Prevalence measures how widespread a particular condition or characteristic is within a specific population at a given time, providing essential insights for healthcare planning and resource allocation. Understanding prevalence helps identify risk factors and target interventions effectively to reduce the burden of disease. Explore the article to learn how prevalence data can inform your health decisions and policy development.
Table of Comparison
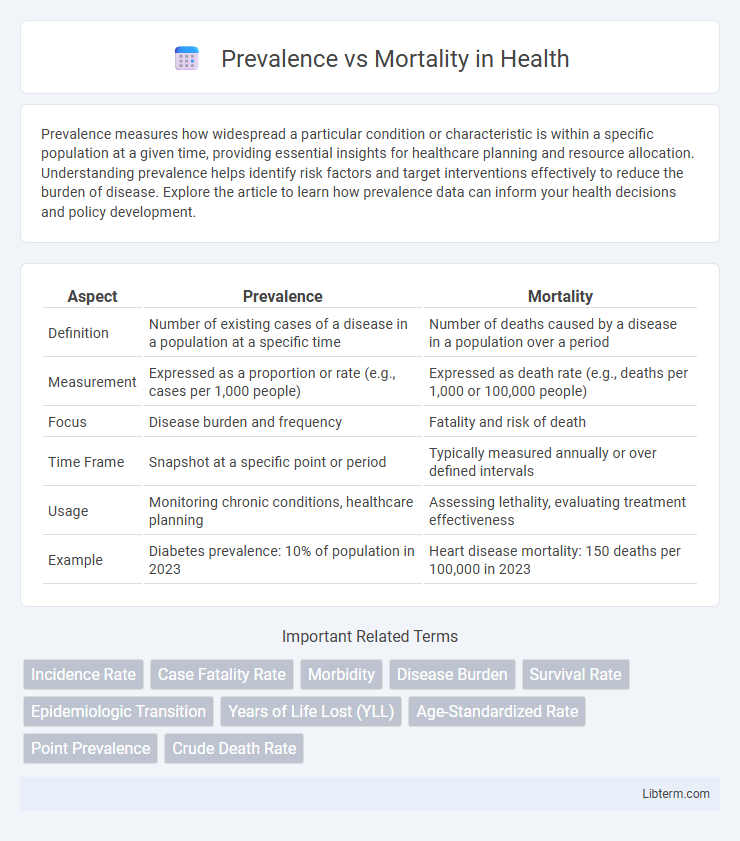
| Aspect | Prevalence | Mortality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Number of existing cases of a disease in a population at a specific time | Number of deaths caused by a disease in a population over a period |
| Measurement | Expressed as a proportion or rate (e.g., cases per 1,000 people) | Expressed as death rate (e.g., deaths per 1,000 or 100,000 people) |
| Focus | Disease burden and frequency | Fatality and risk of death |
| Time Frame | Snapshot at a specific point or period | Typically measured annually or over defined intervals |
| Usage | Monitoring chronic conditions, healthcare planning | Assessing lethality, evaluating treatment effectiveness |
| Example | Diabetes prevalence: 10% of population in 2023 | Heart disease mortality: 150 deaths per 100,000 in 2023 |
Understanding Prevalence and Mortality
Prevalence measures the total number of existing cases of a disease within a population at a specific time, reflecting the overall burden of the condition. Mortality refers to the number of deaths caused by the disease during a given period, indicating its lethality and public health impact. Understanding both prevalence and mortality is essential for effective disease management, resource allocation, and health policy development.
Definitions: What is Prevalence?
Prevalence measures the total number of existing cases of a disease or condition within a specific population at a given time, reflecting the overall burden of the health issue. It is typically expressed as a proportion or percentage, such as cases per 1,000 or 100,000 individuals. Unlike mortality, which quantifies the number of deaths caused by a disease, prevalence includes both new and ongoing cases, providing insight into the extent and persistence of health problems.
Definitions: What is Mortality?
Mortality refers to the incidence of death within a specific population during a certain time period, often expressed as a mortality rate or ratio. It is a key epidemiological measure reflecting the frequency of deaths attributable to particular diseases, conditions, or risk factors. Mortality data are essential for public health assessments, resource allocation, and evaluating the effectiveness of medical interventions.
Key Differences Between Prevalence and Mortality
Prevalence refers to the total number of existing cases of a disease or condition in a population at a specific point in time, reflecting disease burden. Mortality indicates the number of deaths due to a particular disease or condition within a population during a specified period, measuring lethality. The key difference lies in prevalence capturing disease frequency regardless of outcome, while mortality exclusively accounts for fatal outcomes.
How Prevalence is Measured
Prevalence is measured by calculating the total number of existing cases of a disease or condition in a specific population at a given point in time or over a specified period, divided by the total population at risk. This measurement is expressed as a proportion or rate, such as cases per 1,000 or 100,000 individuals, enabling comparison across different populations or time frames. Accurate prevalence data relies on comprehensive case identification through surveys, medical records, or registries to capture both new and existing cases.
How Mortality is Calculated
Mortality is calculated by determining the number of deaths within a specific population during a defined time period, often expressed per 1,000 or 100,000 individuals to standardize comparisons. This metric contrasts with prevalence, which measures the total number of existing cases of a disease at a given time regardless of outcome. Accurate mortality rates rely on comprehensive death registries and demographic data to assess the impact of diseases on population health.
Factors Influencing Prevalence Rates
Prevalence rates are influenced by factors such as disease duration, incidence rate, and population demographics including age and socioeconomic status. Mortality impacts prevalence by reducing the number of existing cases, especially in diseases with high fatality rates. Understanding these dynamics helps in interpreting disease burden and allocating healthcare resources effectively.
Factors Affecting Mortality Rates
Mortality rates are influenced by factors including age distribution, healthcare quality, socioeconomic status, and prevalence of chronic diseases within a population. Higher mortality rates are often associated with limited access to medical facilities, poor nutrition, and environmental hazards. Accurate assessment of these factors is crucial for developing targeted interventions to reduce mortality.
Prevalence vs Mortality: Public Health Implications
Prevalence indicates the total number of existing cases of a disease within a population at a given time, reflecting the burden of illness and informing resource allocation for prevention and management programs. Mortality measures the number of deaths caused by a disease, providing insight into its lethality and the effectiveness of treatment strategies. Understanding the distinction between prevalence and mortality supports public health planning by targeting interventions to reduce disease incidence, improve survival rates, and optimize healthcare services.
Using Prevalence and Mortality in Disease Surveillance
Prevalence measures the total number of existing disease cases in a population at a given time, providing critical insight into the disease burden and resource needs. Mortality quantifies the number of deaths caused by the disease, reflecting its lethality and informing public health priorities. Combining prevalence and mortality data enhances disease surveillance accuracy, enabling targeted interventions and effective allocation of healthcare resources.
Prevalence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com