SCADA systems provide real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, while MES focuses on managing and optimizing manufacturing operations on the shop floor. Integrating SCADA and MES enhances data visibility, improves production efficiency, and ensures better decision-making throughout your manufacturing environment. Explore the rest of the article to discover how combining these technologies can transform your industrial operations.
Table of Comparison
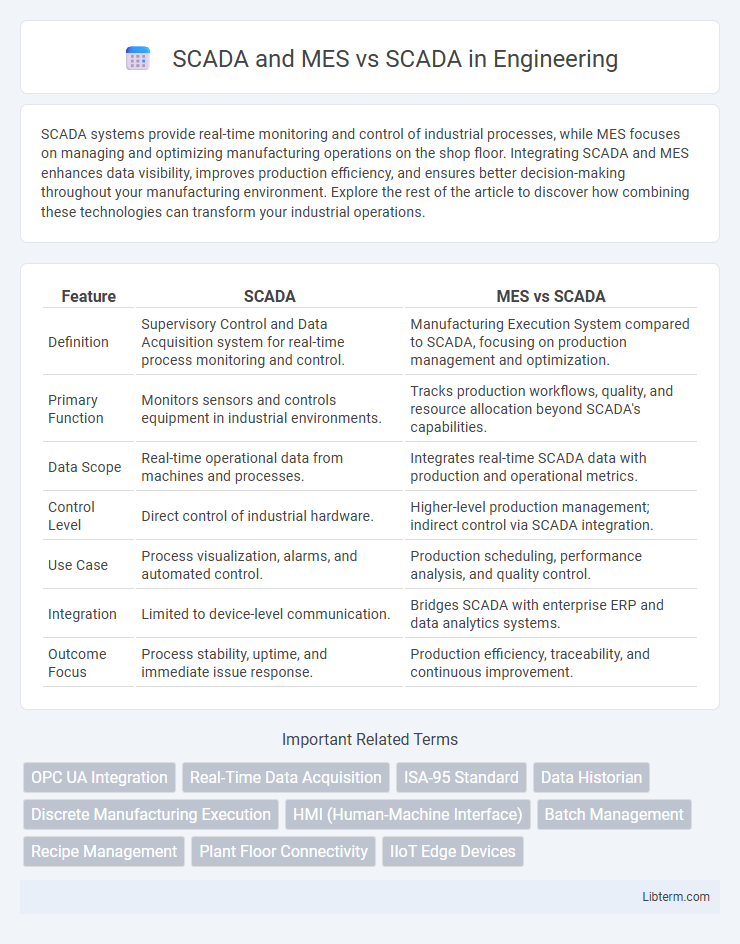
| Feature | SCADA | MES vs SCADA |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition system for real-time process monitoring and control. | Manufacturing Execution System compared to SCADA, focusing on production management and optimization. |
| Primary Function | Monitors sensors and controls equipment in industrial environments. | Tracks production workflows, quality, and resource allocation beyond SCADA's capabilities. |
| Data Scope | Real-time operational data from machines and processes. | Integrates real-time SCADA data with production and operational metrics. |
| Control Level | Direct control of industrial hardware. | Higher-level production management; indirect control via SCADA integration. |
| Use Case | Process visualization, alarms, and automated control. | Production scheduling, performance analysis, and quality control. |
| Integration | Limited to device-level communication. | Bridges SCADA with enterprise ERP and data analytics systems. |
| Outcome Focus | Process stability, uptime, and immediate issue response. | Production efficiency, traceability, and continuous improvement. |
Understanding SCADA: Core Functions and Capabilities
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems primarily focus on real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes by collecting data from sensors and equipment, enabling operators to manage operations remotely. MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) integrate with SCADA to provide detailed production management, including scheduling, quality control, and performance analysis. Understanding SCADA's core functions such as data acquisition, alarm management, and visualization is essential for optimizing process control and ensuring timely operational decisions in manufacturing environments.
