Evolution drives the gradual development of species through natural selection, genetic variation, and adaptation to changing environments. This process shapes biodiversity and influences the survival and reproduction of organisms over generations. Discover how understanding evolution can deepen your insight into the natural world in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
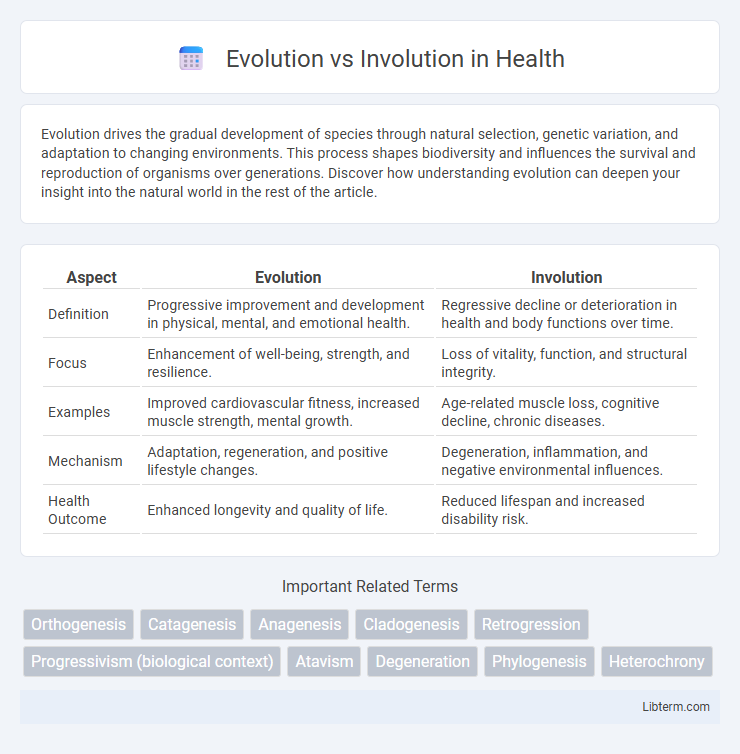
| Aspect | Evolution | Involution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Progressive improvement and development in physical, mental, and emotional health. | Regressive decline or deterioration in health and body functions over time. |
| Focus | Enhancement of well-being, strength, and resilience. | Loss of vitality, function, and structural integrity. |
| Examples | Improved cardiovascular fitness, increased muscle strength, mental growth. | Age-related muscle loss, cognitive decline, chronic diseases. |
| Mechanism | Adaptation, regeneration, and positive lifestyle changes. | Degeneration, inflammation, and negative environmental influences. |
| Health Outcome | Enhanced longevity and quality of life. | Reduced lifespan and increased disability risk. |
Understanding Evolution: A Brief Overview
Evolution refers to the natural process of gradual change and adaptation in living organisms over generations, driven by genetic variation and environmental pressures. It encompasses mechanisms like natural selection, mutation, gene flow, and genetic drift, which contribute to species diversification and complexity. Understanding evolution provides critical insights into biodiversity, the development of traits, and the ancestral relationships among species.
Defining Involution: Concepts and Contexts
Involution refers to a process of inward development or complexity increase without outward expansion or progress, often contrasted with evolution's outward growth and adaptation. In various contexts, such as philosophy, sociology, and biology, involution describes systems becoming more intricate internally, sometimes leading to stagnation or self-containment rather than innovation. Understanding involution involves examining its role in cultural dynamics, organizational behavior, and ecological patterns where internal complexity challenges sustainable advancement.
Key Differences Between Evolution and Involution
Evolution refers to the process of gradual development and adaptation in organisms or ideas, characterized by external progression and complexity increase over time. Involution signifies a turning inward, involving internal refinement, self-realization, or complexity reduction often linked to spiritual or philosophical contexts. Key differences include evolution's outward expansion and adaptation versus involution's inward focus and simplification, with evolution driven by environmental interactions and involution by internal transformation.
Historical Perspectives on Evolution and Involution
Historical perspectives on evolution trace back to Darwin's theory of natural selection, emphasizing gradual biological change and adaptation over time. Involution, often discussed in philosophical and spiritual contexts, refers to a process of inward development or regression, contrasting with the outward progress implied by evolution. Scholarly debates highlight how evolution is viewed as a universal principle of complexity and diversification, while involution suggests a cyclical return to origins or simpler states.
Biological Evolution: Mechanisms and Impact
Biological evolution operates through mechanisms such as natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, and mutation, driving the gradual change in allele frequencies within populations over generations. These processes contribute to adaptation, speciation, and increased biodiversity, fundamentally shaping the complexity of life on Earth. The impact of biological evolution manifests in the development of diverse ecosystems, enhanced survival strategies, and the continuous emergence of new species.
Involution in Social and Cultural Systems
Involution in social and cultural systems refers to a process where growth occurs inwardly without generating new complexities or innovations, often leading to stagnation despite increased effort or resources. This phenomenon is seen in societies where traditional practices intensify but fail to evolve, resulting in diminishing returns on social development and cultural adaptation. Involution contrasts with evolution by prioritizing deepening existing structures over transformative change, highlighting challenges in social progress and cultural dynamism.
Evolution vs Involution in Organizational Change
Evolution in organizational change refers to gradual, adaptive transformations that enhance processes, culture, and structures to meet shifting market demands and improve overall efficiency. Involution, conversely, denotes inward-focused, repetitive cycles that may lead to stagnation or complexity without meaningful progress, often trapping organizations in unproductive patterns. Emphasizing evolutionary change fosters innovation and agility, while involution risks organizational inertia and diminished competitive advantage.
Examples of Evolution and Involution in Nature
In nature, evolution is exemplified by the gradual adaptation of species such as the finches of the Galapagos Islands, where beak shapes evolved to match different food sources, enhancing survival and reproduction. Involution is observed in phenomena like the intricate folding of the cerebral cortex in mammals, maximizing surface area within limited space for improved brain function. Both processes illustrate dynamic biological changes, with evolution emphasizing outward diversification and involution focusing on internal complexity and refinement.
Involution in Modern Society: Causes and Consequences
Involution in modern society arises from escalating complexity without corresponding innovation, leading to stagnation in productivity and creativity within various fields such as education, technology, and urban development. This phenomenon is driven by excessive competition, bureaucratic expansion, and resource misallocation, which constrains meaningful progress and amplifies socio-economic inequalities. The consequences include increased mental health issues, diminished innovation, and systemic inefficiencies that hinder sustainable growth and societal well-being.
Future Implications: Striking a Balance Between Evolution and Involution
Balancing evolution and involution is crucial for sustainable futuristic progress, as evolution drives innovation and outward expansion while involution fosters introspection and system refinement. Future implications hinge on leveraging evolutionary growth without neglecting involution's role in maintaining stability, ethical frameworks, and deeper understanding. Integrating both dynamics ensures adaptive societies capable of thriving amid technological advancements and complex global challenges.
Evolution Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com