Sandblasting is a powerful surface preparation technique that uses high-pressure abrasive particles to clean, smooth, or etch surfaces. It effectively removes rust, paint, and contaminants from metal, wood, or concrete, enhancing durability and paint adhesion. Discover how sandblasting can transform your project and explore the best practices in the full article.
Table of Comparison
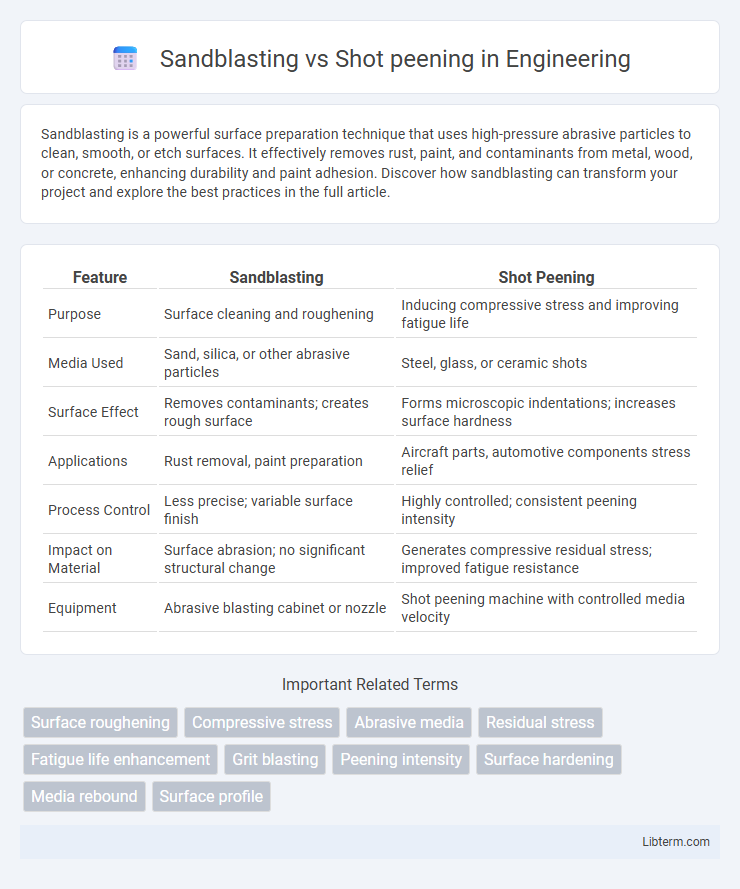
| Feature | Sandblasting | Shot Peening |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Surface cleaning and roughening | Inducing compressive stress and improving fatigue life |
| Media Used | Sand, silica, or other abrasive particles | Steel, glass, or ceramic shots |
| Surface Effect | Removes contaminants; creates rough surface | Forms microscopic indentations; increases surface hardness |
| Applications | Rust removal, paint preparation | Aircraft parts, automotive components stress relief |
| Process Control | Less precise; variable surface finish | Highly controlled; consistent peening intensity |
| Impact on Material | Surface abrasion; no significant structural change | Generates compressive residual stress; improved fatigue resistance |
| Equipment | Abrasive blasting cabinet or nozzle | Shot peening machine with controlled media velocity |
Introduction to Sandblasting and Shot Peening
Sandblasting propels abrasive particles at high velocity to clean or roughen surfaces, enhancing paint adhesion and removing contaminants. Shot peening uses small spherical media to induce compressive stress on metal surfaces, improving fatigue resistance and preventing cracks. Both techniques modify surface properties but target different applications: sandblasting for surface preparation, shot peening for structural integrity.
Understanding the Basics of Sandblasting
Sandblasting involves propelling fine abrasive particles at high velocity to clean, smooth, or etch surfaces, primarily used to remove rust, paint, and other contaminants. This process improves surface preparation for coatings and enhances texture without significantly altering the material's mechanical properties. Key parameters include abrasive type, particle size, air pressure, and nozzle distance, which influence the effectiveness and finish quality.
Fundamentals of Shot Peening
Shot peening is a surface treatment process that uses small spherical media to induce compressive stress on metal parts, enhancing fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. Unlike sandblasting, which primarily cleans and roughens surfaces through abrasive particles, shot peening creates a uniform layer of compressive residual stress by controlled plastic deformation. This fundamental difference makes shot peening essential for improving durability and extending the service life of critical components in aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Sandblasting and Shot Peening
Sandblasting uses high-pressure abrasive particles like sand to clean or etch surfaces, primarily focusing on surface preparation rather than mechanical improvement. Shot peening employs small spherical media, such as steel or ceramic shots, to create compressive stress on metal surfaces, enhancing fatigue resistance and durability. The key differences lie in their purpose: sandblasting is a cleaning or surface texturing process, while shot peening is a mechanical treatment improving material strength.
Surface Preparation Techniques: Sandblasting vs Shot Peening
Sandblasting utilizes high-pressure air to propel abrasive particles for cleaning or roughening surfaces, effectively removing rust, paint, and contaminants. Shot peening employs spherical media to create controlled surface deformation, enhancing fatigue resistance and inducing compressive stress on metal parts. Both techniques are vital in surface preparation but serve different purposes: sandblasting prepares surfaces for coating adhesion, while shot peening improves mechanical properties and durability.
Applications of Sandblasting in Industry
Sandblasting is extensively used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction for surface preparation, rust removal, and paint stripping. Its ability to clean and roughen surfaces makes it ideal for enhancing adhesion before coating or bonding processes. Unlike shot peening, which primarily improves metal fatigue resistance, sandblasting focuses on cleaning and texturing surfaces to prepare them for further treatment or finishing.
Industrial Uses of Shot Peening
Shot peening is extensively used in aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery industries to improve metal fatigue strength by inducing compressive surface stresses. Unlike sandblasting, which primarily cleans and smooths surfaces, shot peening enhances durability and resistance to stress corrosion cracking in critical components such as turbine blades, gears, and suspension springs. Its industrial application extends to prolonging the life of metal parts subjected to cyclic loading and harsh operational environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sandblasting
Sandblasting offers efficient surface cleaning and preparation by using high-pressure abrasive materials to remove rust, paint, and contaminants, enhancing paint adhesion and surface texture. Its advantages include rapid material removal and cost-effectiveness for large surface areas, but it can cause surface damage, material erosion, and generate significant dust, requiring proper protective measures. Unlike shot peening, sandblasting does not impart beneficial compressive stresses to improve material fatigue resistance, limiting its use in applications where surface strengthening is critical.
Pros and Cons of Shot Peening
Shot peening enhances metal durability by inducing compressive stress on surfaces, significantly improving fatigue strength and resistance to cracking. Its precise control over intensity and coverage ensures consistent results, but the process requires specialized equipment and skilled operators, increasing costs. However, improper application can cause surface contamination or distortion, limiting its use for thin or delicate materials compared to sandblasting.
Choosing the Right Method: Sandblasting or Shot Peening
Choosing between sandblasting and shot peening depends on the desired surface finish and mechanical properties. Sandblasting is ideal for cleaning, deburring, or preparing surfaces for coating, offering efficient material removal and a relatively smooth finish. Shot peening enhances metal durability by inducing compressive stress to improve fatigue resistance, making it the preferred method for parts subjected to high stress or cyclic loading.
Sandblasting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com