What is MES? Scope and Objectives in Manufacturing
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) are integrated software platforms designed to monitor, track, and synchronize the entire production process on the factory floor. MES focuses on real-time data acquisition, production scheduling, quality control, and resource management to optimize manufacturing efficiency and ensure product traceability. Unlike SCADA, which primarily supervises and controls industrial equipment, MES provides comprehensive production execution and operational insights to bridge the gap between enterprise resource planning (ERP) and control systems.
SCADA vs. MES: Key Differences in Industrial Environments
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems focus on real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, ensuring operational efficiency and safety through data acquisition and immediate response capabilities. MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) provide comprehensive management of manufacturing operations, including production scheduling, quality control, and workflow optimization to bridge the gap between enterprise resource planning (ERP) and control systems. The key differences lie in SCADA's emphasis on process-level control and data visualization, while MES delivers detailed production management and performance analysis across the entire manufacturing lifecycle.
Integration Benefits: SCADA and MES Working Together
Integrating SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) enhances real-time data exchange and operational visibility across production processes. This synergy streamlines decision-making by synchronizing equipment monitoring from SCADA with MES-driven production scheduling and quality control. Enhanced integration reduces downtime, boosts product traceability, and improves overall manufacturing efficiency through automated workflows and centralized data management.
Data Collection and Visualization: Comparing SCADA and MES Approaches
SCADA systems specialize in real-time data collection and visualization directly from industrial equipment, providing operators with immediate control and status updates. MES platforms extend beyond raw data capture by integrating process, production, and quality data to deliver comprehensive visualization dashboards that support decision-making at the plant floor level. SCADA emphasizes operational monitoring, whereas MES combines data collection with advanced visualization to optimize manufacturing execution and performance insights.
Real-Time Monitoring: SCADA Standalone vs. Combined with MES
SCADA standalone systems provide real-time monitoring by collecting and displaying data directly from field devices, enabling immediate response to operational changes and alarms. When combined with MES, SCADA enhances real-time monitoring by integrating production scheduling, quality management, and resource tracking, offering a holistic view of manufacturing processes. This integration improves decision-making, reduces downtime, and increases production efficiency through synchronized data sharing across both control and execution layers.
Production Process Optimization: Role of MES vs. SCADA
MES directly enhances production process optimization by providing real-time data analytics, workflow management, and traceability across the entire manufacturing floor, enabling informed decision-making and reducing cycle times. SCADA primarily focuses on monitoring and controlling industrial equipment, offering real-time visualization and automation but lacks comprehensive production scheduling and quality management features. Integrating MES with SCADA systems delivers a holistic approach to optimize operations, improve resource allocation, and achieve higher manufacturing efficiency.
Scalability and Flexibility: SCADA Solutions vs. Integrated SCADA-MES Platforms
SCADA solutions offer scalable monitoring and control for industrial processes but often lack the flexibility to adapt seamlessly to complex manufacturing workflows. Integrated SCADA-MES platforms provide enhanced scalability by combining real-time process control with manufacturing execution capabilities, enabling dynamic adjustments and comprehensive data aggregation. This integration supports flexible production planning, quality management, and resource optimization at scale, surpassing standalone SCADA systems in industrial automation performance.
Decision-Making and Analytics: Enhanced Value of SCADA-MES Integration
SCADA-MES integration significantly improves decision-making by providing real-time data analytics and comprehensive operational insights that standalone SCADA systems lack. MES adds context-driven intelligence such as production scheduling, quality control, and resource management, enabling faster, data-driven decisions that optimize manufacturing processes. Enhanced analytics capabilities from combining SCADA and MES support predictive maintenance and process optimization, driving higher efficiency and reduced downtime in industrial environments.
Choosing the Right Solution: When to Use SCADA Alone or with MES
SCADA systems excel in real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, making them ideal for applications requiring immediate data acquisition and equipment automation. MES complements SCADA by providing production management, workflow optimization, and quality control, which are critical for improving manufacturing efficiency and traceability. Choose SCADA alone for simple process control and real-time data needs, while integrating MES is essential when comprehensive production planning, resource management, and performance analysis are required.
SCADA and MES Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com