Pore water pressure plays a critical role in soil mechanics by influencing the stability and strength of soils, especially in saturated conditions. It affects the effective stress within soil layers, directly impacting construction safety and groundwater flow. Explore the rest of the article to understand how controlling pore water pressure can enhance your soil management strategies.
Table of Comparison
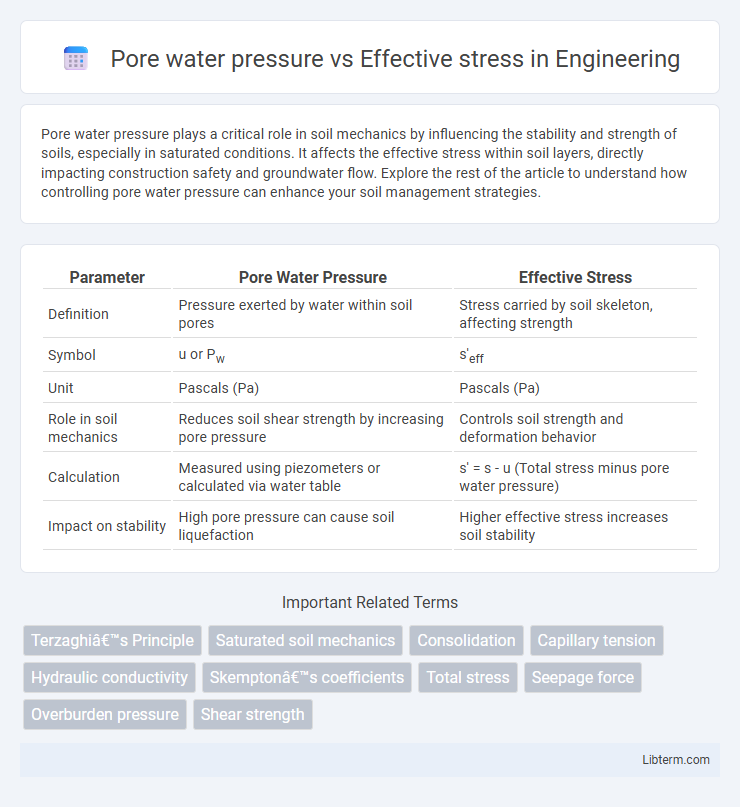
| Parameter | Pore Water Pressure | Effective Stress |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pressure exerted by water within soil pores | Stress carried by soil skeleton, affecting strength |
| Symbol | u or Pw | s'eff |
| Unit | Pascals (Pa) | Pascals (Pa) |
| Role in soil mechanics | Reduces soil shear strength by increasing pore pressure | Controls soil strength and deformation behavior |
| Calculation | Measured using piezometers or calculated via water table | s' = s - u (Total stress minus pore water pressure) |
| Impact on stability | High pore pressure can cause soil liquefaction | Higher effective stress increases soil stability |
Introduction to Pore Water Pressure and Effective Stress
Pore water pressure refers to the pressure exerted by water within the pores of a soil or rock mass, significantly influencing soil strength and stability. Effective stress is defined as the stress transmitted through the soil skeleton, which controls deformation and shear strength, calculated by subtracting pore water pressure from total stress. Understanding the relationship between pore water pressure and effective stress is essential for analyzing soil behavior under various loading and environmental conditions.
Fundamentals of Soil Mechanics
Pore water pressure is the pressure exerted by water within the soil pores, directly influencing the total stress on a soil mass. Effective stress, defined as the difference between total stress and pore water pressure, governs soil strength and deformation behavior. Understanding the relationship between pore water pressure and effective stress is fundamental in soil mechanics for predicting soil stability and behavior under various loading conditions.
Defining Pore Water Pressure
Pore water pressure refers to the pressure exerted by water within the voids of a soil or rock mass, crucial for understanding fluid flow and soil behavior under load. It directly influences the effective stress, which is the stress carried by the soil skeleton and determines soil strength and deformation characteristics. Precise measurement and control of pore water pressure are essential for geotechnical engineering projects, including slope stability, foundation design, and earth dam construction.
Understanding Effective Stress
Effective stress represents the stress carried by the soil skeleton, crucial for soil strength and stability, and is calculated by subtracting pore water pressure from total stress. Pore water pressure, the pressure exerted by water within the soil pores, reduces the effective stress and influences soil deformation and shear strength. Understanding the relationship between pore water pressure and effective stress helps engineers predict soil behavior under various loading and drainage conditions, essential for foundation design and slope stability analysis.
The Principle of Effective Stress
The Principle of Effective Stress states that the strength and deformation of a soil mass depend primarily on the effective stress, which is the total stress minus the pore water pressure. Effective stress controls soil behavior by determining the intergranular contact forces, whereas pore water pressure influences the total stress but does not contribute directly to soil strength. Understanding this principle is essential for analyzing soil stability, particularly in saturated conditions where changes in pore water pressure can significantly affect effective stress and thus soil shear strength.
Relationship Between Pore Water Pressure and Effective Stress
Pore water pressure directly influences the effective stress in soil by reducing the total stress carried by the soil skeleton, which controls soil strength and stability. Effective stress equals the total stress minus the pore water pressure, dictating soil deformation and shear strength parameters. An increase in pore water pressure decreases effective stress, potentially leading to soil liquefaction or failure under load.
Factors Influencing Pore Water Pressure
Pore water pressure, the pressure exerted by water within soil pores, significantly affects effective stress, which governs soil strength and stability. Factors influencing pore water pressure include soil permeability, rate of loading, drainage conditions, and the soil's saturation level, with higher saturation and low permeability typically leading to increased pore water pressure. Changes in pore water pressure directly alter effective stress, impacting soil consolidation and potential shear failure.
Impact of Effective Stress on Soil Behavior
Effective stress directly influences soil strength and deformation by controlling the interparticle forces that govern soil stability, while pore water pressure acts to counterbalance these forces. An increase in pore water pressure reduces effective stress, leading to decreased shear strength and potential soil failure, especially in saturated conditions. Understanding the interplay between pore water pressure and effective stress is crucial for predicting settlement, slope stability, and bearing capacity in geotechnical engineering.
Engineering Applications and Case Studies
Pore water pressure significantly influences effective stress, which governs soil strength and deformation in geotechnical engineering, critical for foundation design, slope stability, and earth dam analysis. Engineering case studies, such as the 1998 Tangshan earthquake, demonstrate that elevated pore water pressure reduced effective stress, triggering soil liquefaction and catastrophic failure. Accurate measurement and control of pore water pressure enhance predictive models, ensuring safer infrastructure and mitigating risks in earthquake-prone and saturated soil environments.
Conclusion: Importance in Geotechnical Design
Pore water pressure directly influences the effective stress within soil, which governs soil strength and deformation behavior critical for geotechnical stability. Accurate assessment of pore water pressure is essential for predicting slope stability, foundation bearing capacity, and earth retaining structures. Understanding the interplay between pore water pressure and effective stress ensures safer and more cost-effective geotechnical designs.
Pore water pressure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com