Root cause analysis identifies the underlying reasons for problems, enabling effective and lasting solutions rather than mere symptom treatment. This methodology improves decision-making processes by addressing core issues and preventing recurrence. Discover how root cause analysis can transform your troubleshooting approach by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
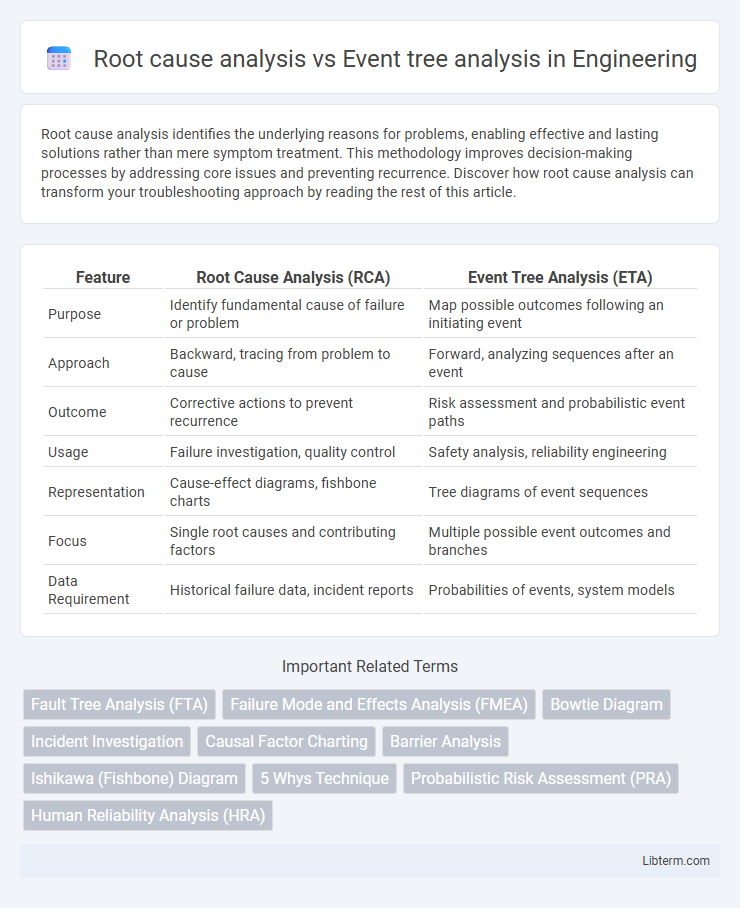
| Feature | Root Cause Analysis (RCA) | Event Tree Analysis (ETA) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify fundamental cause of failure or problem | Map possible outcomes following an initiating event |
| Approach | Backward, tracing from problem to cause | Forward, analyzing sequences after an event |
| Outcome | Corrective actions to prevent recurrence | Risk assessment and probabilistic event paths |
| Usage | Failure investigation, quality control | Safety analysis, reliability engineering |
| Representation | Cause-effect diagrams, fishbone charts | Tree diagrams of event sequences |
| Focus | Single root causes and contributing factors | Multiple possible event outcomes and branches |
| Data Requirement | Historical failure data, incident reports | Probabilities of events, system models |
Understanding Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) systematically identifies fundamental causes of problems to prevent recurrence by using techniques like the 5 Whys and Fishbone Diagram. Unlike Event Tree Analysis (ETA), which focuses on mapping possible event sequences and outcomes, RCA dives deeper into underlying issues driving failures. Effective RCA enhances decision-making by targeting core factors rather than symptoms, leading to lasting corrective actions.
What is Event Tree Analysis?
Event Tree Analysis (ETA) is a systematic, forward-looking risk assessment method used to evaluate the probabilities of different outcome scenarios following an initiating event. ETA maps out possible event sequences and their consequences by branching out from an initial failure or incident, providing insights into system reliability and accident pathways. This technique is widely applied in industries such as nuclear power, aerospace, and chemical processing to anticipate potential failures and enhance safety protocols.
Key Objectives of Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) aims to identify the fundamental causes of a problem to prevent recurrence by systematically examining underlying issues. The key objectives of RCA include uncovering the root causes, improving corrective actions, and enhancing overall system reliability. In contrast, Event Tree Analysis (ETA) focuses on mapping possible outcomes following an initiating event, primarily to assess risk probabilities rather than pinpoint root causes.
Main Applications of Event Tree Analysis
Event Tree Analysis (ETA) is primarily applied in risk assessment and safety engineering to model the sequence of events following an initiating incident, predicting possible outcomes and their probabilities. It is extensively used in nuclear power plants, chemical process industries, and aerospace systems to evaluate system reliability and accident scenarios. Root Cause Analysis (RCA), by contrast, focuses on identifying underlying causes of failures or incidents after they occur, making ETA more proactive in hazard identification and mitigation.
Methodology: Root Cause Analysis Step-by-Step
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) methodology involves systematically identifying the fundamental causes of a problem by collecting data, mapping causal relationships, and verifying root causes through iterative questioning like the "5 Whys." This step-by-step process emphasizes problem definition, data gathering, cause identification, and corrective action implementation to prevent recurrence. Event Tree Analysis (ETA), in contrast, models potential accident sequences probabilistically but does not dissect underlying causes with the same causal depth as RCA.
Methodology: Event Tree Analysis Step-by-Step
Event Tree Analysis (ETA) methodology begins with identifying an initiating event, followed by systematically mapping out possible subsequent events in a tree-like structure to evaluate potential outcomes. Each branch represents a binary decision point (success/failure), with probabilities assigned to quantify risk and identify critical failure paths. This step-by-step approach enables detailed risk assessment by tracing event sequences and estimating their impact on system safety or performance.
Comparative Benefits: RCA vs. ETA
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) excels in identifying the underlying causes of failures by systematically tracing issues back to their origin, making it ideal for troubleshooting complex problems. Event Tree Analysis (ETA) offers a probabilistic approach that maps multiple possible outcomes following an initiating event, which supports risk assessment and decision-making in safety-critical environments. RCA provides in-depth diagnostic insights for problem resolution, while ETA enhances predictive capabilities and scenario planning through quantifying event sequences.
Limitations and Challenges in Both Techniques
Root cause analysis often struggles with identifying multiple interconnected causes, leading to oversimplified conclusions and potentially overlooking systemic issues. Event tree analysis faces challenges in modeling complex, dynamic systems due to uncertainty in event probabilities and dependencies, which can result in incomplete risk assessments. Both techniques require substantial expert judgment, which introduces subjectivity and may affect the consistency and reliability of the analysis outcomes.
Selecting the Right Analysis Method
Selecting the right analysis method requires understanding that Root Cause Analysis (RCA) focuses on identifying the underlying causes of a specific failure or problem to prevent recurrence. Event Tree Analysis (ETA) systematically examines possible event sequences following an initial incident to assess potential outcomes and their probabilities. RCA is ideal for detailed problem-solving, while ETA is more effective for risk assessment and scenario evaluation in complex systems.
Integrating RCA and ETA for Enhanced Risk Management
Integrating Root Cause Analysis (RCA) with Event Tree Analysis (ETA) enhances risk management by combining RCA's detailed identification of failure origins with ETA's systematic exploration of event outcomes and probabilities. This synergy allows organizations to not only pinpoint underlying causes of incidents but also to quantitatively assess the cascading effects and likelihood of potential risks. Leveraging data from both methodologies facilitates comprehensive preventive strategies and more informed decision-making in safety-critical environments.
Root cause analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com