Ribbed slabs optimize structural efficiency by reducing the amount of concrete used while maintaining strength through a grid of ribs beneath the slab surface. This design enhances load distribution and minimizes material costs, making it ideal for large-span constructions. Discover how implementing ribbed slabs can benefit your building projects by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
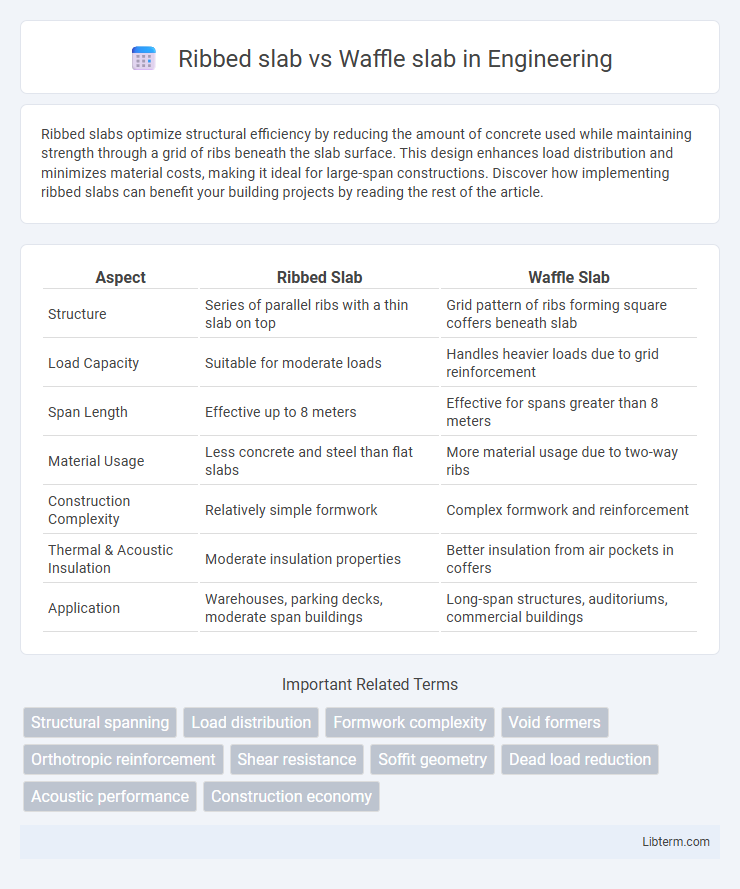
| Aspect | Ribbed Slab | Waffle Slab |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Series of parallel ribs with a thin slab on top | Grid pattern of ribs forming square coffers beneath slab |
| Load Capacity | Suitable for moderate loads | Handles heavier loads due to grid reinforcement |
| Span Length | Effective up to 8 meters | Effective for spans greater than 8 meters |
| Material Usage | Less concrete and steel than flat slabs | More material usage due to two-way ribs |
| Construction Complexity | Relatively simple formwork | Complex formwork and reinforcement |
| Thermal & Acoustic Insulation | Moderate insulation properties | Better insulation from air pockets in coffers |
| Application | Warehouses, parking decks, moderate span buildings | Long-span structures, auditoriums, commercial buildings |
Introduction to Ribbed Slab and Waffle Slab Systems
Ribbed slabs feature parallel beams running in one direction with a thin slab above, providing efficient load distribution and material savings compared to solid slabs. Waffle slabs consist of a grid of reinforced concrete ribs forming a waffle-like pattern beneath the slab, offering high strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced load-bearing capacity. Both systems optimize structural performance and reduce overall material usage in floor construction.
Structural Design Principles
Ribbed slabs utilize a grid of reinforced concrete beams to support loads efficiently, reducing material usage while providing high structural strength in one direction. Waffle slabs feature a two-way ribbing pattern that distributes loads uniformly across both directions, enhancing stiffness and minimizing deflection for larger spans. Structural design principles in ribbed slabs prioritize unidirectional bending resistance, whereas waffle slabs emphasize two-way load transfer and optimal load-bearing capacity.
Key Differences in Construction Techniques
Ribbed slabs use parallel beams (ribs) with a thin slab on top, allowing for reduced weight and material usage, while waffle slabs feature a two-way grid of reinforced ribs creating a waffle-like pattern, offering greater load capacity. Construction of ribbed slabs involves simpler formwork with linear molds, whereas waffle slabs require complex, two-directional formwork to shape the grid ribs. The choice between ribbed and waffle slabs impacts structural performance, material efficiency, and construction time based on project requirements.
Material Usage and Cost Comparison
Ribbed slabs generally use less concrete and steel reinforcement compared to waffle slabs, leading to lower material costs and efficient load distribution for medium-span structures. Waffle slabs, characterized by a grid of ribs on both directions, require more formwork and reinforcement, increasing both material usage and overall construction expenses. Cost-effectiveness depends on project scale and load requirements, with ribbed slabs favored for budget-sensitive projects and waffle slabs chosen for heavier loads and architectural aesthetics.
Load-Bearing Capacity and Performance
Ribbed slabs exhibit high load-bearing capacity through their reinforced concrete ribs, efficiently supporting heavy structural loads with reduced material usage compared to solid slabs. Waffle slabs enhance performance by distributing loads evenly via a grid of ribs in two directions, providing superior stiffness and minimizing deflection in large-span applications. Both slab types improve structural efficiency, with ribbed slabs favoring one-way load transfer and waffle slabs excelling in two-way load distribution for increased load-bearing capacity.
Applications in Modern Architecture
Ribbed slabs are widely used in commercial buildings, parking structures, and industrial facilities due to their efficiency in spanning large areas with reduced concrete volume and enhanced load-bearing capacity. Waffle slabs are favored in modern architecture for spaces requiring long spans and exposed ceilings, such as auditoriums, museums, and office buildings, providing aesthetic appeal alongside structural performance. Both slabs optimize material use while allowing for flexibility in architectural design and mechanical system integration.
Advantages of Ribbed Slab Systems
Ribbed slab systems offer significant advantages including reduced material usage due to the hollow spaces between ribs, leading to lighter structures and lower construction costs. The enhanced load-bearing capacity and improved resistance against bending moments make ribbed slabs ideal for long spans in commercial and industrial buildings. Their simplified formwork and faster construction process contribute to increased project efficiency and reduced labor expenses.
Benefits of Waffle Slab Structures
Waffle slab structures provide enhanced load distribution and greater structural efficiency due to their two-way ribbed system, making them ideal for large-span buildings. These slabs reduce material usage and overall weight while maintaining strength and stiffness, leading to cost-effective construction. Their design also improves thermal insulation and acoustic performance, contributing to better energy efficiency and comfort in buildings.
Limitations and Challenges of Each System
Ribbed slabs face limitations in handling heavy concentrated loads due to their reduced cross-sectional area between ribs, which can lead to increased deflection and potential cracking. Waffle slabs present challenges in construction complexity and cost, requiring precise formwork and additional labor, making them less suitable for small-scale projects. Both systems demand careful consideration of span length and load distribution, as improper design can result in structural inefficiencies and increased maintenance.
Choosing the Right Slab System for Your Project
Ribbed slabs offer efficient load distribution with reduced material use, ideal for medium spans and projects requiring faster construction times. Waffle slabs provide superior strength and rigidity, making them suitable for heavy loads and long spans, often used in commercial buildings and parking structures. Selecting the right slab system depends on project requirements such as load capacity, span length, budget constraints, and architectural complexity.
Ribbed slab Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com