Rotameters provide accurate flow rate measurements using a float within a tapered tube, ideal for clear liquids and gases with moderate flow. Ultrasonic flow meters utilize sound waves to measure flow velocity without contact, making them suitable for dirty or corrosive fluids and various pipe sizes. Explore the rest of the article to discover which flow meter best fits your specific application needs.
Table of Comparison
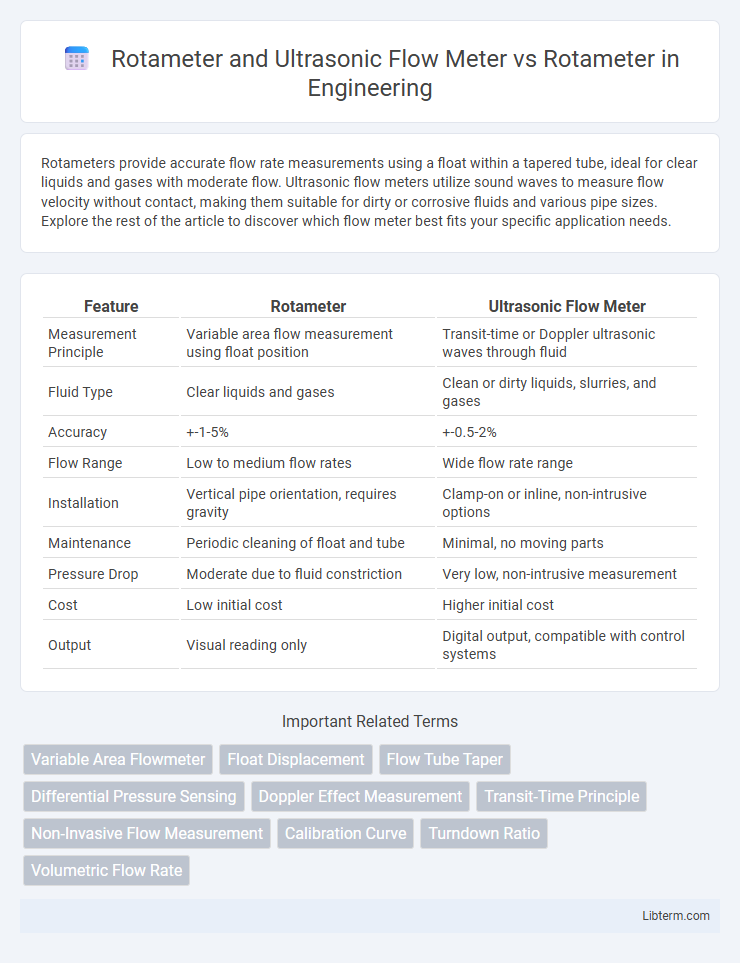
| Feature | Rotameter | Ultrasonic Flow Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Principle | Variable area flow measurement using float position | Transit-time or Doppler ultrasonic waves through fluid |
| Fluid Type | Clear liquids and gases | Clean or dirty liquids, slurries, and gases |
| Accuracy | +-1-5% | +-0.5-2% |
| Flow Range | Low to medium flow rates | Wide flow rate range |
| Installation | Vertical pipe orientation, requires gravity | Clamp-on or inline, non-intrusive options |
| Maintenance | Periodic cleaning of float and tube | Minimal, no moving parts |
| Pressure Drop | Moderate due to fluid constriction | Very low, non-intrusive measurement |
| Cost | Low initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Output | Visual reading only | Digital output, compatible with control systems |
Introduction to Flow Measurement Technologies
Rotameters offer cost-effective, visual flow measurement for low to moderate flow rates using a tapered tube and float mechanism, ideal for simple liquid and gas applications. Ultrasonic flow meters provide non-intrusive, highly accurate measurements through transit-time or Doppler methods, suitable for large pipelines and complex fluids without pressure drop. Comparing these technologies highlights key considerations in accuracy, application suitability, installation complexity, and maintenance for effective flow measurement solutions.
What is a Rotameter?
