Autotopic technology revolutionizes content creation by automatically generating contextually relevant topics to enhance SEO performance and audience engagement. By leveraging advanced algorithms and natural language processing, autotopic tools help streamline your content strategy for maximum impact and efficiency. Discover how autotopic solutions can transform your digital presence throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
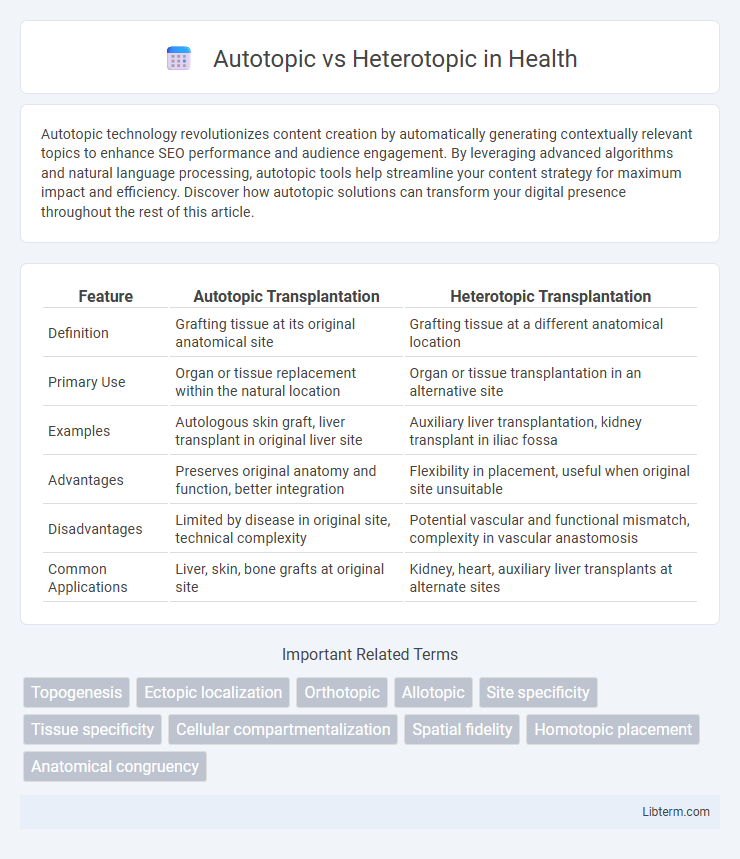
| Feature | Autotopic Transplantation | Heterotopic Transplantation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Grafting tissue at its original anatomical site | Grafting tissue at a different anatomical location |
| Primary Use | Organ or tissue replacement within the natural location | Organ or tissue transplantation in an alternative site |
| Examples | Autologous skin graft, liver transplant in original liver site | Auxiliary liver transplantation, kidney transplant in iliac fossa |
| Advantages | Preserves original anatomy and function, better integration | Flexibility in placement, useful when original site unsuitable |
| Disadvantages | Limited by disease in original site, technical complexity | Potential vascular and functional mismatch, complexity in vascular anastomosis |
| Common Applications | Liver, skin, bone grafts at original site | Kidney, heart, auxiliary liver transplants at alternate sites |
Introduction to Autotopic and Heterotopic
Autotopic refers to organisms or structures originating and functioning within their native environment, while heterotopic describes those existing or functioning in a foreign or different context. In medical and biological contexts, autotopic tissue maintains its original anatomical location, whereas heterotopic tissue develops or is transplanted outside its usual site. Understanding the distinction aids in diagnosing conditions involving tissue displacement and designing targeted therapeutic interventions.
Definitions: Autotopic vs Heterotopic
Autotopic refers to a condition or event occurring in its natural or original location within the body, such as autotransplantation where tissue is transplanted back to its native site. Heterotopic describes occurrences or placements in an abnormal or different location from their usual anatomical site, exemplified by heterotopic ossification, where bone forms outside the skeletal system. Understanding these definitions clarifies distinctions in medical procedures and pathological conditions involving tissue localization.
