Lead Counsel plays a crucial role in managing legal strategies and ensuring the effective coordination of a case from inception to resolution. This position requires expertise in navigating complex legal issues, advising clients, and representing their interests in negotiations and court proceedings. Discover how Lead Counsel can make a significant difference in your legal outcomes by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
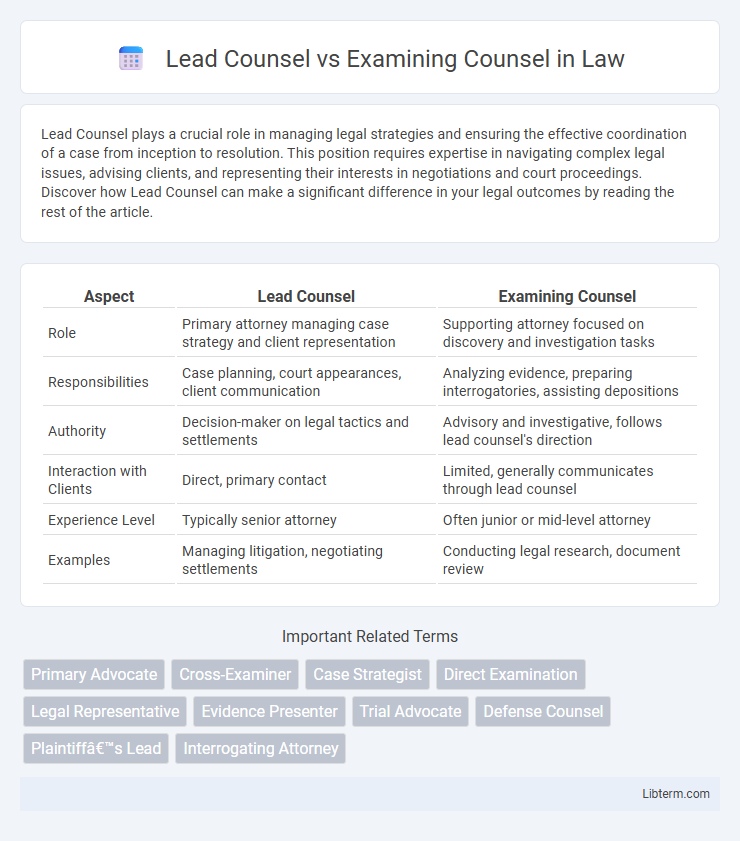
| Aspect | Lead Counsel | Examining Counsel |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Primary attorney managing case strategy and client representation | Supporting attorney focused on discovery and investigation tasks |
| Responsibilities | Case planning, court appearances, client communication | Analyzing evidence, preparing interrogatories, assisting depositions |
| Authority | Decision-maker on legal tactics and settlements | Advisory and investigative, follows lead counsel's direction |
| Interaction with Clients | Direct, primary contact | Limited, generally communicates through lead counsel |
| Experience Level | Typically senior attorney | Often junior or mid-level attorney |
| Examples | Managing litigation, negotiating settlements | Conducting legal research, document review |
Introduction to Lead Counsel and Examining Counsel
Lead Counsel typically oversees the overall litigation strategy, managing case development and client communication throughout the legal process. Examining Counsel specializes in analyzing and questioning evidence and witness testimony during trial or depositions to support or challenge claims. Both roles are critical in complex litigation, with Lead Counsel directing case objectives while Examining Counsel focuses on detailed case examination and factual validation.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Lead Counsel directs the overall litigation strategy, manages case development, and coordinates with clients and experts to ensure strong legal representation. Examining Counsel specializes in scrutinizing evidence, questioning witnesses, and preparing case analyses to support courtroom arguments. Both roles collaborate closely, with Lead Counsel overseeing the broader case objectives while Examining Counsel focuses on detailed fact-finding and examination tactics.
Historical Context and Evolution
Lead Counsel historically emerged as the primary attorney responsible for strategy and overall case management in legal proceedings, often representing the client's main interests. Examining Counsel developed from inquisitorial legal traditions, tasked with investigating facts and questioning witnesses to uncover evidence during trials. Over time, the roles have evolved with common law and civil law systems, reflecting changes in legal procedures and the increasing specialization of trial responsibilities.
Qualifications and Required Skill Sets
Lead Counsel must possess extensive trial experience, strong legal research abilities, and exceptional courtroom advocacy skills to manage complex litigation effectively. Examining Counsel requires a keen eye for detail, strong analytical skills, and expertise in evidence evaluation to conduct thorough witness examinations and fact-finding. Both roles demand excellent communication and negotiation skills but differ in trial leadership versus focused investigative proficiency.
Lead Counsel: Duties and Influence in Litigation
Lead Counsel directs case strategy, manages trial preparation, and leads client communications, ensuring cohesive and persuasive advocacy during litigation. This role wields significant influence by shaping legal arguments, coordinating with experts, and orchestrating discovery efforts to optimize case outcomes. By driving decisions and negotiating settlements, Lead Counsel plays a pivotal role in advancing the litigation process efficiently and effectively.
Examining Counsel: Focus on Witness Examination
Examining Counsel plays a critical role in legal proceedings by directly questioning witnesses to elicit relevant facts and establish the case narrative. Their objective is to clarify details, challenge inconsistencies, and gauge the credibility of testimony through strategic questioning techniques. Expertise in witness examination allows Examining Counsel to influence the jury's perception and strengthen the overall argument presented in court.
Collaboration and Interaction in Legal Proceedings
Lead Counsel assumes primary responsibility for developing case strategy and managing client relations, while Examining Counsel specializes in questioning witnesses and gathering pertinent facts to support the case. Effective collaboration between Lead Counsel and Examining Counsel ensures a comprehensive approach to evidence presentation and litigation tactics. Their interaction facilitates seamless communication, enabling accurate fact-finding and a cohesive courtroom performance that strengthens the legal argument.
Impact on Case Strategy and Outcomes
Lead Counsel holds primary responsibility for developing and executing the overall case strategy, directly influencing crucial decisions such as trial approach, evidence presentation, and settlement negotiations. Examining Counsel typically focuses on specific investigative tasks, examining witnesses and gathering detailed information that supports Lead Counsel's strategic framework. The collaboration between Lead Counsel's broad strategic oversight and Examining Counsel's targeted inquiry significantly shapes case outcomes by ensuring both comprehensive preparation and precise evidence handling.
Common Challenges Faced in Each Role
Lead Counsel often encounters challenges related to managing client expectations and coordinating complex litigation strategies under tight deadlines. Examining Counsel faces difficulties in thoroughly analyzing voluminous case materials while maintaining objectivity in depositions and evidentiary reviews. Both roles demand high levels of expertise in case law interpretation and effective communication to overcome procedural hurdles efficiently.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Lead Counsel and Examining Counsel
Choosing between Lead Counsel and Examining Counsel depends on the scope of the case and specific legal needs. Lead Counsel typically manages overall case strategy, client communication, and trial preparation, while Examining Counsel focuses on detailed fact investigation and specific aspects of evidence evaluation. Selecting the appropriate counsel ensures effective representation tailored to case complexity and objective.
Lead Counsel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com