ45, with fiber supporting frequencies in the terahertz range, enabling vast data transfer over long distances without signal degradation. RJ45 connectors, relying on copper cables, experience limited bandwidth and speed due to electromagnetic interference and signal attenuation over extended runs.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Fiber optic connectors require precise alignment and cleanliness during installation to ensure optimal signal transmission, demanding specialized tools and trained technicians. RJ45 connectors offer simpler installation with crimping tools and are more tolerant to environmental factors, making them suitable for quick setups in typical office or home networks. Maintenance for fiber optic systems involves periodic cleaning and inspection to prevent signal loss, while RJ45 connectors primarily require occasional cable testing and replacement if physical damage occurs.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Fiber optic connectors generally have higher initial costs compared to RJ45 connectors due to the advanced technology and precision required for installation and maintenance. RJ45 connectors offer a more budget-friendly solution for short-distance and less data-intensive applications, making them ideal for small businesses or residential networks with limited funding. When planning network infrastructure investments, factors such as long-term scalability, signal integrity, and potential upgrade expenses should be evaluated alongside upfront connector costs.
Use Cases: When to Choose Fiber Optic
Fiber optic connectors are ideal for long-distance data transmission, high-speed internet, and environments requiring minimal electromagnetic interference, such as data centers, telecom networks, and enterprise backbones. RJ45 connectors suit shorter distances within local area networks (LANs), like office or home networking, where cost-effectiveness and ease of installation are priorities. Choose fiber optic connectors when bandwidth demands exceed 10 Gbps, signal integrity is critical, or network infrastructure must support future scalability.
Use Cases: When to Choose RJ45
RJ45 connectors are ideal for local area networks (LANs) where ease of installation and cost-effectiveness are priorities, particularly in office and home environments using Ethernet cables for data transmission speeds up to 10 Gbps. They are commonly chosen for connecting computers, routers, switches, and other network devices where cable runs are relatively short, typically less than 100 meters. RJ45 connectors excel in environments with less electromagnetic interference, making them suitable for typical indoor networking applications.
Security and Reliability Factors
Fiber optic connectors offer superior security by transmitting data through light signals, making them immune to electromagnetic interference and highly resistant to signal tapping compared to RJ45 connectors, which use electrical signals over copper cables. The enhanced reliability of fiber optic connectors stems from their lower signal attenuation and higher bandwidth capacity, ensuring consistent, high-speed data transmission over longer distances without degradation. In contrast, RJ45 connectors, while more common and cost-effective, are susceptible to crosstalk, electromagnetic interference, and physical damage, which can compromise network security and reliability.
Future Trends in Network Connectivity
Fiber optic connectors are rapidly advancing with innovations like angled physical contact (APC) and ultra-low insertion loss designs, supporting faster data transmission and greater bandwidth necessary for future 5G and 6G network deployments. RJ45 connectors, primarily used for copper Ethernet cables, face limitations in speed and distance, prompting a gradual shift towards fiber optics in data centers and enterprise networks seeking scalability and reduced latency. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid network architectures combining fiber optic connectors for backbone infrastructure and RJ45 for local connections, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency in evolving network ecosystems.
Fiber Optic Connector Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com