Key Differences Between Autotopic and Heterotopic
Autotopic refers to transplantation or growth occurring at the original or native site of the tissue or organ, while heterotopic denotes transplantation or growth at a different location than the original. A key difference lies in the anatomical positioning; autotopic procedures maintain the natural environment, optimizing function and integration, whereas heterotopic placements involve ectopic sites, which may require alternative vascular or structural support. Autotopic techniques often prioritize original biomechanical and physiological conditions, whereas heterotopic methods are used when the native site is unsuitable or compromised.
Historical Background and Evolution
Autotopic and heterotopic concepts emerged from historical contexts in topology and spatial theory, primarily influenced by Michel Foucault's analysis of space and social structures. Autotopic spaces denote self-contained, internally coherent environments where social relations are stable and unchanging, whereas heterotopic spaces represent "other" or counter-sites that juxtapose multiple spaces within a single site, reflecting dynamic social and cultural shifts. The evolution of these terms highlights their application across disciplines like architecture, geography, and sociology, tracing how societal transformations have redefined the function and interpretation of space.
Mechanisms Underlying Autotopic Processes
Autotopic processes involve neural mechanisms where sensory information is processed within the same cortical area that receives direct sensory input, enabling precise spatial localization and integration. Key mechanisms include topographic mapping, where neurons maintain spatial relationships corresponding to external stimuli, and local synaptic plasticity that enhances signal fidelity and discrimination. These processes are supported by specialized receptor fields and recurrent neural circuits that optimize sensory perception and motor responses.
Characteristics of Heterotopic Manifestations
Heterotopic manifestations are characterized by the presence of tissue in abnormal locations distinct from their origin, such as heterotopic bone or gastric mucosa found outside their typical anatomical sites. These ectopic tissues can cause functional disturbances or pathological changes, often leading to complications like inflammation or impaired organ function. Unlike autotopic tissues, which maintain their native microenvironment, heterotopic tissues adapt to foreign surroundings, often triggering unique molecular responses and structural remodeling.
Clinical Significance in Medical Practice
Autotopic transplantation involves relocating tissue within its original anatomical site, reducing rejection risk and preserving local function, crucial in clinical settings like skin grafts and liver segment transplants. Heterotopic transplantation places tissue in a different anatomical location, often used when the original site is unsuitable, exemplified by heterotopic heart or kidney transplants, demanding careful immunosuppressive management. Understanding the differences impacts surgical planning, post-operative care, and long-term graft survival rates, critically influencing patient outcomes and transplant success.
Diagnostic Approaches: Autotopic vs Heterotopic
Autotopic diagnostic approaches involve evaluating tissues or organs in their original, anatomically correct locations, utilizing imaging modalities like MRI or CT scans to assess natural structural integrity and function. Heterotopic diagnostics focus on tissues or grafts located in abnormal positions, requiring specialized imaging techniques and biopsy analysis to identify functional viability and potential rejection in transplanted or ectopic sites. Comparing these methods reveals that autotopic diagnostics prioritize native anatomical context, while heterotopic approaches demand tailored assessments accounting for altered physiology and integration challenges.
Treatment Strategies and Outcomes
Autotopic treatment strategies involve using patients' own tissues for transplantation, reducing immune rejection risks and improving integration outcomes. Heterotopic approaches rely on donor tissues or synthetic substitutes, often requiring immunosuppression and posing higher risks of complications. Clinical outcomes favor autotopic methods with enhanced graft survival and functional restoration, while heterotopic treatments remain essential when autologous options are unavailable.
Future Perspectives and Research Directions
Autotopic and heterotopic transplantation techniques continue to evolve with advancements in regenerative medicine and biomaterial engineering, offering promising avenues for tissue integration and functionality. Future perspectives emphasize personalized approaches combining stem cell technology and 3D bioprinting to enhance graft survival and reduce immune rejection. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing vascularization, improving scaffold design, and integrating real-time monitoring systems to elevate the success rates of both autotopic and heterotopic procedures.
Autotopic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com