Eviction is the legal process by which a landlord removes a tenant from a rental property due to non-payment of rent, lease violations, or other breaches of the rental agreement. Understanding the eviction timeline, tenant rights, and necessary court procedures can help you navigate this challenging situation more effectively. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to protect your rights and handle an eviction case.
Table of Comparison
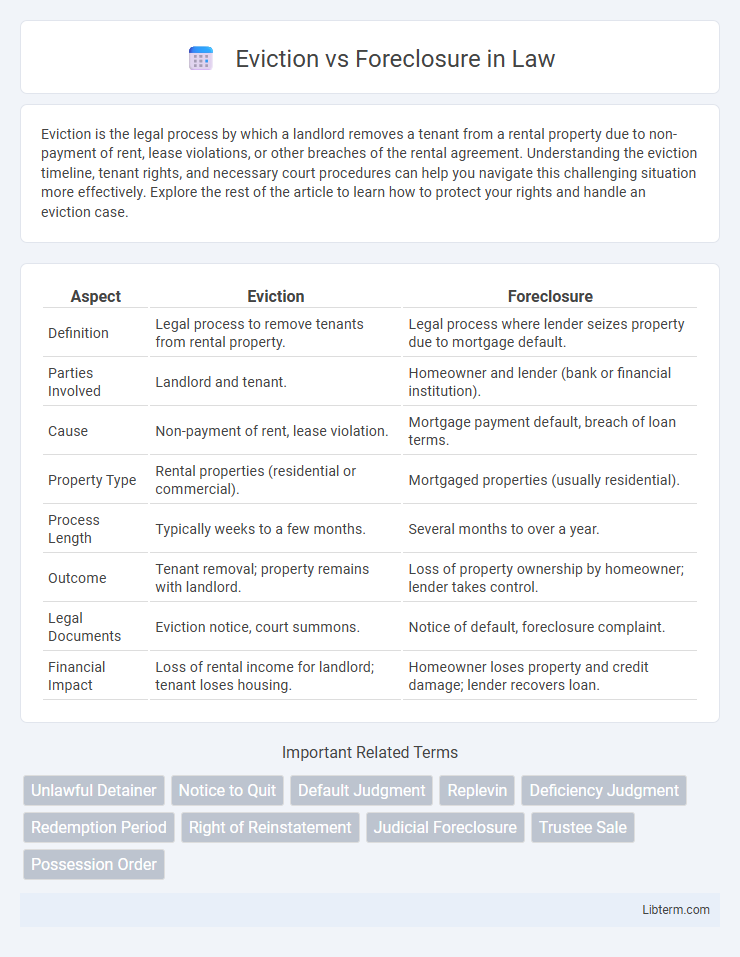
| Aspect | Eviction | Foreclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process to remove tenants from rental property. | Legal process where lender seizes property due to mortgage default. |
| Parties Involved | Landlord and tenant. | Homeowner and lender (bank or financial institution). |
| Cause | Non-payment of rent, lease violation. | Mortgage payment default, breach of loan terms. |
| Property Type | Rental properties (residential or commercial). | Mortgaged properties (usually residential). |
| Process Length | Typically weeks to a few months. | Several months to over a year. |
| Outcome | Tenant removal; property remains with landlord. | Loss of property ownership by homeowner; lender takes control. |
| Legal Documents | Eviction notice, court summons. | Notice of default, foreclosure complaint. |
| Financial Impact | Loss of rental income for landlord; tenant loses housing. | Homeowner loses property and credit damage; lender recovers loan. |
Understanding Eviction and Foreclosure
Eviction is the legal process by which a landlord removes a tenant from rental property due to lease violations or non-payment of rent. Foreclosure occurs when a lender seizes and sells a property after the homeowner defaults on their mortgage payments, leading to loss of ownership. Both processes involve court proceedings but differ fundamentally in property rights--eviction pertains to tenant occupancy, while foreclosure concerns homeownership and mortgage debt.