A Rotameter is a precision flow measurement device that uses a tapered tube and a float to indicate fluid flow rate visually. Ultrasonic flow meters differ by employing sound waves to measure flow velocity without obstruction, enabling non-invasive and maintenance-free operation. Rotameters provide reliable readings for clear liquids and gases, while ultrasonic meters offer versatility for dirty or corrosive fluids where direct contact should be avoided.
How Rotameters Work: Principles and Applications
Rotameters operate based on the variable area flow measurement principle, where fluid flow lifts a float in a tapered tube, and the float's position indicates the flow rate. These devices are widely used for monitoring water, chemicals, and gases in industrial and laboratory settings due to their simple design and reliable performance without the need for external power. While ultrasonic flow meters employ sound waves to measure flow velocity nondestructively and offer high accuracy for large pipes, rotameters remain preferred for their ease of use, low maintenance, and direct visual indication in smaller-scale applications.
Ultrasonic Flow Meters: An Overview
Ultrasonic flow meters use high-frequency sound waves to measure fluid velocity, providing accurate and non-intrusive flow measurement without direct contact with the fluid. Compared to rotameters, which rely on mechanical float movement within a tapered tube, ultrasonic flow meters offer superior precision, especially in large pipe diameters and opaque or corrosive fluids. Their ability to measure bidirectional flow and minimal pressure drop makes ultrasonic flow meters a preferred choice in industrial and process applications.
Key Working Principles of Ultrasonic Flow Meters
Ultrasonic flow meters operate by transmitting high-frequency sound waves through a fluid to measure flow velocity based on the time difference between upstream and downstream signals, providing precise, non-intrusive flow measurement. In contrast, rotameters utilize a float inside a tapered tube that rises or falls with flow rate to offer a simple mechanical flow indication. The ultrasonic technique offers greater accuracy, no pressure drop, and suitability for various fluid types compared to the rotameter's reliance on gravity and mechanical movement.
Rotameter vs Ultrasonic Flow Meter: Key Differences
Rotameters measure flow rates using a tapered tube and float, providing direct, visual readings ideal for low to medium flow applications with moderate accuracy. Ultrasonic flow meters use sound waves to determine flow velocity, offering higher accuracy, non-invasive measurement, and suitability for a wide range of fluids and pipe sizes. Key differences include maintenance needs, with rotameters requiring regular cleaning and ultrasonic meters being maintenance-free, and installation flexibility, as ultrasonic meters can be clamped externally without pipe modifications.
Advantages of Using Rotameters
Rotameters provide highly accurate flow measurement with a simple, reliable design that requires no external power, ensuring consistent performance in various fluid applications. Their transparent tubes allow for easy visual flow rate verification, making them ideal for quick inspections without specialized equipment. Rotameters also excel in measuring clean, low-viscosity fluids with minimal maintenance compared to ultrasonic flow meters, which can be more complex and sensitive to installation conditions.
Benefits of Ultrasonic Flow Meters
Ultrasonic flow meters offer higher accuracy and non-intrusive measurement compared to rotameters, making them ideal for applications requiring precise flow rate data without pipe alterations. They provide real-time digital output, low maintenance due to no moving parts, and can measure flow in reverse directions and in larger pipe diameters. These benefits result in improved reliability and reduced operational costs over traditional rotameters, especially in complex industrial systems.
Typical Industries and Applications for Each Technology
Rotameters are widely used in chemical processing, water treatment, and pharmaceuticals due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness in measuring clean, low-viscosity fluids. Ultrasonic flow meters find typical applications in oil and gas, HVAC systems, and wastewater monitoring where non-invasive, accurate measurement of various fluids, including aggressive or dirty media, is essential. Industries requiring precise flow measurement under challenging conditions often prefer ultrasonic technology, while rotameters suit straightforward, low-cost flow monitoring needs.
Choosing the Right Flow Meter: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right flow meter requires evaluating factors such as measurement accuracy, fluid type, and installation environment. Rotameters provide reliable visual flow indication for clear, clean liquids but may struggle with low flow rates and opaque fluids. Ultrasonic flow meters offer non-intrusive measurement with high precision suitable for various fluids, especially in applications demanding minimal maintenance and real-time data monitoring.
Rotameter and Ultrasonic Flow Meter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com