Automated welding enhances precision and efficiency by utilizing robotic systems to perform welding tasks with consistent quality and speed. This technology reduces labor costs, minimizes human error, and improves safety in industrial applications. Discover how automated welding can optimize your manufacturing processes by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
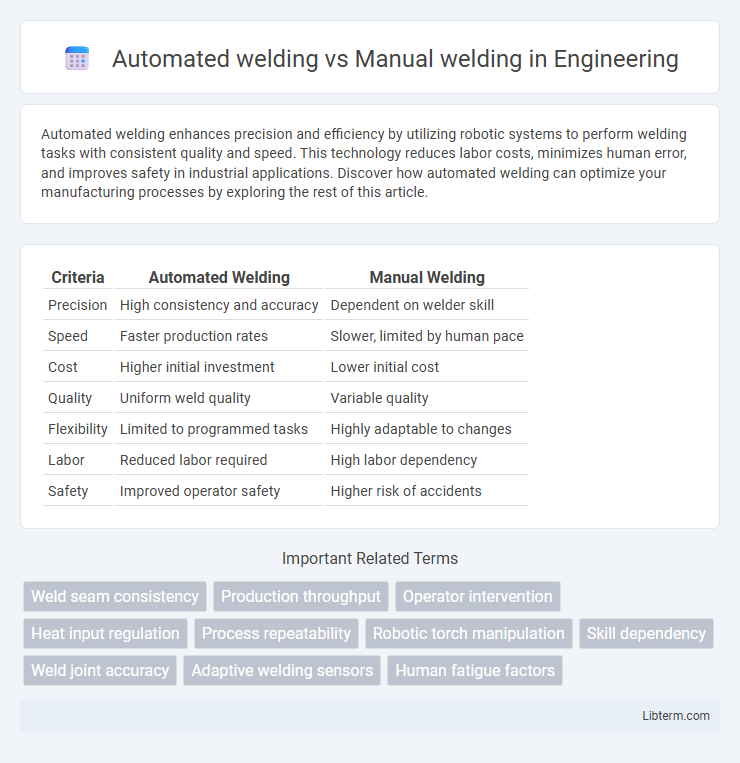
| Criteria | Automated Welding | Manual Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | High consistency and accuracy | Dependent on welder skill |
| Speed | Faster production rates | Slower, limited by human pace |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial cost |
| Quality | Uniform weld quality | Variable quality |
| Flexibility | Limited to programmed tasks | Highly adaptable to changes |
| Labor | Reduced labor required | High labor dependency |
| Safety | Improved operator safety | Higher risk of accidents |
Introduction to Automated vs Manual Welding
Automated welding utilizes robotic systems and computer-controlled machinery to perform precise, consistent welds, significantly enhancing productivity and reducing human error. Manual welding relies on skilled operators using hand-held tools to control the welding process, offering flexibility for complex or intricate tasks but with greater variability. The choice between automated and manual welding depends on factors such as production volume, weld quality requirements, and job complexity.
Key Differences Between Automated and Manual Welding
Automated welding offers consistent precision, higher speed, and reduced human error compared to manual welding, which relies heavily on the welder's skill and experience. While manual welding provides greater flexibility for complex or customized tasks, automated welding excels in repetitive, large-scale production with enhanced safety and efficiency. The key differences lie in control methods, cost-effectiveness for high-volume projects, and the ability to maintain uniform quality.
Advantages of Automated Welding
Automated welding offers consistent weld quality and higher precision by using programmed robotic systems that reduce human error. It significantly increases production speed and efficiency, lowering labor costs and minimizing material waste. Enhanced safety is achieved by limiting workers' exposure to hazardous fumes and intense light, making automated welding ideal for high-volume industrial applications.
Benefits of Manual Welding
Manual welding offers superior control and adaptability, allowing skilled welders to adjust techniques in real-time to accommodate complex shapes and materials. It provides greater flexibility for small-scale or custom projects where automation machinery may be impractical or cost-prohibitive. The tactile feedback and experience of a welder can result in higher-quality welds in intricate or non-standard applications.
Limitations of Automated Welding
Automated welding systems face limitations such as high initial investment costs and reduced flexibility when handling complex or custom welds, which manual welding can accommodate more easily. These systems often struggle with variable joint conditions and intricate part geometries that require human judgment and adaptability. Maintenance and programming requirements for automated welding machinery also contribute to operational downtime and increase technical skill demands.
Challenges in Manual Welding
Manual welding presents challenges such as inconsistent weld quality due to human error and operator fatigue, which can lead to defects or weak joints. The reliance on skilled labor increases training costs and limits productivity, particularly in high-volume or complex welding tasks. Safety risks are higher in manual welding, as operators are exposed to harmful fumes, intense heat, and potential burns without the protective advantages of automated systems.
Cost Comparison: Automated vs Manual Welding
Automated welding systems involve high initial capital investment but significantly reduce labor costs and increase production speed, resulting in lower long-term operational expenses compared to manual welding. Manual welding incurs minimal startup costs but demands skilled labor, leading to higher ongoing wage expenses and potential variability in quality that can increase rework costs. Overall, automated welding offers greater cost efficiency in high-volume production environments, while manual welding remains more cost-effective for low-volume or specialized projects.
Quality and Consistency Analysis
Automated welding delivers superior quality and consistency by precisely controlling heat input, speed, and filler material, minimizing human error and weld defects such as porosity and cracks. Manual welding, while flexible for complex or small-scale tasks, often results in variability in weld quality due to operator skill and fatigue, leading to inconsistent penetration and bead profiles. Industry studies indicate automated systems achieve up to 90% reduction in rework rates, significantly enhancing productivity and structural integrity in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Automated welding is extensively used in automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and shipbuilding industries where precision and high-volume production are critical, enabling consistent weld quality and faster throughput. Manual welding remains prevalent in construction, repair work, and custom fabrication due to its flexibility in handling diverse materials and complex geometries in low-volume or on-site applications. Both methods are integral to heavy machinery, pipelines, and infrastructure projects, with automated systems optimizing repetitive tasks while manual welding supports intricate or adaptive welding needs.
Future Trends in Welding Technology
Automated welding systems increasingly incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to enhance precision, reduce errors, and optimize weld quality in real-time. Emerging trends include integration with IoT-enabled sensors and robotics, enabling predictive maintenance and seamless workflow automation across manufacturing environments. Manual welding remains vital for complex or custom tasks, but future advancements prioritize hybrid systems combining human expertise with automated technologies to boost productivity and consistency.
Automated welding Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com