A compliance matrix systematically aligns project requirements with specific deliverables, ensuring every criterion is addressed effectively. It enhances transparency and accountability by clearly mapping obligations to corresponding responses, reducing the risk of oversight. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to create a comprehensive compliance matrix tailored to your project needs.
Table of Comparison
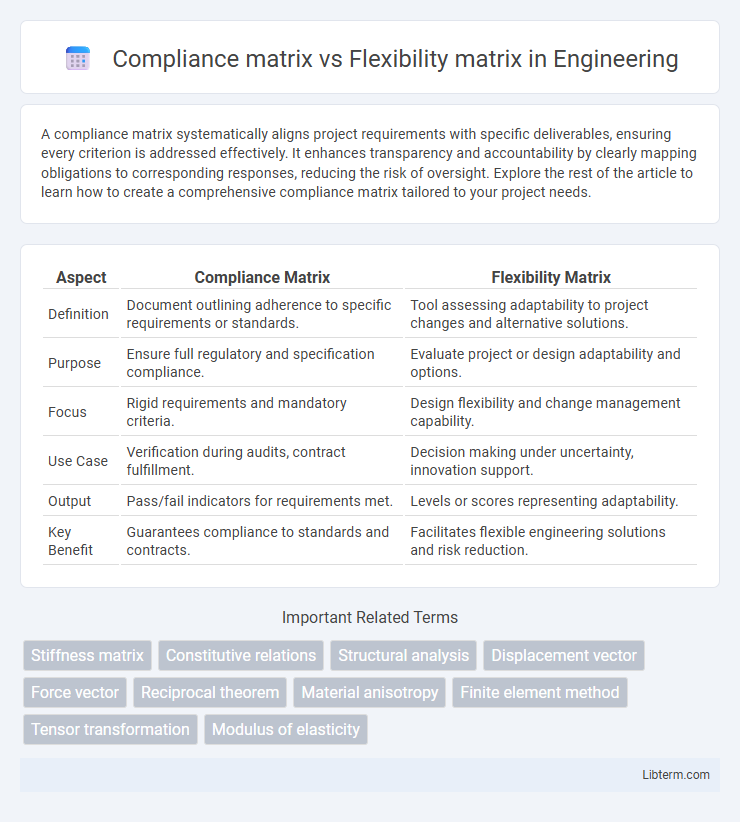
| Aspect | Compliance Matrix | Flexibility Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Document outlining adherence to specific requirements or standards. | Tool assessing adaptability to project changes and alternative solutions. |
| Purpose | Ensure full regulatory and specification compliance. | Evaluate project or design adaptability and options. |
| Focus | Rigid requirements and mandatory criteria. | Design flexibility and change management capability. |
| Use Case | Verification during audits, contract fulfillment. | Decision making under uncertainty, innovation support. |
| Output | Pass/fail indicators for requirements met. | Levels or scores representing adaptability. |
| Key Benefit | Guarantees compliance to standards and contracts. | Facilitates flexible engineering solutions and risk reduction. |
Introduction to Compliance and Flexibility Matrices
Compliance matrices systematically track whether project deliverables meet predefined requirements, ensuring alignment with specifications and contractual obligations. Flexibility matrices evaluate the range within which project parameters can vary without compromising objectives, highlighting adaptability and risk tolerance in project management. Both matrices serve as critical tools for balancing strict adherence to standards with the need for agile responses to changing project conditions.
Defining Compliance Matrix
A compliance matrix is a structured tool used to align project requirements with deliverables, ensuring all specifications are met and documented for regulatory or contractual adherence. It systematically maps each requirement to corresponding evidence or actions, providing a clear framework for verification and accountability. This matrix is essential in quality management and risk mitigation by maintaining transparency and traceability throughout the project lifecycle.
Defining Flexibility Matrix
The Flexibility Matrix is a strategic tool designed to evaluate and categorize various options based on their adaptability to changing requirements, market conditions, or operational constraints. It maps decision variables against potential scenarios, highlighting areas where flexibility provides competitive advantages or mitigates risks. Unlike the Compliance Matrix, which assesses adherence to predefined standards or specifications, the Flexibility Matrix emphasizes the capacity to adjust, innovate, and respond dynamically within project or organizational frameworks.
Mathematical Formulations
The Compliance matrix is formulated through the relation \(C = K^{-1}\), where \(C\) is the compliance matrix and \(K\) is the stiffness matrix, representing material deformation under applied loads. The Flexibility matrix \(F\) is often expressed as the inverse of the stiffness matrix as well, \(F = K^{-1}\), but specifically relates forces to displacements in structural analysis. While both matrices involve matrix inversion, the Compliance matrix emphasizes strain-to-stress relationships in materials, whereas the Flexibility matrix focuses on displacement-to-force relationships within mechanical systems.
Key Differences Between Compliance and Flexibility Matrices
Compliance matrices quantify adherence to predefined standards or requirements, ensuring systematic evaluation and regulatory alignment. Flexibility matrices measure adaptability and responsiveness to changing conditions or stakeholder needs, highlighting innovation and dynamic problem-solving. Key differences lie in compliance matrices prioritizing rigid structure and accountability, while flexibility matrices emphasize variability and customization in processes or project management.
Physical Interpretations
A compliance matrix quantifies the deformation response of a structure under applied forces, representing flexibility in terms of displacements or strains relative to loads, and is the inverse of the stiffness matrix. The flexibility matrix characterizes the structural system's ability to undergo specific displacements or rotations when subjected to unit forces, providing direct insight into the physical deformability of components. Both matrices serve complementary roles in structural analysis, with the compliance matrix reflecting system compliance and the flexibility matrix offering a straightforward representation of displacement-based responses.
Applications in Engineering and Mechanics
A compliance matrix in engineering quantifies how structures deform under applied forces, crucial for designing flexible mechanical components and predicting elastic behavior. The flexibility matrix, often used interchangeably with the compliance matrix, specifically maps applied forces to resultant displacements, enabling precise control in robotic manipulators and structural analysis. Both matrices facilitate optimization in mechanical systems by balancing stiffness and adaptability, enhancing performance in complex engineering applications such as finite element modeling and vibration analysis.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Matrix
The Compliance matrix offers clear advantages in ensuring strict adherence to predefined requirements and standards, facilitating objective evaluation and minimizing ambiguity during project assessments. Its limitation lies in reduced adaptability, as it may hinder innovation and responsiveness to evolving project needs or unexpected changes. Conversely, the Flexibility matrix promotes adaptability and responsiveness, allowing dynamic adjustments and fostering creativity, but it can introduce subjectivity and inconsistency, complicating the evaluation process and potentially leading to differing interpretations of compliance.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Which Matrix
The Compliance Matrix is ideal for projects requiring strict adherence to predefined standards, regulations, or contractual obligations, ensuring all requirements are systematically met and verified. In contrast, the Flexibility Matrix suits environments with evolving criteria or innovation-driven goals, where adaptability and prioritizing between competing needs are crucial for decision-making. Selecting between these matrices depends on the project's rigidity, the necessity for compliance control, and the degree of flexibility needed in handling changing requirements.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
The Compliance matrix ensures stringent adherence to predefined standards, offering clear benchmarks for regulatory and quality assurance processes. In contrast, the Flexibility matrix promotes adaptive strategies that accommodate evolving requirements and stakeholder needs, fostering innovation and resilience. Future perspectives emphasize integrating both matrices through hybrid frameworks, leveraging AI and data analytics to balance compliance rigor with operational agility and competitive advantage.
Compliance matrix Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com