Key Differences Between Eviction and Foreclosure
Eviction is the legal process by which a landlord removes a tenant for nonpayment or lease violations, while foreclosure is the lender's process to repossess a property after the homeowner defaults on the mortgage. Eviction targets tenants and involves rental agreements, whereas foreclosure affects property owners and centers on mortgage debt. The timeline for eviction is generally shorter, often weeks, compared to foreclosure, which can take months or years due to legal procedures and potential loan modifications.
Legal Processes Involved
Eviction involves a legal process where a landlord terminates a tenant's lease due to nonpayment of rent or lease violations, typically requiring a formal notice and court eviction proceedings. Foreclosure is a judicial or non-judicial process initiated by a lender to repossess a property after the homeowner defaults on mortgage payments, involving notices of default, possible auction, and transfer of ownership. Both processes require strict compliance with state-specific laws and timelines, where failure to follow legal protocols can delay or reverse actions.
Causes Leading to Eviction
Non-payment of rent is the primary cause leading to eviction, often resulting from financial hardships such as job loss, medical expenses, or reduced income. Lease violations, including unauthorized pets or property damage, also trigger eviction processes. Landlords may initiate eviction proceedings to regain possession of the property for reasons including tenant neglect or illegal activities on the premises.
Causes Leading to Foreclosure
Foreclosure occurs primarily due to the homeowner's inability to meet mortgage payment obligations, often triggered by financial hardships such as job loss, medical expenses, or unexpected economic downturns. Declining property values can exacerbate the situation by increasing loan-to-value ratios, making refinancing or selling difficult. Tax delinquencies and failure to maintain property insurance may also contribute to foreclosure by allowing lenders to step in and recoup their investments.
Rights of Tenants vs Homeowners
Tenants facing eviction have the right to receive proper notice and may qualify for relocation assistance depending on local laws, while homeowners in foreclosure retain the right to contest the process and seek loan modifications to avoid losing their property. Tenant protections vary by jurisdiction but often include safeguards against sudden displacement, whereas homeowners have legal avenues such as bankruptcy or short sales to protect their equity. Both eviction and foreclosure proceedings require strict adherence to due process to ensure the rights of occupants are respected before removal or sale.
Financial Impacts of Eviction and Foreclosure
Eviction often leads to immediate financial strain through lost rental income and legal fees, while foreclosure results in severe long-term credit damage and asset loss. Tenants facing eviction may struggle with homelessness and diminished rental history, hindering future housing opportunities. Foreclosure typically causes a significant drop in credit scores, limiting access to loans and increasing borrowing costs for years.
Preventive Measures and Solutions
Eviction prevention strategies include negotiating payment plans, seeking rental assistance programs, and utilizing legal aid to challenge wrongful eviction notices. Foreclosure solutions emphasize mortgage modification, refinancing options, and government-sponsored relief programs such as the Home Affordable Modification Program (HAMP) to avoid losing property. Both processes benefit from early intervention, financial counseling, and proactive communication with landlords or lenders to mitigate the risk of property loss.
Timeline: Eviction vs Foreclosure
Eviction typically occurs after a landlord files a complaint following missed rent payments, with the process lasting between 1 to 3 months depending on state laws. Foreclosure involves a lender initiating legal action due to loan default, often taking 3 to 12 months or longer to complete, influenced by judicial or non-judicial procedures. The eviction timeline is generally shorter, while foreclosure timelines vary significantly based on the complexity of the mortgage and court system involvement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Eviction occurs when a landlord removes a tenant due to nonpayment of rent or lease violations, while foreclosure is a legal process where a lender repossesses a property due to the homeowner's failure to meet mortgage payments. Frequently asked questions about eviction include the timeline for notices, tenants' rights during the process, and potential legal defenses. Common foreclosure inquiries address the steps before foreclosure, options to avoid it such as loan modification, and the impact on credit scores.
Eviction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com