Ensuring safety in every environment is crucial to protect lives and prevent accidents. Proper safety measures, regular training, and the use of reliable equipment contribute significantly to reducing risks. Discover how you can enhance safety protocols effectively by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
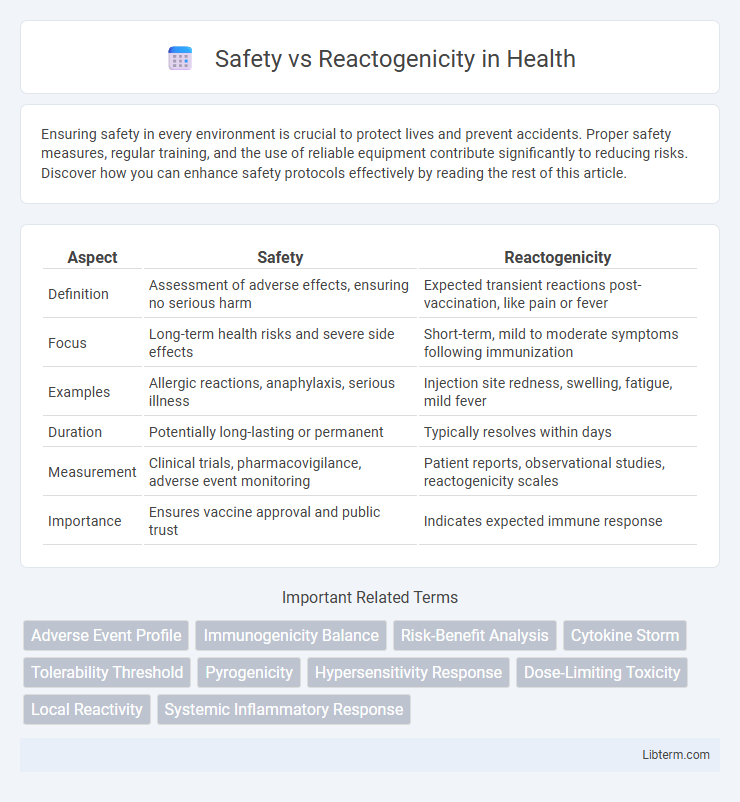
| Aspect | Safety | Reactogenicity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment of adverse effects, ensuring no serious harm | Expected transient reactions post-vaccination, like pain or fever |
| Focus | Long-term health risks and severe side effects | Short-term, mild to moderate symptoms following immunization |
| Examples | Allergic reactions, anaphylaxis, serious illness | Injection site redness, swelling, fatigue, mild fever |
| Duration | Potentially long-lasting or permanent | Typically resolves within days |
| Measurement | Clinical trials, pharmacovigilance, adverse event monitoring | Patient reports, observational studies, reactogenicity scales |
| Importance | Ensures vaccine approval and public trust | Indicates expected immune response |
Understanding Safety and Reactogenicity in Medical Interventions
Safety in medical interventions assesses the likelihood of serious adverse effects, ensuring treatments do not cause harm to patients. Reactogenicity refers to the short-term, expected immune responses such as pain, redness, or fever that indicate the body's reaction to a vaccine or medication. Balancing safety and reactogenicity helps optimize therapeutic efficacy while minimizing discomfort and risk for patients.
Key Differences Between Safety and Reactogenicity
Safety refers to the overall assessment of adverse effects associated with a medical intervention, ensuring no serious or long-term harm to patients. Reactogenicity specifically measures the immediate, short-term side effects such as pain, redness, or fever post-vaccination, often indicating an immune response. While safety covers broad clinical outcomes, reactogenicity focuses on predictable, transient reactions that help evaluate vaccine tolerability.
Why Both Safety and Reactogenicity Matter in Clinical Trials
Safety ensures that a treatment does not cause harmful effects, protecting patient well-being during clinical trials. Reactogenicity, which refers to the temporary, expected immune responses such as fever or soreness, provides critical data on how the body reacts to the intervention. Balancing safety and reactogenicity allows researchers to assess both the risk profile and the tolerability of new therapies, guiding regulatory approval and patient acceptance.
Common Measures of Safety in Drug Development
Common measures of safety in drug development include monitoring adverse events, laboratory test abnormalities, and vital sign changes throughout clinical trials. Reactogenicity, a specific subset of adverse events, refers to expected, transient reactions such as injection site pain, redness, or systemic symptoms like fever. These safety indicators are systematically recorded and analyzed to evaluate the risk-benefit profile of a drug prior to regulatory approval.
Typical Reactogenicity Reactions and Their Implications
Typical reactogenicity reactions include localized pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site, along with systemic symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and headache. These responses indicate the immune system's activation and are generally transient, resolving within a few days without long-term effects. Understanding the balance between safety and reactogenicity is crucial for vaccine development, as mild to moderate reactogenicity often correlates with effective immunogenicity but must remain within acceptable safety thresholds.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Safety Assessment
Short-term safety assessment in vaccines primarily monitors immediate adverse reactions, such as local pain, fever, or allergic responses within days to weeks post-administration. Long-term safety assessment involves tracking potential delayed effects, including rare autoimmune or neurologic events, over months to years via post-marketing surveillance and cohort studies. Balancing reactogenicity, the expected transient immune response, against comprehensive short-term and long-term safety data ensures optimized vaccine risk-benefit profiles for regulatory approval.
Monitoring and Reporting Reactogenicity Events
Monitoring and reporting reactogenicity events are crucial for ensuring vaccine safety and maintaining public trust. Healthcare providers systematically record symptoms like pain, redness, swelling, fever, and fatigue following immunization to promptly identify adverse reactions. Robust surveillance systems and real-time data analysis enable early detection of safety signals and facilitate timely public health interventions.
Regulatory Standards for Safety Versus Reactogenicity
Regulatory standards for safety versus reactogenicity prioritize minimizing adverse events while ensuring vaccines induce adequate immune responses. Agencies like the FDA and EMA set rigorous criteria for acceptable reactogenicity profiles, balancing the frequency and severity of local and systemic reactions against demonstrated protective efficacy. Continuous post-marketing surveillance and pharmacovigilance complement pre-approval assessments, ensuring long-term safety without compromising immunogenicity.
Communicating Safety and Reactogenicity to the Public
Communicating safety and reactogenicity to the public requires clear explanations of common side effects versus rare adverse events to build trust in vaccines. Emphasizing transparent data from clinical trials and real-world studies helps contextualize mild, temporary reactogenicity symptoms like soreness or fever without causing alarm. Public health messages must balance reassurance with factual information to improve vaccine acceptance and adherence.
Balancing Safety and Reactogenicity in Vaccine Development
Balancing safety and reactogenicity in vaccine development requires optimizing immune response while minimizing adverse effects such as fever, pain, and swelling. Advancements in adjuvant formulations and delivery platforms enhance immunogenicity without compromising patient tolerance or safety profiles. Continuous monitoring during clinical trials ensures that vaccines meet stringent regulatory standards, maintaining a favorable benefit-risk ratio essential for public health acceptance.
Safety Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com