Sinus rhythm refers to the normal heartbeat pattern initiated by the sinoatrial node, ensuring efficient cardiac function and proper blood circulation. Maintaining a regular sinus rhythm is crucial for your overall cardiovascular health and can help prevent arrhythmias and other heart conditions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how sinus rhythm impacts your heart and what signs to watch for.
Table of Comparison
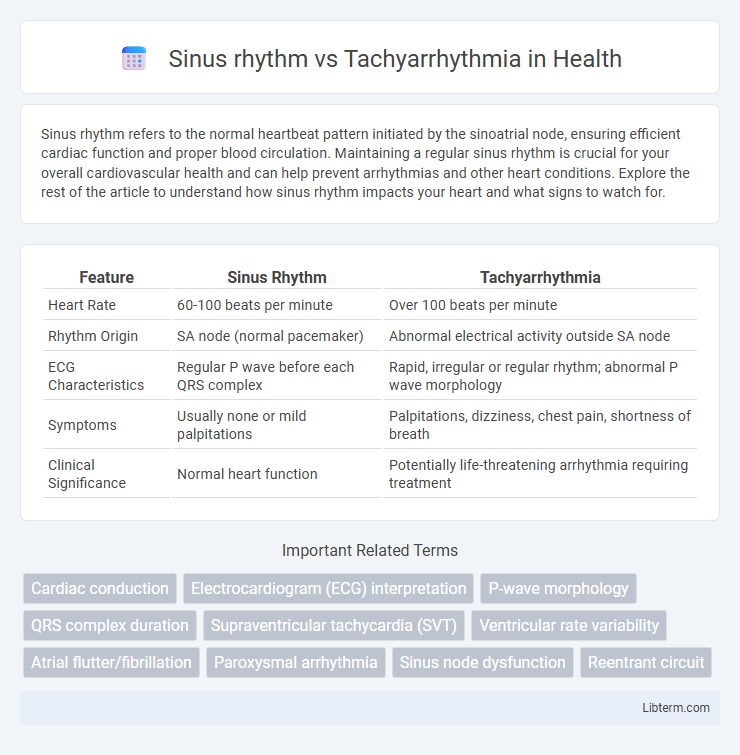
| Feature | Sinus Rhythm | Tachyarrhythmia |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate | 60-100 beats per minute | Over 100 beats per minute |
| Rhythm Origin | SA node (normal pacemaker) | Abnormal electrical activity outside SA node |
| ECG Characteristics | Regular P wave before each QRS complex | Rapid, irregular or regular rhythm; abnormal P wave morphology |
| Symptoms | Usually none or mild palpitations | Palpitations, dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath |
| Clinical Significance | Normal heart function | Potentially life-threatening arrhythmia requiring treatment |
Understanding Sinus Rhythm: The Heart's Natural Pace
Sinus rhythm represents the heart's natural electrical activity, originating from the sinoatrial node, ensuring coordinated atrial and ventricular contractions for efficient blood flow. Its regular pattern is critical for maintaining optimal cardiac output and systemic circulation. In contrast, tachyarrhythmia involves an abnormally fast heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute, disrupting normal rhythm and potentially leading to compromised cardiac function or hemodynamic instability.
Defining Tachyarrhythmia: Types and Clinical Significance
Tachyarrhythmia refers to a group of cardiac arrhythmias characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate originating from improper electrical activity in the atria or ventricles. Common types include atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, and supraventricular tachycardia, each with distinct electrophysiological mechanisms and clinical implications. These rapid rhythms can lead to symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, or syncope and increase the risk of stroke, heart failure, and sudden cardiac death, highlighting their critical importance in cardiovascular disease management.
