Engaging in regular physical activity boosts your energy levels, improves cardiovascular health, and enhances mental well-being. Incorporating diverse exercises into your routine helps maintain optimal fitness and prevent chronic diseases. Explore the full article to learn effective ways to stay active and energized.
Table of Comparison
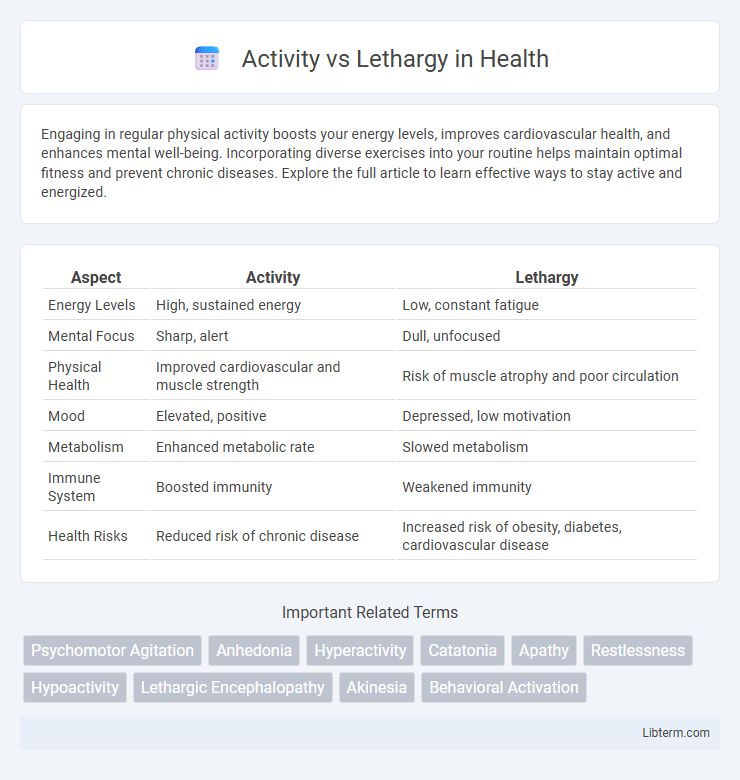
| Aspect | Activity | Lethargy |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Levels | High, sustained energy | Low, constant fatigue |
| Mental Focus | Sharp, alert | Dull, unfocused |
| Physical Health | Improved cardiovascular and muscle strength | Risk of muscle atrophy and poor circulation |
| Mood | Elevated, positive | Depressed, low motivation |
| Metabolism | Enhanced metabolic rate | Slowed metabolism |
| Immune System | Boosted immunity | Weakened immunity |
| Health Risks | Reduced risk of chronic disease | Increased risk of obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease |
Understanding Activity and Lethargy
Activity refers to the state of being physically or mentally engaged, characterized by movement, energy expenditure, and purposeful actions. Lethargy denotes a condition marked by low energy, sluggishness, and decreased motivation or ability to perform tasks. Understanding activity and lethargy involves recognizing their impact on health, productivity, and overall well-being, as well as identifying underlying causes such as lifestyle, nutrition, or medical conditions.
Causes of Increased Activity
Increased activity can result from physiological factors such as hyperthyroidism, where excess thyroid hormones elevate metabolism and energy levels. Psychological conditions like anxiety or mania also trigger heightened physical and mental activity through stimulation of the central nervous system. Certain medications and stimulants, including caffeine and amphetamines, chemically induce increased activity by enhancing neurotransmitter release and neural excitability.
Common Triggers of Lethargy
Common triggers of lethargy include poor sleep quality, nutritional deficiencies, sedentary lifestyle, and chronic stress. Medical conditions such as hypothyroidism, anemia, and diabetes often contribute to persistent fatigue and reduced energy levels. Environmental factors like exposure to excessive heat or lack of sunlight also play a significant role in diminishing overall vitality.
Physical and Mental Signs of Each State
Physical signs of activity include increased heart rate, enhanced muscle tone, and elevated energy levels, while lethargy manifests as sluggish movements, muscle weakness, and fatigue. Mentally, active states promote alertness, concentration, and motivation, whereas lethargy often causes impaired focus, drowsiness, and slowed cognitive processing. Monitoring these distinct physical and mental indicators aids in distinguishing between activity and lethargy for effective health management.
Health Impacts: Activity vs Lethargy
Regular physical activity significantly reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity by improving cardiovascular health and metabolic function. In contrast, prolonged lethargy and sedentary behavior contribute to increased inflammation, muscle atrophy, and impaired glucose metabolism, elevating the likelihood of morbidity. Engaging in consistent exercise promotes mental well-being by releasing endorphins and enhancing cognitive function, while inactivity is linked to higher rates of depression and anxiety.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Energy Levels
Regular physical activity enhances mitochondrial function and boosts endorphin production, leading to increased energy levels and reduced fatigue. Sedentary behavior decreases cardiovascular efficiency and disrupts circadian rhythms, contributing to chronic lethargy. Nutritional intake, sleep quality, and stress management also critically modulate metabolic processes that determine overall vitality.
Balancing Rest and Movement
Balancing rest and movement is essential for maintaining optimal physical and mental health, as regular physical activity improves cardiovascular function, boosts mood, and enhances cognitive abilities. Excessive lethargy can lead to muscle atrophy, increased risk of chronic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes, and diminished energy levels. Integrating moderate exercise like walking or yoga with adequate sleep and downtime supports sustained vitality and prevents burnout.
Strategies to Overcome Lethargy
Implementing regular physical exercise enhances energy levels by boosting circulation and stimulating endorphin production. Adopting a consistent sleep schedule and balanced diet supports metabolic functions, reducing fatigue and improving alertness. Mindfulness practices and task segmentation help improve focus and motivation, effectively combating lethargy.
Benefits of Staying Active
Regular physical activity enhances cardiovascular health, boosts metabolism, and strengthens muscles, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. Staying active improves mental well-being by releasing endorphins, which alleviate stress and anxiety while enhancing cognitive function and memory retention. Consistent exercise also promotes better sleep quality, increased energy levels, and overall longevity.
Creating a Sustainable Activity Routine
Establishing a sustainable activity routine involves balancing physical exertion with adequate rest to prevent lethargy and maintain energy levels. Consistent moderate exercise, such as daily walking or yoga, enhances metabolism, improves mood, and supports cardiovascular health. Tracking progress and setting realistic goals promotes adherence and long-term benefits for overall wellness.
Activity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com