Key Differences Between Sinus Rhythm and Tachyarrhythmia
Sinus rhythm is the normal heart rhythm originating from the sinoatrial node, characterized by a regular rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute and consistent P wave morphology on ECG. Tachyarrhythmia involves an abnormally fast heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute, often caused by abnormal electrical activity leading to irregular or rapid rhythms such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, or supraventricular tachycardia. The key differences lie in rate regularity, origin of electrical impulses, and ECG patterns, where sinus rhythm exhibits stable, predictable waves, whereas tachyarrhythmia shows variability and potential hemodynamic instability.
Causes of Sinus Rhythm vs Tachyarrhythmia
Sinus rhythm originates from the sinoatrial (SA) node, driven by normal autonomic regulation and electrolyte balance, reflecting a healthy heart's intrinsic pacing. Tachyarrhythmia arises from abnormal electrical impulses due to conditions like ischemic heart disease, electrolyte imbalances, myocardial infarction, or hyperthyroidism, disrupting normal rhythm and accelerating heart rate. Structural heart changes, drug effects, and heightened sympathetic activity further contribute to the development of tachyarrhythmias.
Symptoms: Recognizing Normal vs Abnormal Heart Rhythms
Sinus rhythm typically presents with a regular heartbeat ranging from 60 to 100 beats per minute, often accompanied by normal pulse strength and absence of dizziness or palpitations, indicating healthy cardiac function. Tachyarrhythmia, characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute, commonly induces symptoms such as rapid or irregular heartbeat, chest pain, shortness of breath, and lightheadedness. Early recognition of these symptoms through electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring is crucial for differentiating between normal sinus rhythm and pathological tachyarrhythmia, guiding timely medical intervention.
Diagnostic Tools for Rhythm Identification
Electrocardiography (ECG) remains the primary diagnostic tool for distinguishing sinus rhythm from tachyarrhythmia by analyzing P-wave morphology, regularity, and heart rate. Holter monitors provide continuous rhythm assessment, capturing transient tachyarrhythmias that standard ECGs might miss. Advanced diagnostic tools like electrophysiological studies offer detailed mapping of arrhythmic foci, critical for complex cases unidentifiable through non-invasive methods.
EKG Features: Sinus Rhythm vs Tachyarrhythmia
Sinus rhythm on an EKG shows a regular rate between 60-100 beats per minute with a P wave before each QRS complex, indicating normal atrial depolarization. Tachyarrhythmia is characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate over 100 beats per minute, often showing irregular rates, absent or abnormal P waves, and narrow or wide QRS complexes depending on the type. Distinguishing features include consistent P wave morphology and PR intervals in sinus rhythm versus variable or chaotic atrial activity in tachyarrhythmias.
Complications Associated with Tachyarrhythmia
Tachyarrhythmia, characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate, can lead to severe complications such as heart failure, stroke, and sudden cardiac arrest due to impaired cardiac output and turbulent blood flow. Sinus rhythm, representing a normal heart rate and electrical activity, maintains effective cardiac function and minimizes the risk of thromboembolic events. Persistent tachyarrhythmias increase myocardial oxygen demand and reduce coronary perfusion, exacerbating ischemic injury and increasing morbidity.
Treatment Approaches: Restoring and Maintaining Normal Rhythm
Treatment approaches for sinus rhythm aim to preserve the heart's natural pacemaker function using lifestyle modifications and medications such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers to maintain steady cardiac cycles. Tachyarrhythmia management includes antiarrhythmic drugs, catheter ablation, and electrical cardioversion to restore sinus rhythm by targeting abnormal electrical pathways causing rapid heart rates. Long-term strategies incorporate implantable devices like pacemakers or defibrillators to prevent recurrence and stabilize heart rhythm.
Preventative Measures and Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining sinus rhythm and preventing tachyarrhythmia involves managing risk factors such as hypertension, obesity, and sleep apnea through regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, and weight control. Limiting alcohol intake, avoiding stimulants like caffeine and nicotine, and managing stress with relaxation techniques contribute to stable cardiac electrical activity. Routine medical check-ups and adherence to prescribed medications help detect and control early arrhythmogenic triggers, improving overall cardiovascular health.
Sinus rhythm Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com